Prioritization of Psychological and Contextual Factors Contributing to Parent–Child Relationship Quality
Keywords:
Parent–child relationship, emotional regulation, communication quality, parenting style, attachmentAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to identify and prioritize the key psychological and contextual factors that influence the quality of parent–child relationships among Malaysian families.
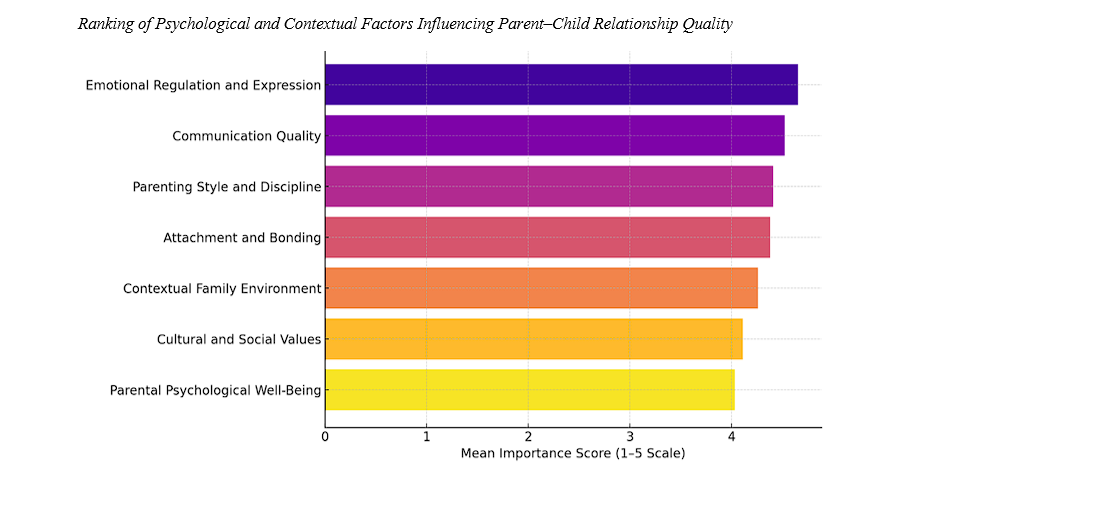
Methods and Materials: This research employed a sequential exploratory mixed-methods design consisting of two distinct phases. In the qualitative phase, a systematic literature review was conducted to identify psychological and contextual determinants of parent–child relationship quality until theoretical saturation was achieved. The data were coded and categorized thematically using NVivo 14 software. Seven major themes emerged: emotional regulation and expression, communication quality, parenting style and discipline, attachment and bonding, contextual family environment, cultural and social values, and parental psychological well-being. In the quantitative phase, a structured questionnaire derived from the qualitative findings was distributed to 210 Malaysian parents selected through stratified random sampling. Participants rated each factor on a 5-point Likert scale, and data were analyzed using SPSS version 26, applying descriptive statistics and the Friedman ranking test to determine the relative importance of each factor.
Findings: The results indicated significant differences in the perceived importance of the seven identified factors (χ² = 64.21, p < .001). Emotional regulation and expression received the highest mean importance score (M = 4.65), followed by communication quality (M = 4.52), parenting style and discipline (M = 4.41), and attachment and bonding (M = 4.38). Contextual family environment (M = 4.26), cultural and social values (M = 4.11), and parental psychological well-being (M = 4.03) ranked lower but remained statistically significant. These findings highlight the predominance of emotional and communicative processes in shaping family relationship quality.
Conclusion: The study concludes that parent–child relationship quality in Malaysian families is primarily determined by emotional regulation, communication, and parenting style, while contextual and cultural factors play complementary roles.
Downloads
References
Abbasi, G., khalilnezhadevati, M., & Rezaei, M. (2023). Investigating the Relationship Between Parent-Child Conflict and Attachment Styles With Future Anxiety in Nursing Students. Jarac, 5(4), 145-153. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jarac.5.4.16
Ankori, G., Solan, M., Plishty, S., Klomek, A. B., Apter, A., & Yagil, Y. (2025). The Role of Parental Qualities in Supporting Children With ADHD. Children, 12(7), 845. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12070845
Bahmani, T., Naseri, N. S., & Fariborzi, E. (2022). Relation of Parenting Child Abuse Based on Attachment Styles, Parenting Styles, and Parental Addictions. Current Psychology, 42(15), 12409-12423. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-021-02667-7
Čerešník, M. (2023). Perceived Parenting Styles and Attachment of Adolescents Aged 10 to 15 Years. The New Educational Review, 72(2), 25-37. https://doi.org/10.15804/tner.23.72.2.02
Hoenicka, M. A. K., López-de-la-Nieta, O., Rubio, J. L. M., Shinohara, K., Neoh, M. J. Y., Dimitriou, D., Esposito, G., & Iandolo, G. (2022). Parental Bonding in Retrospect and Adult Attachment Style: A Comparative Study Between Spanish, Italian and Japanese Cultures. PLoS One, 17(12), e0278185. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0278185
Hofstra, E., Kasius, M. C., & Vermeiren, R. (2023). Treating Children With Disturbed Attachment and an Intellectual Disability: Effectiveness of Theraplay-Based Treatment. International Journal of Play Therapy, 32(4), 230-242. https://doi.org/10.1037/pla0000204
Huang, Y. (2021). The Association Between Parental Attachment and the Parenting: A Review and Preliminary Meta-Analysis. Psychological Thought, 14(2), 339-362. https://doi.org/10.37708/psyct.v14i2.596
Kim, S. H., Baek, M.-J., & Park, S. (2021). Association of Parent–child Experiences With Insecure Attachment in Adulthood: A Systematic Review and Meta‐analysis. Journal of Family Theory & Review, 13(1), 58-76. https://doi.org/10.1111/jftr.12402
Koycheva, M. (2021). The Relationship Between Parental Reflective Function, Attachment and Development of Child Psychopathology. Педагогически Форум, 9(1), 11-17. https://doi.org/10.15547/pf.2021.002
Lavenda, O., & Hertz, O. (2024). Mentalization and Attachment Style as Underlying Mechanisms of Linking Collective Efficacy With Parental Self-Efficacy. Social Sciences, 13(11), 591. https://doi.org/10.3390/socsci13110591
Li, P., Chen, Q., Wang, Y., Jiang, L., Xin, G., Hui, Y., Gao, T., Q, L., & Wang, X. H. (2025). Parent–child Attachment and Sibling Relationship Quality in Rural China: Moderating Roles of Favoritism and Gender. Family Relations, 74(4), 1871-1888. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.13180
Lyubushina, A. A. (2025). Parenting Stress and Family Relationships: Analysis of Modern Research. Vestnik Kostroma State University Series Pedagogy Psychology Sociokinetics, 31(1), 92-99. https://doi.org/10.34216/2073-1426-2025-31-1-92-99
Moradi, M., Farhangi, A., & Tizdast, T. (2023). Modeling Children's Behavioral Problems Based on Attachment Styles With Parent-Child Relationship Mediation. Jayps, 4(2), 9-17. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.4.2.2
Nordahl, D., Rognmo, K., Bohne, A., Landsem, I. P., Moe, V., Wang, C. E. A., & Høifødt, R. S. (2020). Adult Attachment Style and Maternal-Infant Bonding: The Indirect Path of Parenting Stress. BMC psychology, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-020-00424-2
Parameswasri, J. (2023). Role of Parent-Child Relationship in Coping Styles of Emerging Adults. Indian Journal of Health Studies, 05(02), 73-88. https://doi.org/10.56490/ijhs.2023.5204
Rosu, C. A. (2020). Importanța Familiei În Construirea Relațiilor Cu Sinele Și Cu Ceilalți. Altarul Reîntregirii, 3(3), 97-110. https://doi.org/10.29302/ar.2020.3.8
Šimonji-Černak, R., & Mićanović-Cvejić, Ž. (2020). Emotional Attachment in Partner Relationships as a Predictor of Depression. Zbornik Matice Srpske Za Drustvene Nauke(173), 51-64. https://doi.org/10.2298/zmsdn2073051s
Svendsrud, H., Fredriksen, E., Moe, V., Smith, L., Tsotsi, S., Ullebø, A. K., Brean, G. V., Kaasen, A., & Bekkhus, M. (2023). Becoming Dad: Expectant Fathers’ Attachment Style and Prenatal Representations of the Unborn Child. Children, 10(7), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/children10071187
Tan, R., Yang, Y., Huang, T., Lin, X., & Hua, G. (2023). Parent–child Attachment and Mental Health in Young Adolescents: A Moderated Mediation Analysis. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1298485
Walsh, G., & Zadurian, N. (2022). Exploring the Links Between Parental Attachment Style, Child Temperament and Parent-Child Relationship Quality During Adolescence. Journal of Child and Family Studies, 32(9), 2721-2736. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10826-022-02447-2
Wu, W. (2024). The Effects of Parent-Child Attachment Style and Parenting Style on Children's Emotional Competence. Journal of Education Humanities and Social Sciences, 26, 627-633. https://doi.org/10.54097/4bc2zt07
Yun, T., Bi, X.-Y., & Deng, M. (2020). The Impact of Parent–Child Attachment on Self-Injury Behavior: Negative Emotion and Emotional Coping Style as Serial Mediators. Frontiers in psychology, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.01477
Zaharim, N. M., & Hashim, I. H. M. (2022). Child Well‐being in the Context of Family Harmony: Parental Marital Relationship as Mediator and Parent–child Attachment Style as Moderator. Asian Social Work and Policy Review, 17(1), 52-63. https://doi.org/10.1111/aswp.12273
Zvara, B. J., Lathren, C., & Mills‐Koonce, W. R. (2020). Maternal and Paternal Attachment Style and Chaos as Risk Factors for Parenting Behavior. Family Relations, 69(2), 233-246. https://doi.org/10.1111/fare.12423