The Effectiveness of Emotion Regulation Training on Frustration Tolerance and Executive Functions in Adolescents of Tehran City
Keywords:
Emotion Regulation Training, Frustration Tolerance, Executive Functions, AdolescentsAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of emotion regulation training on frustration tolerance and executive functions among adolescents in Tehran City.
Methods and Materials: The research method was quasi-experimental with a pretest–posttest design including a control group. The statistical population comprised all secondary school adolescents in Tehran during 2025, from which 30 participants were selected through convenience sampling and randomly assigned to experimental and control groups. The experimental group participated in ten 90-minute sessions of emotion regulation training, whereas the control group received no intervention. To assess the study variables, the Harrington Frustration Tolerance Questionnaire (2005) and the Barkley Deficits in Executive Functioning Scale (2011) were used.
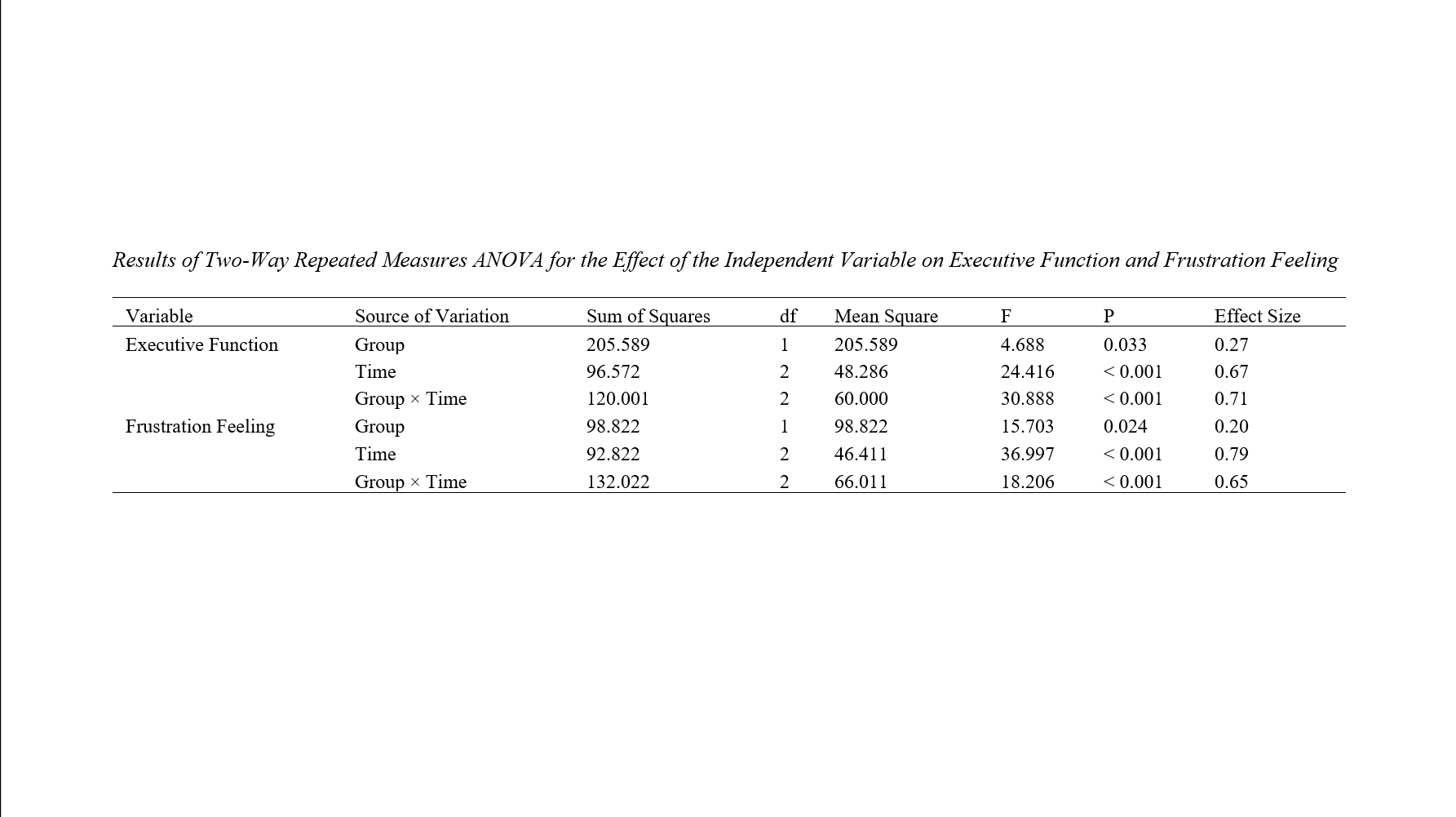
Findings: Findings indicated that emotion regulation training led to a significant increase in frustration tolerance and improvement in executive functions—including inhibitory control, cognitive flexibility, and self-regulation—in the experimental group (p < .05).
Conclusion: These results suggest that emotion regulation training can effectively enhance cognitive and emotional resilience in adolescents by improving self-awareness, emotional management, and flexible thinking skills. Therefore, implementing such training programs in educational and counseling settings is recommended to promote mental health and executive functioning among adolescents.
Keywords: Emotion Regulation Training, Frustration Tolerance, Executive Functions, Adolescents
Downloads
References
Ahmed, S. P. (2019). Neurocognitive bases of emotion regulation development in adolescence. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience, 15, 11–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dcn.2015.07.006
Barkley, R. A., & Benton, C. M. (2024). Focus on Executive Functions. Part 3: Emotion Regulation, Self-Motivation, and Planning/Problem-Solving. The ADHD Resource Hub, 2(6), 90-99. https://doi.org/10.1521/adhdhub.2024.2.6.1
Cécillon, F. X., Mermillod, M., Leys, C., Lachaux, J. P., Le Vigouroux, S., & Shankland, R. (2024). Trait Anxiety, Emotion Regulation, and Metacognitive Beliefs: An Observational Study Incorporating Separate Network and Correlation Analyses to Examine Associations with Executive Functions and Academic Achievement. Children, 11(1), 123. https://doi.org/10.3390/children11010123
Deveney, C. M. (2020). Frustration Paradigm and Cognitive Control in Children. Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 61(9), 987–995. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/PMC7523008
Eisenberg, N. (2010). Emotion-Related Self-Regulation and Children's Maladjustment. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 7, 495–525. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.clinpsy.121208.131208
Eisenberg, N. (2023). Emotion Regulation and Executive Functioning in Intervention Outcomes. Children, 10(1), 139. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10010139
Fombouchet, A. (2025). Relationships between emotion regulation strategies and executive functions in adolescence. Developmental science, 28(2), e13567. https://doi.org/10.1111/desc.13567
Frick, P. J. (2003). Callous-unemotional traits and developmental pathways to severe conduct problems. Journal of Clinical Child and Adolescent Psychology, 32(4), 537–548. https://doi.org/10.1207/S15374424JCCP3204_07
Ghosh, R. (2024). Effect of Mindfulness and Emotion Regulation Skills of Dialectical Behaviour Therapy on Executive Functions in Patients With Bipolar Affective Disorder, Current Episode Manic Master's thesis, Central Institute of Psychiatry (India)]. https://search.proquest.com/openview/bb2fcc1012ba1095e325e986ba024ffa/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=2026366&diss=y
Giancola, P. R. (2008). Executive functioning and aggression in adolescents. Aggression and Violent Behavior, 13(5), 357–368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.avb.2008.06.001
Hong, Y. (2025). Children's executive functions predict emotion regulation preferences. Cognition and Emotion, 39(6), 1312–1328. https://doi.org/10.1080/02699931.2024.2438078
Keskiner, E. Ş., Şahin, E., Topkaya, N., & Yiğit, Z. (2024). Behavioral Emotion Regulation Strategies and Symptoms of Psychological Distress Among Turkish University Students. Behavioral sciences (Basel, Switzerland), 15(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15010006
Lantrip, C. (2016). Executive Function and Emotion Regulation Strategy Use in Adolescents. Applied Neuropsychology: Child, 5(1), 50–55. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622965.2014.960567
Mazidi, M., Preece, D. A., Becerra, R., Gross, J. J., & MacLeod, C. (2025). Beliefs About Emotions in Self and Others: Links With Emotion Regulation and Psychological Distress. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/es6ac_v1
Northrup, J. B. (2025). Improving Emotion Regulation and Executive Function in At-Risk Adolescents via VR. Applied Sciences, 15(3), 1223. https://doi.org/10.3390/app15031223
Perlman, S. B. (2014). Developmental differences in frustration on working memory tasks. Child development, 85(3), 1139–1152. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12189
Rachma, A., & Hendrawan, D. (2025). Pathway Linking Executive Function Problems and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Among Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Emotion Dysregulation. Psikohumaniora Jurnal Penelitian Psikologi, 10(1), 43-58. https://doi.org/10.21580/pjpp.v10i1.23353
Seymour, K. E. (2025). Emotion regulation beyond executive dysfunction in adolescents. Child and adolescent psychiatry and mental health, 19, 12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13034-025-00898-1
Van Meter, A. (2023). The Effect of Emotion Regulation on Executive Function. Journal of Child and Adolescent Psychopharmacology, 33(8), 312–320. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/PMC10544783