Family Conflict and Adolescent Self-Injury: The Mediating Role of Alexithymia
Keywords:
Adolescent self-injury, family conflict, alexithymia, emotional regulationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the relationship between family conflict and adolescent self-injury, with a focus on the mediating role of alexithymia.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational design was employed using a sample of 396 South African secondary school students selected based on the Morgan and Krejcie sampling table. Standardized instruments were used to assess family conflict, alexithymia, and self-injurious behavior. Data were analyzed using SPSS-27 for Pearson correlation and AMOS-21 for structural equation modeling (SEM). Assumptions for normality, linearity, and multicollinearity were confirmed prior to analysis. The structural model tested both direct and indirect effects to evaluate the mediating function of alexithymia in the relationship between family conflict and self-injury.
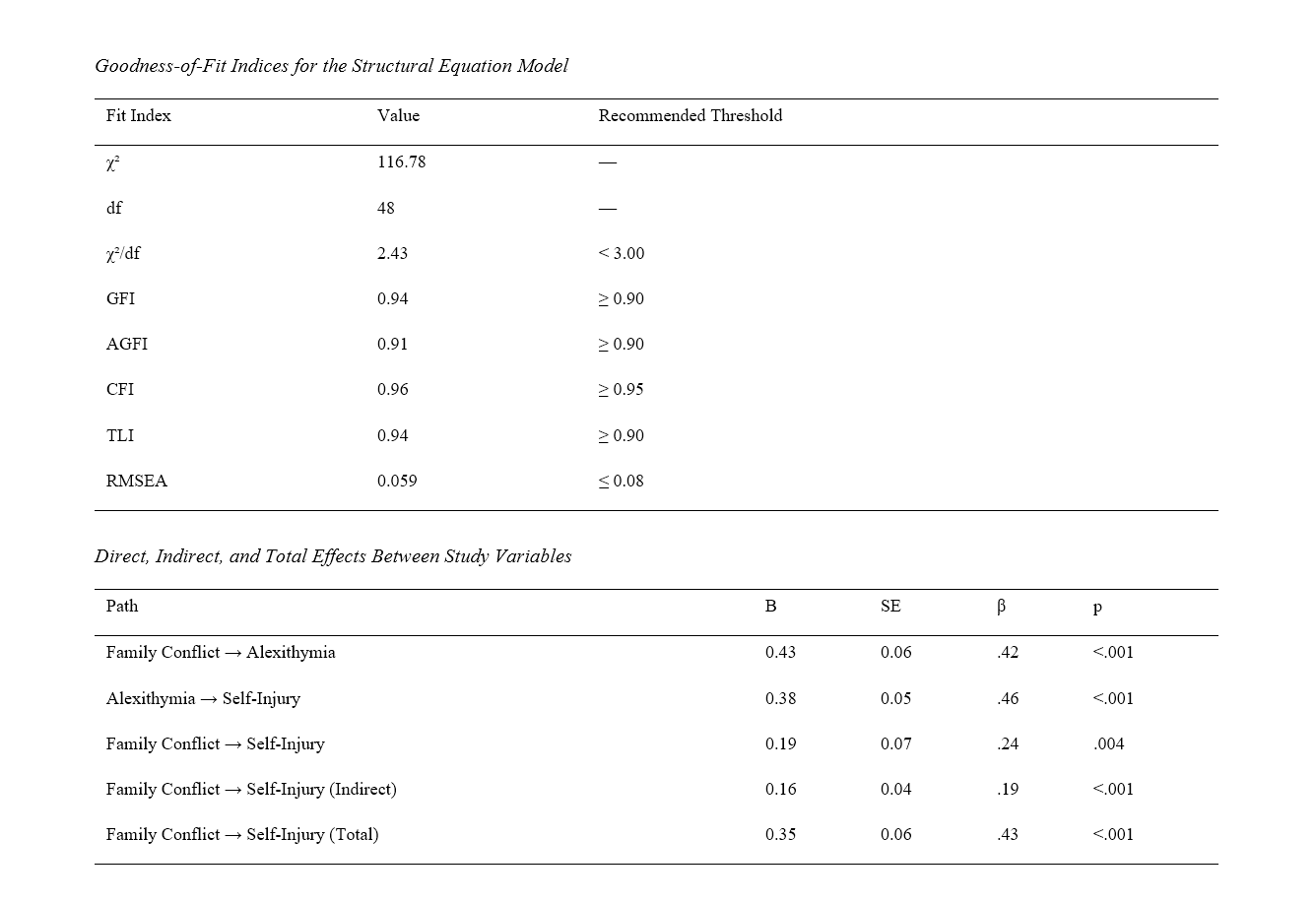
Findings: Pearson correlations showed significant positive relationships among all variables: family conflict and alexithymia (r = .42, p < .01), family conflict and self-injury (r = .34, p < .01), and alexithymia and self-injury (r = .49, p < .01). The structural model demonstrated excellent fit indices (χ²/df = 2.43, CFI = 0.96, RMSEA = 0.059). Path analysis revealed significant direct effects of family conflict on alexithymia (B = 0.43, β = .42, p < .001), alexithymia on self-injury (B = 0.38, β = .46, p < .001), and family conflict on self-injury (B = 0.19, β = .24, p = .004). The indirect effect of family conflict on self-injury through alexithymia was also significant (B = 0.16, β = .19, p < .001), confirming partial mediation.
Conclusion: Findings underscore alexithymia as a critical emotional mechanism linking family conflict to self-injurious behavior in adolescents. Interventions targeting emotional awareness and family communication may help mitigate the risks associated with adolescent self-harm, especially in culturally diverse contexts.
Downloads
References
Adrian, M., McCauley, E., Berk, M., Asarnow, J. R., Korslund, K. E., Avina, C., Gallop, R., & Linehan, M. M. (2019). Predictors and Moderators of Recurring Self‐harm in Adolescents Participating in a Comparative Treatment Trial of Psychological Interventions. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 60(10), 1123-1132. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcpp.13099
Agüero, G., Medina, V., Obradovich, G., & Berner, E. (2018). Self-Injurious Behaviors Among Adolescents. A Qualitative Study of Characteristics, Meanings, and Contexts. Archivos Argentinos De Pediatria, 116(6). https://doi.org/10.5546/aap.2018.eng.394
Bandzeladze, T., Arutiunov, L., & Espinosa, P. (2019). The Role of Family Factors and Self-Regulation: Problem Behavior in Georgian Adolescents. Revista de Estudios e Investigación en Psicología y Educación, 6(2), 146-155. https://doi.org/10.17979/reipe.2019.6.2.5775
Bjørndal, L. D., Ebrahimi, O. V., & Bauermeister, S. (2024). The Dynamic Interplay Between Mental Health Difficulties and the Family Environment in Early Adolescence. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/9j4hp
Campbell, M. S., Berg, C. A., & Wiebe, D. J. (2019). Parental Self-Control as a Moderator of the Association Between Family Conflict and Type 1 Diabetes Management. Journal of Pediatric Psychology, 44(8), 999-1008. https://doi.org/10.1093/jpepsy/jsz040
Cao, G., & Tam, V. C. W. (2021). Using an Interactional Perspective to Examine Patterns of Conflict Resolution Among Chinese Adolescents and Parents Involved in Schoolwork Conflicts. International Journal of Chinese Education, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.1177/22125868211005859
DeVille, D. C., Whalen, D. J., Breslin, F. J., Morris, A. S., Khalsa, S. S., Paulus, M. P., & Barch, D. M. (2020). Prevalence and Family-Related Factors Associated With Suicidal Ideation, Suicide Attempts, and Self-Injury in Children Aged 9 to 10 Years. JAMA Network Open, 3(2), e1920956. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.20956
Kelada, L., Hasking, P., & Melvin, G. (2016). The Relationship Between Nonsuicidal Self‐Injury and Family Functioning: Adolescent and Parent Perspectives. Journal of marital and family therapy, 42(3), 536-549. https://doi.org/10.1111/jmft.12150
Li, Y., Li, X., Li, Y., Xiao, Y., Li, C., Chen, J., Yao, L., Luo, L., Su, D., Jia, J., Cheng, H.-f., Liu, T., & Du, N. (2023). The Effects of Family Environment Cognition and Its Difference Perceived by Adolescents and Their Parents on the Treatment Effect of Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Behaviors in Adolescents: A 1-Year Prospective Cohort Study. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1183916
Li, Y., & Warner, L. A. (2015). Parent–Adolescent Conflict, Family Cohesion, and Self‐Esteem Among Hispanic Adolescents in Immigrant Families: A Comparative Analysis. Family Relations, 64(5), 579-591. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.12158
Manuela Almeida da Silva, S., & Dell’Aglio, D. D. (2022). Self-Injury in Adolescence From the Bioecological Perspective of Human Development. Psicologia - Teoria E Prática, 24(1). https://doi.org/10.5935/1980-6906/eptphd13325.en
Maria Letícia Coelho de, O., Gómez‐Baya, D., Tomé, G., Reis, M., Maltoni, J., Neufeld, C. B., Matos, M. G. d., & Carolina Saraiva de Macedo, L. (2020). Comportamentos Autolesivos, Ajuste Psicológico E Relações Familiares Em Adolescentes Da Região Amazônica No Brasil. Análisis Y Modificación De Conducta, 46(173-4). https://doi.org/10.33776/amc.v46i173-4.3644
McCauley, D. M., Weymouth, B. B., Feinberg, M. E., & Fosco, G. M. (2018). Evaluating School and Peer Protective Factors in the Effects of Interparental Conflict on Adolescent Threat Appraisals and Self‐efficacy. Journal of adolescence, 71(1), 28-37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2018.12.005
Moraes, D. X., Moreira, É. d. S., Sousa, J. M., Raquel Rosa Mendonça do, V., Pinho, E. S., Paula Cândida da Silva, D., & Caixeta, C. C. (2020). “The Pen Is the Blade, My Skin the Paper”: Risk Factors for Self-Injury in Adolescents. Revista Brasileira de Enfermagem, 73(suppl 1). https://doi.org/10.1590/0034-7167-2020-0578
Nelson, B. W., Pollak, O. H., Clayton, M. G., Telzer, E. H., & Prinstein, M. J. (2023). An RDoC-based Approach to Adolescent Self-Injurious Thoughts and Behaviors: The Interactive Role of Social Affiliation and Cardiac Arousal. Development and Psychopathology, 36(3), 1005-1015. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579423000251
Pawłowska, B., Potembska, E., Zygo, M., Olajossy, M., & Dziurzyńska, E. (2016). Prevalence of Self-Injury Performed by Adolescents Aged 16–19 Years. Psychiatria Polska, 50(1), 29-42. https://doi.org/10.12740/pp/36501
Pearson, I., Chase, E., Kim, C., San, N. M., Ja, H., Hlaing, Z. M., Oo, N., Lae, K., Soe, E. E., Zobrist, B., Zimmerman, C., & Ranganathan, M. (2025). Conflict Exposure and Mental Health: A Survey of Adolescent Girls and Young Women in Myanmar Post the 2021 Coup D’état. Conflict and Health, 19(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13031-025-00668-y
Roberts, J. A., Pullig, C., & David, M. E. (2019). Family Conflict and Adolescent Compulsive Buying Behavior. Young Consumers Insight and Ideas for Responsible Marketers, 20(3), 208-218. https://doi.org/10.1108/yc-10-2018-0870
Sari, E. L., Fitria, Y., Kurniyawan, E. H., Dewi, E. I., & Deviantony, F. (2024). Family Function and Self-Harm Behavior in Early Adolescents: A Cross-Sectional Study. Psychiatry Nursing Journal (Jurnal Keperawatan Jiwa), 6(2), 62-70. https://doi.org/10.20473/pnj.v6i2.60753
Tuohy, E., Gallagher, P., Rawdon, C., Murphy, N., McDonnell, C., Swallow, V., & Lambert, V. (2025). Parent-Adolescent Communication, Self-Efficacy, and Self-Management of Type 1 Diabetes in Adolescents. The Science of Diabetes Self-Management and Care, 51(1), 73-84. https://doi.org/10.1177/26350106241304424
Vafaei, T., Samavi, S. A., Whisenhunt, J., & Najarpourian, S. (2023). An Investigation of Self-Injury in Female Adolescents: A Qualitative Study. Quality & Quantity, 57(6), 5599-5622. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-023-01632-9
Wan, Z., Fang, S., & Zhao, C. (2025). The Effect of Interparental Conflict on Non-Suicidal Self-Injury in Middle School Students: A Moderated Mediation Model of Self-Esteem and Regulatory Emotional Self-Efficacy. BMC psychology, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-025-02681-5
Wei, C., B, L., Wang, Y., Wang, Y., & Xu, Q. (2024). The Roles of Psychological Needs Satisfaction and Impulsivity to Parent-Child Conflict and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1501983
Wei, H., Zhang, Y., Sun, N., Wang, Y., & Li, Y. (2024). The Correlation Between Non-Suicidal Self-Injury and Mobile Phone Social Media Dependence in Adolescents. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4280256/v1
Wu, Y., Rong, Y., & Wu, Y. (2022). Good Can Be Stronger Than Bad: The Daily Relationship Among Maternal Warmth, Mother-Teen Conflict and Adolescents’ Self-Esteem. Current Psychology, 42(29), 25745-25754. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03718-3
Yang, Z., Cui, Y., Yang, Y., Wang, Y., Zhang, H., Liang, Y., Zhang, Y., & Shang, L. (2021). The Relationship Between Mental Health Problems and Systemic Family Dynamics Among High School and University Students in Shaanxi Province, China. International Journal of Public Health, 66. https://doi.org/10.3389/ijph.2021.1603988
Yekta, M. S., Farahani, M. N., Khanipour, H., & Shahgholian, M. (2023). Investigating the Effective Factors in the Formation of Deliberate Self-Harm in Adolescence: Mental Health Professionals’ Viewpoints. Practice in Clinical Psychology, 11(2), 151-166. https://doi.org/10.32598/jpcp.11.2.839.1
Zhao, H., Yan, X., Wang, F., Jiang, J., & Zhang, X. (2015). Influence of Parent—Adolescent Conflict Frequency on Adolescent Family Satisfaction and Self-Satisfaction in China: Conflict Coping Tactics as Moderators. Psychological Reports, 117(3), 897-915. https://doi.org/10.2466/21.10.pr0.117c28z7
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






