Identifying Generational Gaps in Emotional Expression among Youth and Parents
Keywords:
Emotional expression, parent–child relationships, generational differences, emotional regulationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the generational gaps in emotional expression between youth and their parents, focusing on differences in communication styles, regulation strategies, and cultural influences within Canadian families.
Methods and Materials: A qualitative research design was employed using an interpretive phenomenological approach to capture participants’ lived experiences of emotional communication across generations. The study involved 20 participants from Canada, including 10 adolescents aged 15–20 years and 10 parents aged 40–55 years. Data were collected through semi-structured interviews and analyzed using thematic analysis in NVivo 14. Theoretical saturation guided the sampling process, and themes were identified through iterative coding and constant comparison.
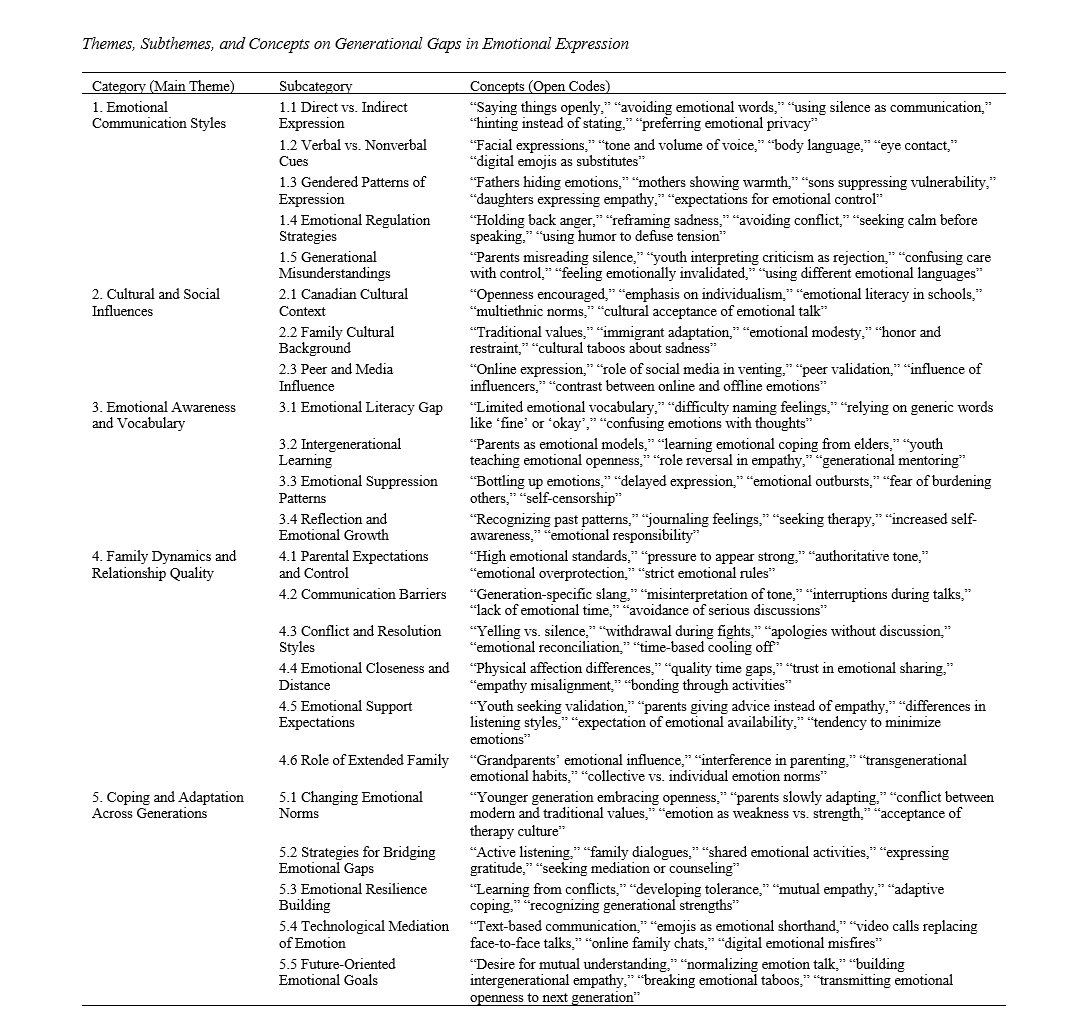
Findings: Five major themes emerged from the analysis: (1) emotional communication styles, highlighting contrasts between direct and indirect expression; (2) cultural and social influences, emphasizing the interplay of traditional and contemporary emotional norms; (3) emotional awareness and vocabulary, revealing differences in emotional literacy between generations; (4) family dynamics and relationship quality, identifying emotional distance and mismatched support expectations; and (5) coping and adaptation across generations, showing gradual mutual adjustment through empathy and communication.
Conclusion: Generational differences in emotional expression reflect broader cultural, psychological, and developmental shifts within families. While these gaps may cause miscommunication and emotional tension, they also provide opportunities for intergenerational learning and resilience through dialogue, empathy, and shared emotional growth.
Downloads
References
Born, V. d. L., & Vasbø, K. B. (2024). “Doing Authority”: Stories of Parental Authority Across Three Generations. Journal of marriage and family, 87(1), 114-133. https://doi.org/10.1111/jomf.13028
Chen, Y. Y., Zhou, Z., Qu, Y., & Lee, T. H. (2025). From Family Relationship to Regulation: Parent–Child Amygdala Activation Similarity Is Linked to Prefrontal Recruitment and Youth Emotional Adaptation. https://doi.org/10.1101/2025.07.21.665810
Church, L., Bounoua, N., Stumps, A., Matyi, M. A., & Spielberg, J. M. (2025). Examining the Unique Contribution of Parent Anxiety Sensitivity on Adolescent Neural Responses During an Emotion Regulation Task. Development and Psychopathology, 1-11. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579425000227
Johnson, H. J., Rasooly, T., Frater, A., Gioia, G. A., & Vaughan, C. (2025). A - 43 Executive Functioning and Concussion in Autistic Youth. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 40(Supplement_1), i43-i43. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/acaf058.43
Jones, J. D., Fraley, R. C., Stern, J., Lejuez, C. W., & Cassidy, J. (2024). Developmental Trajectories of Adolescent Internalizing Symptoms and Parental Responses to Distress. Development and Psychopathology, 37(2), 603-614. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579424000361
Ke, J., Luo, B., Huang, C., Tong, Y., Wang, Y., Li, X., Ma, W., Zhao, L., & Liao, S. (2024). Associations Between the Number of Siblings, Parent–child Relationship and Positive Youth Development of Adolescents in Mainland China: A Cross‐sectional Study. Child Care Health and Development, 50(3). https://doi.org/10.1111/cch.13259
Kennedy-Turner, J., Németh, Z., & Anderson, L. (2025). Is Familial Expressed Emotion Associated With Self-Harm and Suicidality in Childhood and Adolescence? A Systematic Review. Adolescent Research Review. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40894-025-00261-7
Mera, S., Zimmer‐Gembeck, M. J., Conlon, E. G., Ryan, K. M., & Dower, A. (2025). A Scoping Review of the Role of Mindful Parenting in Youth’s Emotional, Behavioral, and Social Adjustment, Coping, and Emotion Regulation. International Journal of Behavioral Development. https://doi.org/10.1177/01650254251381983
Nguyen, G. H., Oh, S., Schneider, C. C., Teoh, J. Y., Engstrom, M., Santana-Gonzalez, C., Porter, D. A., & Quevedo, K. (2023). Neurofeedback and Affect Regulation Circuitry in Depressed and Healthy Adolescents. Biology, 12(11), 1399. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology12111399
Nielsen, E. S., Kallesøe, K. H., Hansen, A. S., Frostholm, L., Lalouni, M., Bonnert, M., & Rask, C. U. (2025). Parental Distress and Symptom Severity in Referred Youths With Functional Abdominal Pain Disorders: A Cross-Sectional Study Prior to Internet-Based Cognitive Behavioral Therapy. Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology, 18. https://doi.org/10.1177/17562848251383414
Orgilés, M., Belzunegui-Pastor, À., Morales, A., & Espada, J. P. (2023). Parental Stress as a Mediator Between Parents’ Emotion Regulation and Youth’s Psychological Symptoms During the COVID-19 Lockdown: A Cross-Sectional Study. Psychology Society & Education, 15(1), 40-47. https://doi.org/10.21071/pse.v15i1.15383
Passanisi, S., Galletta, F., Bombaci, B., Cherubini, V., Tiberi, V., Minuto, N., Bassi, M., Iafusco, D., Piscopo, A., Mozzillo, E., Candia, F. D., Rabbone, I., Pozzi, E., Franceschi, R., Cauvin, V., Maffeis, C., Piona, C., & Salzano, G. (2024). Device-Related Skin Reactions Increase Emotional Burden in Youths With Type 1 Diabetes and Their Parents. Journal of Diabetes Science and Technology, 18(6), 1293-1299. https://doi.org/10.1177/19322968241253285
Rodríguez-Mondragón, L., Moreno‐Encinas, A., Graell, M., Román, F. J., & Sepúlveda, A. R. (2024). A Case–control Study to Differentiate Parents' Personality Traits on Anorexia Nervosa and Affective Disorders. Family Process, 63(4), 2099-2118. https://doi.org/10.1111/famp.12994
Saldana, L., & Polo, A. J. (2024). Latinx Parent–child Acculturative Stress Profiles and Their Relation to Expressed Emotion and Academic Achievement. Cultural diversity & ethnic minority psychology, 30(4), 829-840. https://doi.org/10.1037/cdp0000702
Shi, Z., Qu, Y., Wang, Q., & Li, Y. (2024). Parental Psychological Control and Emotional Well-Being Among Emerging Adults: The Moderating Role of Parent-Oriented Self-Construals. International Journal of Behavioral Development, 48(3), 261-268. https://doi.org/10.1177/01650254241233545
Suk, J.-W., Blair, J., Vaughan, B. S., Lerdahl, A., Garvey, W. F., Edwards, R., Leibenluft, E., & Hwang, S. (2023a). Mediating Effect of Amygdala Activity on Response to Fear vs. Happiness in Youth With Significant Levels of Irritability and Disruptive Mood and Behavior Disorders. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 17. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2023.1204574
Suk, J.-W., Blair, J., Vaughan, B. S., Lerdahl, A., Garvey, W. F., Edwards, R., Leibenluft, E., & Hwang, S. (2023b). Mediating Effect of Amygdala Activity on Responses to Fear vs. Happiness in Youths With Disruptive Mood and Behavior Disorders. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-2545913/v1
Yeung, J. W. K., Chen, H.-F., Lo, H. H. M., Xu, L., & Xu, C. (2023). Minor Forms of Parental Maltreatment and Educational Achievement of Immigrant Youths in Young Adulthood: A Longitudinal Study. International journal of environmental research and public health, 20(1), 873. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20010873