The Impact of Family Conflict on Academic Disengagement Mediated by Emotional Exhaustion in Adolescents
Keywords:
Family conflict, Emotional exhaustion, Academic disengagement, AdolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the relationship between family conflict and academic disengagement among adolescents, with emotional exhaustion examined as a potential mediating variable.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive–correlational research design was employed, with a sample of 388 secondary school students from Armenia selected based on Krejcie and Morgan’s sample size table using stratified random sampling. Standardized instruments were administered, including the Family Conflict subscale of the Family Environment Scale, the Emotional Exhaustion subscale of the Maslach Burnout Inventory–Student Survey, and the Academic Disengagement subscale of the Student Engagement Instrument. Data analysis was performed using SPSS-27 for descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation, and AMOS-21 for Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) to test the hypothesized mediation model. Model fit was evaluated using χ²/df, GFI, AGFI, CFI, RMSEA, and TLI indices, with significance set at p < .05.
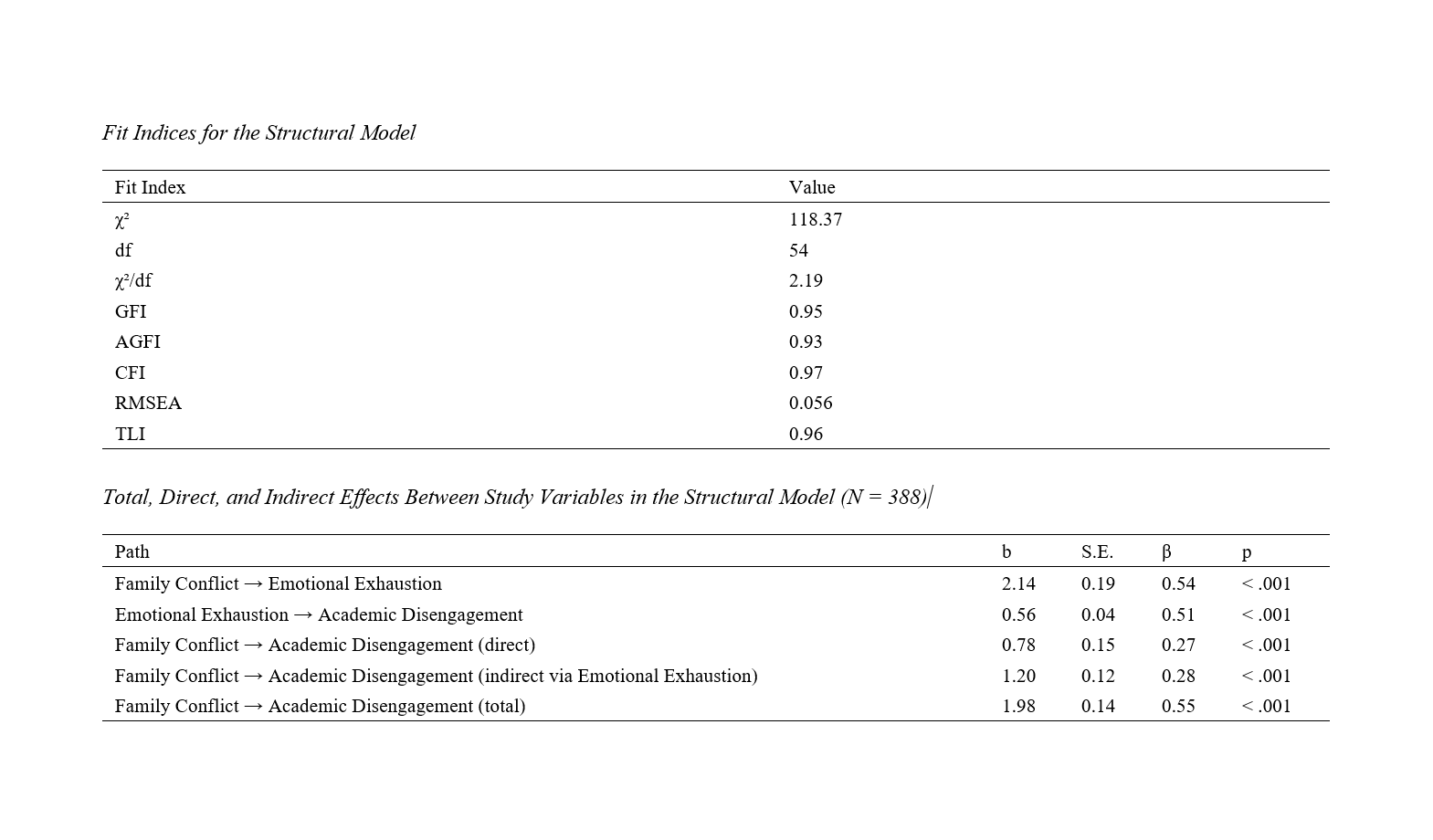
Findings: Pearson correlation results indicated that family conflict was positively correlated with both emotional exhaustion (r = .54, p < .001) and academic disengagement (r = .46, p < .001), while emotional exhaustion had the strongest correlation with academic disengagement (r = .62, p < .001). The SEM analysis demonstrated good model fit (χ²/df = 2.19, GFI = 0.95, AGFI = 0.93, CFI = 0.97, RMSEA = 0.056, TLI = 0.96). Family conflict significantly predicted emotional exhaustion (β = 0.54, p < .001) and academic disengagement both directly (β = 0.27, p < .001) and indirectly via emotional exhaustion (β = 0.28, p < .001). The total effect of family conflict on academic disengagement was β = 0.55 (p < .001), confirming partial mediation.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that emotional exhaustion serves as a significant psychological mechanism linking family conflict to academic disengagement among adolescents.
Downloads
References
Aftab, S. R., & Malik, J. A. (2021). Mediating Role of Moral Disengagement Between Emotional Manipulation and Psychological Well-Being: Does Age Matter? Behavioral Sciences, 11(9), 117. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs11090117
Aldbyani, A., Al‐Abyadh, M. H. A., Ma, B., Lv, Y., Leng, J., & Guo, Q. (2023). Dispositional Mindfulness Associated With Less Academic Burnout Among Muslim Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic. South African Journal of Education, 43(3), 1-7. https://doi.org/10.15700/saje.v43n3a2231
Baka, Ł., & Prusik, M. (2021). Towards Better Understanding of the Harmful Impact of Hindrance and Challenge Stressors on Job Burnout of Nurses. A One-Year Cross-Lagged Study on Mediation Role of Work-Family Conflict. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.696891
Baka, Ł., Prusik, M., & Jasielska, D. (2023). Toward a Better Understanding of the Health Impairment Process. Types of Demand and Burnout Component Matter. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.1037053
Bao, D., Mydin, F., Surat, S., Lyu, Y., Pan, D., & Cheng, Y. (2024). Challenge-Hindrance Stressors and Academic Engagement Among Medical Postgraduates in China: A Moderated Mediation Model. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 17, 1115-1128. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s448844
Bayot, M., Boone, A., Godderis, L., & Lenoir, A.-L. (2024). Multidimensional Factors of Burnout in General Practice: A Cross Sectional Survey. BJGP open, BJGPO.2023.0171. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgpo.2023.0171
Haq, I. U., Zainab, B., Jan, J. A., Anwar, F., & Sharif, M. I. (2021). Hindrance Stressors and Job Outcomes: The Moderating Role of Political Skills. Journal of employment counseling, 58(3), 98-118. https://doi.org/10.1002/joec.12168
Husain, S. S. S., Rathi, N. A. M., Zubir, Z., Munchar, J., Khalid, P. Z. M., & Rahmat, N. H. (2025). Students’ Motivation to Learn and Burnout: How Do They Relate? International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science, IX(III), 2619-2631. https://doi.org/10.47772/ijriss.2025.90300205
Kersten, A., Woerkom, M. v., Kooij, D., & Bauwens, R. (2022). Paying Gratitude Forward at Work. Journal of Personnel Psychology, 21(3), 137-148. https://doi.org/10.1027/1866-5888/a000296
Klusmann, U., Aldrup, K., Roloff, J., Lüdtke, O., & Hamre, B. K. (2022). Does Instructional Quality Mediate the Link Between Teachers’ Emotional Exhaustion and Student Outcomes? A Large-Scale Study Using Teacher and Student Reports. Journal of Educational Psychology, 114(6), 1442-1460. https://doi.org/10.1037/edu0000703
Landay, K., Arena, D. F., & King, D. A. (2021). Passion in the Pit: The Effects of Harmonious and Obsessive Passion on Nurse Burnout. Journal of managerial psychology, 37(3), 192-205. https://doi.org/10.1108/jmp-03-2021-0181
Lee, M., Lee, K. J., Lee, S. M., & Cho, S. (2020). From Emotional Exhaustion to Cynicism in Academic Burnout Among Korean High School Students: Focusing on the Mediation Effects of Hatred of Academic Work. Stress and Health, 36(3), 376-383. https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.2936
Li, H.-T. (2022). Escalation of Relationship Conflict Into Work Disengagement: Uncovering Mediation Mechanisms. International Journal of Conflict Management, 34(1), 80-103. https://doi.org/10.1108/ijcma-05-2021-0071
Ma, Y. (2022). On the Relationship Between English as a Foreign Language Learners’ Positive Affectivity, Academic Disengagement, and Communication Apprehension. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.828873
Mann, K. J., Sizemore, S. J., & O’Brien, K. E. (2024). Expanding Deep Acting: Effects of Engagement and Disengagement Deep Acting on Emotional Exhaustion. International Journal of Stress Management, 31(1), 93-104. https://doi.org/10.1037/str0000306
Nuradilla, S. (2024). Analysis of Academic Hardiness Factors Affecting Student Emotional Exhaustion in Malang Using Logit and Probit Models. Jurnal Matematika Statistika Dan Komputasi, 20(3), 606-622. https://doi.org/10.20956/j.v20i3.33220
Ogunfowora, B., Nguyen, V. Q., Lee, C. S., Babalola, M. T., & Ren, S. (2022). Do Moral Disengagers Experience Guilt Following Workplace Misconduct? Consequences for Emotional Exhaustion and Task Performance. Journal of Organizational Behavior, 44(3), 476-494. https://doi.org/10.1002/job.2668
Ramos‐Vera, C., Basauri-Delgado, M., Calizaya-Milla, Y. E., & Saintila, J. (2025). Exploring the Mediation of Stress and Emotional Exhaustion on Academic Ineffectiveness and Cynicism Among University Students. Psychiatry Investigation, 22(4), 365-374. https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2024.0111
Rashid, M. H. A., Rahman, A. L. A., Mohamad, H. A., Salam, U., Wan Muhammad Fitri Wan Amir, N., Sharifah Syazwa Amierah Syed, K., & Rahmat, N. H. (2025). Exploring the Influence of Sources of Burnout in Learning E-Language Courses. International Journal of Research and Innovation in Social Science, IX(III), 2737-2752. https://doi.org/10.47772/ijriss.2025.90300215
Tumelo, T. N., & Donald, F. M. (2025). Perceived Job Insecurity, Facades of Conformity, Emotional Exhaustion and Disengagement. Sa Journal of Industrial Psychology, 51. https://doi.org/10.4102/sajip.v51i0.2221
Umer, F., Nadeem, A., & Tufail, M. W. (2022). Emotional Exhaustion and Academic Performance in University Students: Mediating Role of Cynicism. Pakistan Journal of Applied Psychology, 2(2). https://doi.org/10.52461/pjap.v2i2.1493
Xu, C., Yao, Z., & Xiong, Z. (2022). The Impact of Work-Related Use of Information and Communication Technologies After Hours on Time Theft. Journal of Business Ethics, 187(1), 185-198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-022-05167-1
Yang, N. (2023). The Causes, Effects, and Interventions of Workplace Emotional Exhaustion. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media, 6(1), 516-520. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7048/6/20220459
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








