The Effectiveness of Neurofeedback on Working Memory Performance and Cognitive Planning Ability in Children with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder
Keywords:
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), Cognitive Planning, Working Memory, NeurofeedbackAbstract
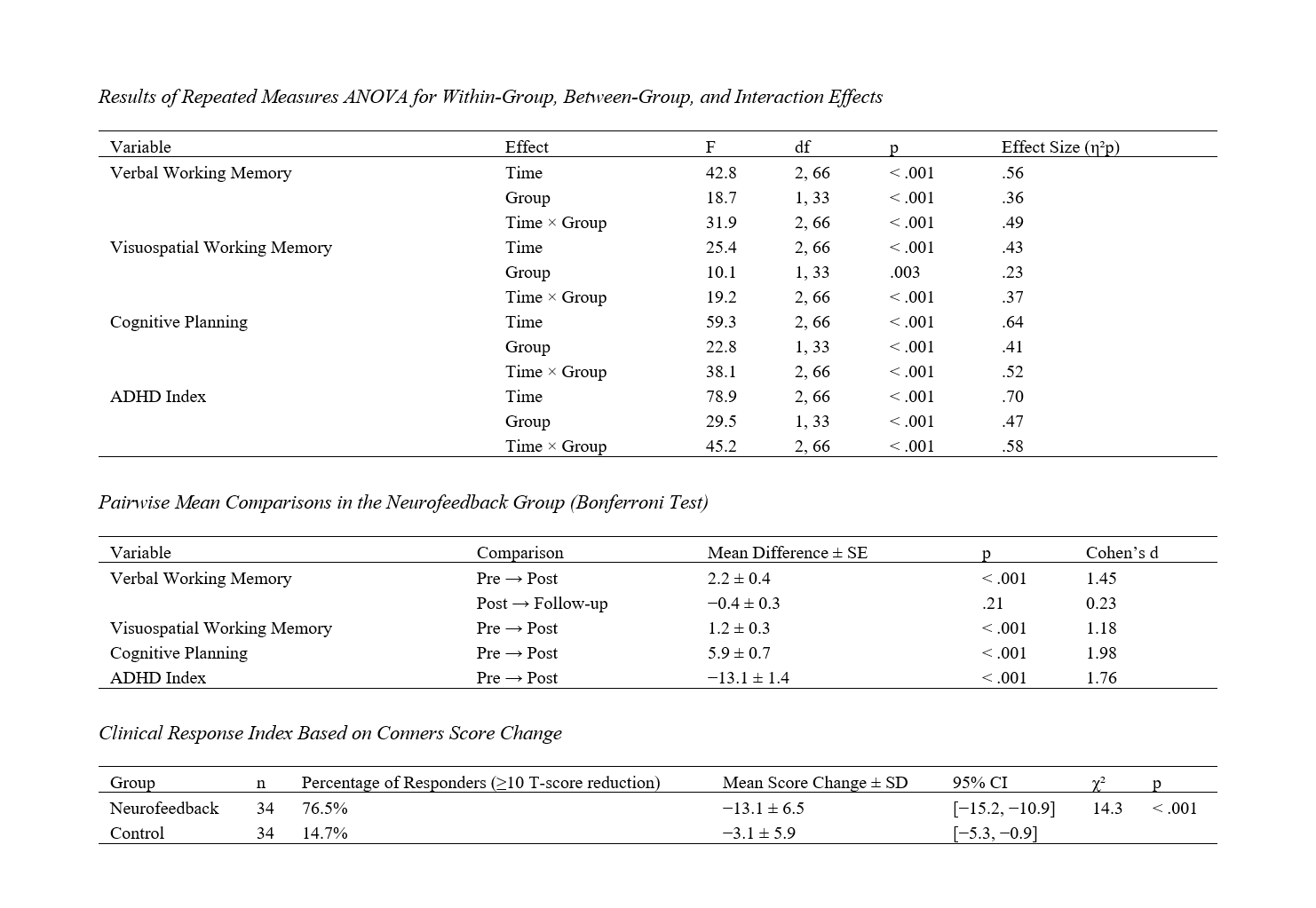
The present study aimed to examine the effectiveness of neurofeedback on working memory performance and cognitive planning ability in children with ADHD. This semi-experimental study employed a pretest–posttest control group design with a follow-up phase. The statistical population consisted of all children aged 7 to 14 years diagnosed with ADHD who attended the Shiva Counseling and Psychology Center in Rasht in 2025. From this population, 70 children (35 in the experimental group and 35 in the control group) were selected through purposive sampling. The experimental group received 20 sessions of neurofeedback training (two sessions per week, each lasting 30 to 40 minutes). The neurofeedback protocol involved reducing the theta/beta ratio in the F4 region, enhancing sensorimotor rhythm (SMR), and decreasing theta and delta activity in the frontal and Cz regions. Data collection instruments included the Conners-3 Questionnaire, the Wechsler Digit Span Subtest, the Corsi Block-Tapping Test for visuospatial memory, and the Tower of London Test for cognitive planning. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and mixed-design ANOVA with repeated measures in SPSS version 29. Results revealed that the mean scores of verbal and visuospatial working memory, cognitive planning ability, and the reduction of ADHD index significantly improved in the neurofeedback group compared to the control group in both posttest and follow-up stages (p < .001). The effects of time, group, and the interaction between time × group were significant across all variables (partial η² ranging from .43 to .70). Bonferroni post hoc tests indicated that the changes from pretest to posttest were significant and remained stable at the follow-up phase. Moreover, 76.5% of children in the neurofeedback group demonstrated a clinically significant reduction (more than 10 T-score points on the Conners Questionnaire). The findings suggest that neurofeedback, through the modulation of brainwave patterns in frontal and central regions, can produce lasting improvements in working memory and cognitive planning abilities among children with ADHD.
Downloads
References
Barkley, R. A. (2015). Attention-Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Handbook for Diagnosis and Treatment. New York: Guilford Press. https://journals.sagepub.com/doi/abs/10.1177/019874299401900205
Himmelmeier, L., & Werheid, K. (2024). Neurofeedback Training in Children with ADHD: A Systematic Review of Personalization and Methodological Features Facilitating Training Conditions. Clinical EEG & Neuroscience, 55(6), 625-635. https://doi.org/10.1177/15500594241279580
Hunkin, H., King, D. L., & Zajac, I. T. (2021). EEG Neurofeedback During Focused Attention Meditation: Effects on State Mindfulness and Meditation Experiences. Mindfulness, 12(4), 841-851. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12671-020-01541-0
Jounghani, A. R., Gozdas, E., Dacorro, L., Avelar-Pereira, B., Reitmaier, S., Fingerhut, H., Hong, D. S., Elliott, G., Hardan, A. Y., Hinshaw, S. P., & Hosseini, S. M. H. (2024). Neuromonitoring-guided working memory intervention in children with ADHD. Iscience, 27(11), 111087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2024.111087
Kofler, M. J., Groves, N. B., Chan, E. S. M., Marsh, C. L., Cole, A. M., Gaye, F., Cibrian, E., Tatsuki, M., & Singh, L. J. (2024). Working memory and inhibitory control deficits in children with ADHD: An experimental evaluation of competing model predictions. Frontiers in Psychiatry. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1277583
Kwon, S. Y. (2023). The Effect of Mobile Neurofeedback Training in Children With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience, 22(1), 67-78. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.23.1054
Li, G., Hu, Y., Zhang, W., Wang, J., Ji, W., Manza, P., Volkow, N. D., Zhang, Y., & Wang, G.-J. (2023). Brain functional and structural magnetic resonance imaging of obesity and weight loss interventions. Molecular Psychiatry, 28(4), 1466-1479. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41380-023-02025-y
Louthrenoo, O., Boonchooduang, N., Likhitweerawong, N., Charoenkwan, K., & Srisurapanont, M. (2022). The Effects of Neurofeedback on Executive Functioning in Children With ADHD: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Attention Disorders, 26(7), 976-984. https://doi.org/10.1177/10870547211045738
Shari, S., Sedaghat, M., Shoja Kazemi, M., & Moradi, H. (2021). Evaluation of neurofeedback training on executive functioning, cognitive flexibility, and attention in students with learning disorders. Scientific Journal of Ilam University of Medical Sciences, 3(3), 62-74. https://doi.org/10.52547/sjimu.30.3.62
Sheikh, M., Aghasoleimani Najafabadi, M., Shahrbanian, S., & Alavizadeh, S. M. (2022). Effectiveness of Neurofeedback With Selected Training Program on Motor Function, Anxiety, and Sleep Habits in Children With Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD). The Scientific Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 11(3), 356-369. https://doi.org/10.32598/sjrm.11.3.1
Shojaei, B. (2024). Reducing Symptoms of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Elementary Students: The Effectiveness of Neurofeedback. Annals of medicine and surgery, 86(5), 2651-2656. https://doi.org/10.1097/ms9.0000000000001861
Viviani, G., & Vallesi, A. (2021). EEG-neurofeedback and executive function enhancement in healthy adults: A systematic review. Psychophysiology, 58(9), e13874. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.13874
Wu, G., He, Q., Li, D., Zhang, Z., Miao, J., & Shu, Y. (2024). Comparative Efficacy of Neurofeedback Interventions for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder in Children: A Network Meta-Analysis. Brain and Behavior, 14(12), e70194. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.70194
Yaghoobi Karimi, R., Azadi, S., & Rahmani Seryasat, O. (2023). Studying The Influences of Visual Neurofeedback Below the Range Of Δ Frequency Band. Transactions on Machine Intelligence, 6(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.47176/tmi.2023.1
Zhang, F., Li, X., Wang, J., & Chen, S. (2024). Comparative Efficacy of Neurofeedback Interventions for Children With Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Network Meta-Analysis. Brain and Behavior, 14(5), e70194. https://doi.org/10.1002/brb3.70194
Zhong, X., Yuan, X., & Dai, Y. (2025). Neurofeedback training for executive function in ADHD children: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Scientific reports, 15, 28148. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-025-94242-4