Dimensions of Emotional Exhaustion among Adolescents Experiencing Family Conflict
Keywords:
Emotional exhaustion, family conflict, adolescents, qualitative research, Indonesia, emotional regulation, coping strategiesAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore and identify the core dimensions of emotional exhaustion among adolescents experiencing family conflict in Indonesia.
Methods and Materials: This qualitative study employed an exploratory design to examine the lived experiences of adolescents exposed to recurrent family conflicts. Using a purposive sampling approach, 22 adolescents aged 13 to 19 years (12 females and 10 males) from various urban and semi-urban regions in Indonesia participated in the research. Data were collected through semi-structured, in-depth interviews conducted in Bahasa Indonesia. Interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analyzed using NVivo 14 software. Thematic analysis, following Braun and Clarke’s six-step approach, was applied to identify core themes and subthemes. Theoretical saturation determined the final sample size. Rigor and credibility were ensured through member checking, peer debriefing, and an external audit of the coding framework.
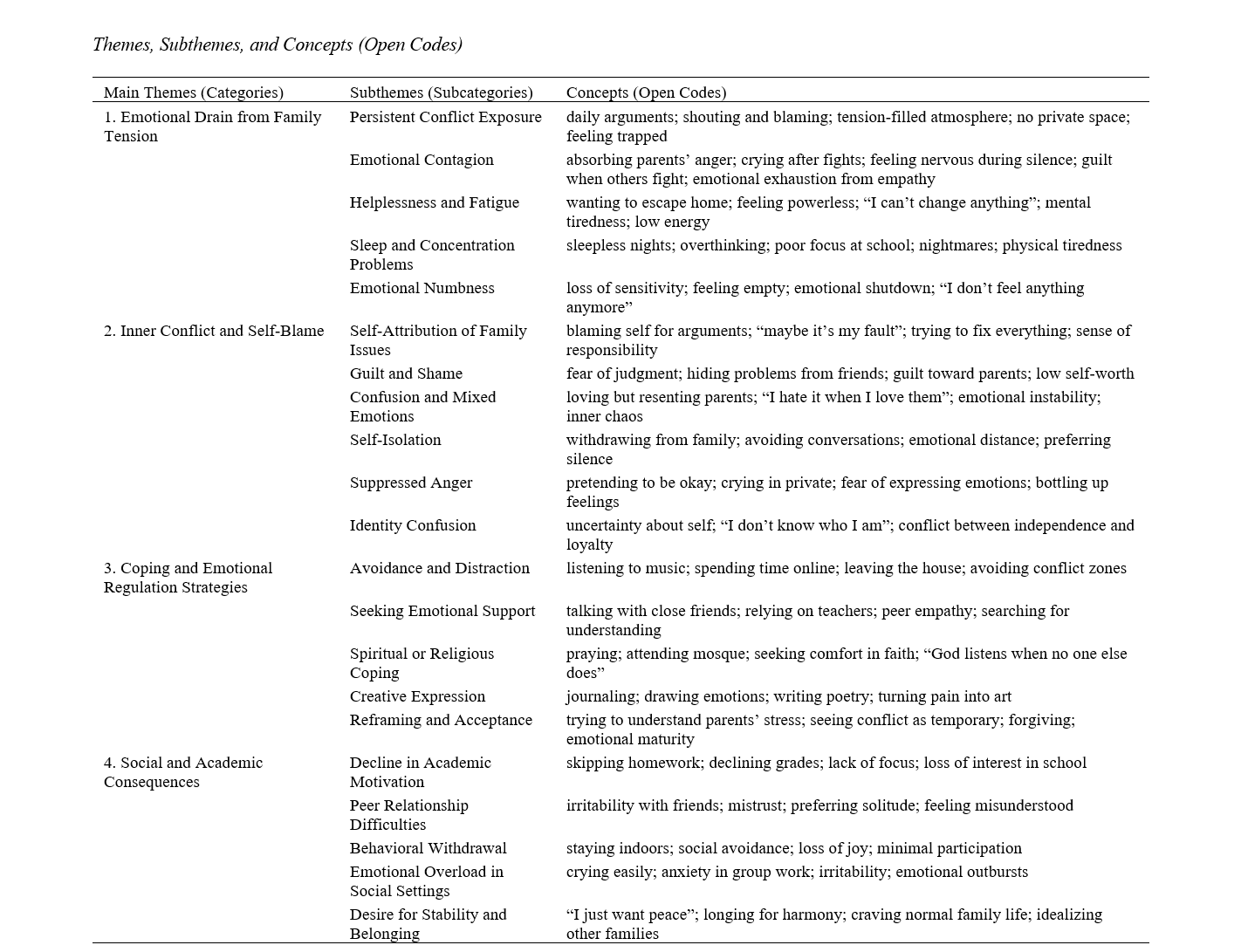
Findings: Data analysis revealed four overarching themes: (1) Emotional Drain from Family Tension, (2) Inner Conflict and Self-Blame, (3) Coping and Emotional Regulation Strategies, and (4) Social and Academic Consequences. Adolescents described chronic fatigue, helplessness, and emotional numbness resulting from prolonged family disputes. Feelings of guilt, shame, and internalized responsibility for family discord intensified emotional exhaustion. Coping strategies ranged from avoidance and spiritual reliance to creative expression and reframing. However, ineffective regulation often perpetuated distress. Emotional exhaustion further extended into diminished academic engagement, social withdrawal, and a strong yearning for family harmony. The findings collectively highlight emotional exhaustion as a relational, systemic, and culturally embedded process.
Conclusion: Emotional exhaustion among adolescents experiencing family conflict emerges as a multidimensional phenomenon rooted in persistent relational strain, internalized guilt, and limited emotional regulation resources. Strengthening family communication, emotional literacy, and support systems can mitigate exhaustion and promote adolescent emotional resilience.
Downloads
References
Abas, B., Bukhari, S. A., Farrukh, M., & Iqbal, S. (2024). Examining the Socio-Psychological Dynamics of Interpersonal and Organizational Deviances: The Moderating Influence of Interpersonal Justice and Perceived Organizational Support. Leadership & Organization Development Journal, 45(6), 935-953. https://doi.org/10.1108/lodj-07-2023-0350
Chiang, S. C., & Bai, S. (2024). Testing Family-of-Origin Sensitization: Parent-Adolescent Conflict, Emotional Reactivity, and Adolescent Internalizing Psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 37(4), 2172-2180. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579424001779
Dodanwala, T. C., & Shrestha, P. (2021). Work–family Conflict and Job Satisfaction Among Construction Professionals: The Mediating Role of Emotional Exhaustion. On the Horizon the International Journal of Learning Futures, 29(2), 62-75. https://doi.org/10.1108/oth-11-2020-0042
E.O, O., Enamudu, G. P., & Faith, N. (2024). Adolescent Pregnancy in Nigeria: A MIMIC Modelling of Risk and Protective Factors. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Applied Science, IX(V), 182-194. https://doi.org/10.51584/ijrias.2024.905016
Elattar, N. F. M., A.Zaki, R., & Mohamed, S. M. N. (2022). Relationship Between Adolescents’ Perception of Inter-Parental Conflict, the Feeling of Emotional Security in Their Family, and Academic Achievement. Egyptian Journal of Health Care, 13(2), 1803-1816. https://doi.org/10.21608/ejhc.2022.260893
Farrukh, M., Abas, B., Ghazzawi, I. A., & Rafiq, M. (2024). From Bad Bosses to Weakened Marriages: The Role of Abusive Supervision in Emotional Exhaustion, Work–family Conflict and Marital Strain. Management Decision, 63(7), 2597-2615. https://doi.org/10.1108/md-01-2024-0198
Feng, J. (2025). Emotional Exhaustion as a Mediator Between Emotional Labor and Work-to-Family Conflict. Scientific and Social Research, 7(1), 98-102. https://doi.org/10.26689/ssr.v7i1.9333
Hsieh, C. C., Liang, J. K., & Li, H. C. (2022). Bi-Directional Work-Family Conflict of Home-Based Teachers in Taiwan During COVID-19: Application Of job Demands-Resources Model. Journal of Professional Capital and Community, 7(4), 353-367. https://doi.org/10.1108/jpcc-04-2022-0022
Khisomudin, M., Solehudin, S., & Hasanah, N. N. (2024). Pengaruh Konflik Pekerjaan-Keluarga, Kelelahan Emosional Dan Stres Kerja Terhadap Kinerja Di PT Penerbit Erlangga Karawang. Jurnal Ilmiah Universitas Batanghari Jambi, 24(3), 2712. https://doi.org/10.33087/jiubj.v24i3.5378
LaMontagne, L., Diehl, D. C., Doty, J., & Smith, S. (2022). The Mediation of Family Context and Youth Depressive Symptoms by Adolescent Emotion Regulation. Youth & Society, 55(3), 552-580. https://doi.org/10.1177/0044118x211067266
Lestari, D., & Budiono, B. (2021). Pengaruh Work Family Conflict Dan Emotional Exhaution Terhadap Kinerja Perawat Wanita Melalui Organizational Commitment Pada Rumah Sakit Petrokimia Gresik. Jurnal Ilmu Manajemen, 9(1), 167. https://doi.org/10.26740/jim.v9n1.p167-181
Moroń, M., Jach, Ł., Atłas, K., & Moroń, R. (2023). Parental and Pandemic Burnout, Internalizing Symptoms, and Parent-Adolescent Relationships: A Network Analysis. Journal of psychopathology and behavioral assessment, 45(2), 428-443. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10862-023-10036-w
Napitupulu, C. M., & Desiana, P. M. (2023). Role Conflict – Job Resources Impact on Emotional Exhaustion: Work-Family Conflict as Mediator. 1667-1675. https://doi.org/10.2991/978-94-6463-234-7_175
Okechukwu, B. I. U., Anayo, C. C., Paschaline, O., & Udochukwu, C. (2023). The Moderating Role of Psychological Capital on the Relationship Between Work-Family Conflict and Burnout Among Artisans. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science, VII(X), 2064-2076. https://doi.org/10.47772/ijriss.2023.701157
Peláez-Fernández, M. Á., Mérida‐López, S., Yudes, C., & Extremera, N. (2024). How Can the Social Family Climate Contribute to Emotional Intelligence in Preventing Suicidal Ideation and Promoting Life Satisfaction Among Adolescents? Applied Research in Quality of Life, 19(5), 2915-2932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-024-10354-5
Segovia, A. O., & Recuero, L. H. (2023). Actor–partner Effects of Coping Strategies on Emotional Exhaustion in Dual‐earner Couples. Family Relations, 73(2), 1219-1234. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.12948
Silva, A. d., Gao, M., Barni, D., Donato, S., Miller‐Graff, L. E., & Cummings, E. M. (2020). Interparental Conflict on Italian Adolescent Adjustment: The Role of Insecurity Within the Family. Journal of Family Issues, 42(3), 671-692. https://doi.org/10.1177/0192513x20927749
Silva, A. J. (2024). How Guilt Drives Emotional Exhaustion in Work–Pet Family Conflict. Animals, 14(23), 3503. https://doi.org/10.3390/ani14233503
Wang, Y., Xia, Q., Yue, H., & Teng, W. (2024). Chinese Rural Kindergarten Teachers’ Work–Family Conflict and Their Turnover Intention: The Role of Emotional Exhaustion and Professional Identity. Behavioral Sciences, 14(7), 597. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14070597
Wardana, D. A., & Waskito, J. (2024). Peran Kelelahan Emosional Sebagai Pemediasi Pada Pengaruh Tuntutan Pekerjaan, Dukungan Supervisor, Dan Rekan Kerja Terhadap Work-Family Conflict (Studi Di Pt TMNC Manufacturing International). Jurnal Manajemen Dirgantara, 17(1), 250-269. https://doi.org/10.56521/manajemen-dirgantara.v17i1.1175
Yan, W., Cheng, Z., Di, X., Wang, H., Du, X., Li, L., & Song, C. (2024). Patient Mistreatment, Work-Family Conflict and Emotional Exhaustion Among Nurses: A Moderated Mediation Model of Social Sharing and Perceived Organizational Support. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4247921/v1
Yaseen, F., Ain, Q. U., & Jamal, Y. (2021). The Emotional Labor and Burnout in Married Female Doctors of Pakistan: The Moderating Role of Work-Family Conflict. Gomal University Journal of Research, 37(04), 422-432. https://doi.org/10.51380/gujr-37-04-05
Yeh, T. F., Chang, Y. C., Hsu, Y. H., Huang, L. L., & Yang, C. C. (2020). Causes of Nursing Staff Burnout: Exploring the Effects of Emotional Exhaustion, Work–family Conflict, and Supervisor Support. Japan Journal of Nursing Science, 18(2). https://doi.org/10.1111/jjns.12392
Zhang, H., Tang, L., Ye, Z., Zou, P., Shao, J., Wu, M., Zhang, Q., Qiao, G., & Mu, S. (2020). The Role of Social Support and Emotional Exhaustion in the Association Between Work-Family Conflict and Anxiety Symptoms Among Female Medical Staff: A Moderated Mediation Model. BMC psychiatry, 20(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-020-02673-2