Development and Validation of an Executive Functions Package and Determination of Its Effectiveness on Communication Skills and Self-Care in Adolescents Aged 14–20 Years with Developmental Intellectual Disability
Keywords:
self-care, executive functions, intellectual disabilityAbstract
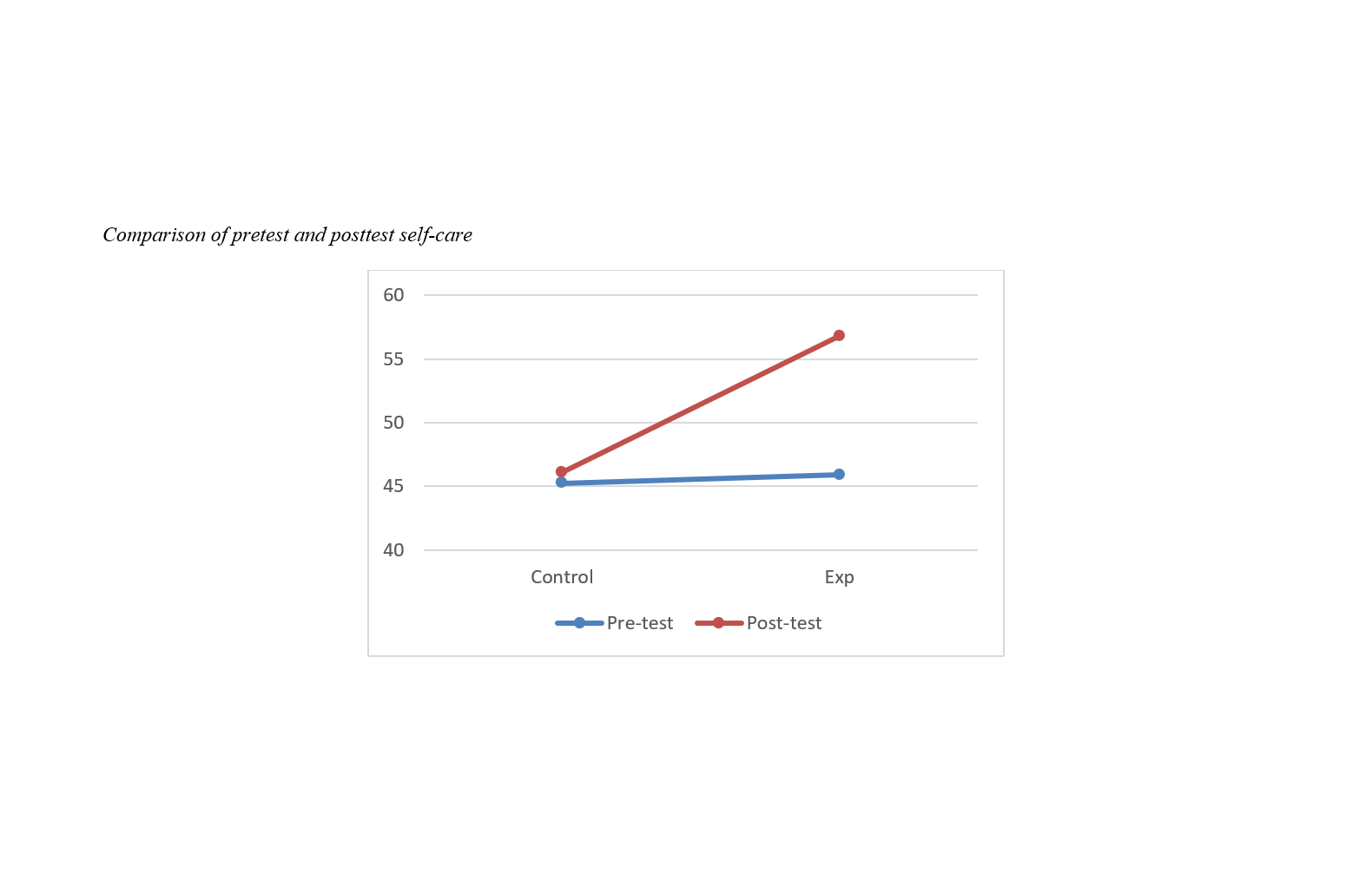
This study aimed to develop and validate a cognitive rehabilitation package targeting executive functions and to determine its effectiveness on communication skills and self-care in adolescents aged 14–20 years with developmental intellectual disability. The research employed a mixed-methods (qualitative–quantitative) design. In the qualitative phase, the executive functions cognitive rehabilitation intervention package was developed through a systematic review and concurrent meta-analysis of articles indexed in scientific databases published between 2014 and 2024, and its content was subsequently approved by experts in the field. In the quantitative phase, using a quasi-experimental method with a pretest–posttest control group design, 30 adolescents with intellectual disability enrolled in special education schools in Kashan County were selected through convenience sampling and randomly assigned to experimental and control groups (15 participants per group). The intervention program was implemented in 12 one-hour sessions. Data in the qualitative phase were collected using library and documentary methods and interviews, and in the quantitative phase using the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire by Hoffman and Kashdan (2010) and the National Adaptive Behavior Scale developed by Malekshahi, Kamkari, and Makvandi (2018). The validity of the developed package was examined using thematic analysis, and its effectiveness was analyzed using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) in SPSS version 24. The findings indicated that the mean Content Validity Ratio (CVR) and Content Validity Index (CVI) of the developed package were 0.62 and 0.79, respectively, demonstrating adequate validity of the designed intervention. Statistical results showed significant improvements in self-care and communication skills at the posttest stage in the experimental group compared with the control group. Therefore, it can be concluded that the executive functions rehabilitation package is effective in improving self-care and communication skills in adolescents with developmental intellectual disability and can be utilized to enhance these competencies in this population.
Downloads
References
Asrofin, B., & Kristiana, E. (2023). The Effectiveness Of The Drill And Practice Method On Menstrual Personal Hygiene Behavior In Teenagers With Intellectual Disabilities At Extraordinary School (Slb) Shanti Kosala Mastrip Nganjuk. Journal for Quality in Women's Health, 6(1), 31-36. https://doi.org/10.30994/jqwh.v6i1.202
Babiak, O. (2020). Communication Peculiarities of Adolescents with Mental Retardation in Student Group. Journal La Edusci, 1(3), 17. https://doi.org/10.37899/journallaedusci.v1i3.183
Baragash, R. S., Al-Samarraie, H., & Zaqout, F. (2022). Augmented Reality and Functional Skills Acquisition Among Individuals With Special Needs: A Meta-Analysis of Group Design Studies. Journal of Special Education Technology, 37(1), 74-81. https://doi.org/10.1177/0162643420910413
Bauer, V., Bouchara, T., Duris, O., Labossière, C., Clément, M. N., & Bourdot, P. (2023). Head-mounted augmented reality to support reassurance and social interaction for autistic children with severe learning disabilities. Frontiers in Virtual Reality, 4, 1106061. https://doi.org/10.3389/frvir.2023.1106061
Chiappini, M., Dei, C., Micheletti, E., & Storm, F. A. (2024). High-Functioning Autism and Virtual Reality Applications: A Scoping Review. Applied Sciences, 14(7), 3132. https://doi.org/10.3390/app14073132
Gitit, K. (2020). Associations between memory and verbal fluency tasks. Journal of Communication Disorders, 83, 105968. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcomdis.2019.105968
Gómez-Pérez, M. M., & Calero, M. D. (2023). The influence of intelligence and sex on interpersonal skills and executive functions in children. High Ability Studies, 34(1), 21-37. https://doi.org/10.1080/13598139.2022.2033173
Hashemi Razini, H., & Karampour, M. (2015). The Effectiveness of Executive Functions Training on the Social and Communication Skills of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Clinical Psychology Studies, 6(20), 161-185. https://jcps.atu.ac.ir/article_1868.html?lang=en
Howard, J., Herold, B., Major, S., Leahy, C., Ramseur, K., Franz, L., Deaver, M., Vermeer, S., Carpenter, K. L. H., Murias, M., Huang, W. A., & Dawson, G. (2023). Associations between executive function and attention abilities and language and social communication skills in young autistic children. Autism. https://doi.org/10.1177/13623613231154310
Kim, J., & Chung, Y. J. (2023). A case study of group art therapy using digital media for adolescents with intellectual disabilities. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 14, 1172079. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1172079
Mejvar, S., Arjmandnia Ali, A., Shokoohi-Yekta, M., Ghobari-Bonab, B., & JafarKhani, F. (2024). The Effectiveness of an Executive Functions Training Program Using Augmented Reality on the Communication Skills of Children with High-Functioning Autism Spectrum Disorder. Journal of Cognition in Psychology and Psychiatry, 11(6), 1-17. https://doi.org/10.32598/shenakht.11.6.1
Mumbardó-Adam, C., Vicente, E., Simó-Pinatella, D., & Balboni, G. (2023). Understanding how self-determination affects the quality of life of young people with intellectual disability. International Journal of Disability, Development and Education. https://doi.org/10.1080/1034912X.2023.2212619
Northrup, J. B. (2025). Improving Emotion Regulation and Executive Function in At-Risk Adolescents via VR. Applied Sciences, 15(3), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031223
Nouwens, S., Groen, M. A., Kleemans, T., & Verhoeven, L. (2021). How executive functions contribute to reading comprehension. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 91(1), 169-192. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjep.12355
O'Flanagan, S., & Nicolson, R. (2023). Survey results on training in developmental disabilities in Canadian psychiatry residency programs. Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry, 32(1), 4-17. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9879034/
Pasqualotto, A., & Venuti, P. (2020). A multifactorial model of dyslexia: evidence from executive functions and phonological‐based treatments. Learning disabilities Research & Practice, 35(3), 150-164. https://doi.org/10.1111/ldrp.12228
Peña-Farfán, C., Peralta-Bautista, F., Panamá-Mazhenda, K., Bravo-Buri, S., Robles-Bykbaev, Y., Robles-Bykbaev, V., & Lema-Condo, E. (2023). A Smart Mirror Based on Computer Vision and Deep Learning to Support the Learning of Sexual Violence Prevention and Self-care Health in Youth with Intellectual Disabilities. International Conference on Information Technology & Systems, Cham.
Rachma, A., & Hendrawan, D. (2025). Pathway Linking Executive Function Problems and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Among Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Emotion Dysregulation. Psikohumaniora Jurnal Penelitian Psikologi, 10(1), 43-58. https://doi.org/10.21580/pjpp.v10i1.23353
Sabzi, R., Mihandoost, Z., Nadimi, A., & Parandin, S. (2023). Investigating the Effectiveness of Executive Functions Training on Emotional Self-Regulation Ability and Test Anxiety in Female Students with Mathematics Learning Disability. Journal of Disability Studies, 13, 23-33. https://jdisabilstud.org/browse.php?a_id=2833&sid=1&slc_lang=en
Sargolzae, M., Jenaabadi, H., & Arab, A. (2018). Effectiveness of problem-solving metacognitive training and excitement regulation on emotional processing, impulsivity and sensuality of students with specific learning disorder (malfunctioning in mathematics). Journal of Learning Disabilities, 7(4), 42-67. https://jld.uma.ac.ir/m/article_681.html?lang=en
Schworer, E., Fidler, D. J., Kaur, M., Needham, A. W., Prince, M. A., & Daunhauer, L. A. (2022). Infant precursors of executive function in Down syndrome. Journal of Intellectual Disability Research, 66, 108-120. https://doi.org/10.1111/jir.12824
Seymour, K. E. (2025). Emotion regulation beyond executive dysfunction in adolescents. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 19, 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-025-00898-1
Tikdari, F., Kamyaabi, M., Tajrobe-Kaar, M., & Soltani, A. (2023). The Effectiveness of Executive Functions Training on Improving Social Skills and Emotional Processing in Children with Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder. Journal of Pediatric Nursing, 10(2), 47-56. https://jpen.ir/browse.php?a_id=731&sid=1&slc_lang=en
Tuffrey-Wijne, I., & McEnhill, L. (2008). Communication difficulties and intellectual disability in end-of-life care. International Journal of Palliative Nursing, 14(4), 189-194. https://doi.org/10.12968/ijpn.2008.14.4.29133