Social Anxiety and Academic Burnout as Predictors of School Avoidance Behavior
Keywords:
Social anxiety, academic burnout, school avoidance behavior, adolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the predictive roles of social anxiety and academic burnout in explaining school avoidance behavior among high school students.
Methods and Materials: A correlational descriptive research design was employed, involving 392 high school students from various public and private schools in Peru. The participants were selected based on Morgan and Krejcie’s sample size determination table. Standardized self-report instruments were used to measure social anxiety, academic burnout, and school avoidance behavior. Data analysis was conducted using SPSS version 27. Descriptive statistics were computed, followed by Pearson correlation analysis to assess bivariate relationships and multiple linear regression to determine the combined predictive power of the independent variables on school avoidance behavior.
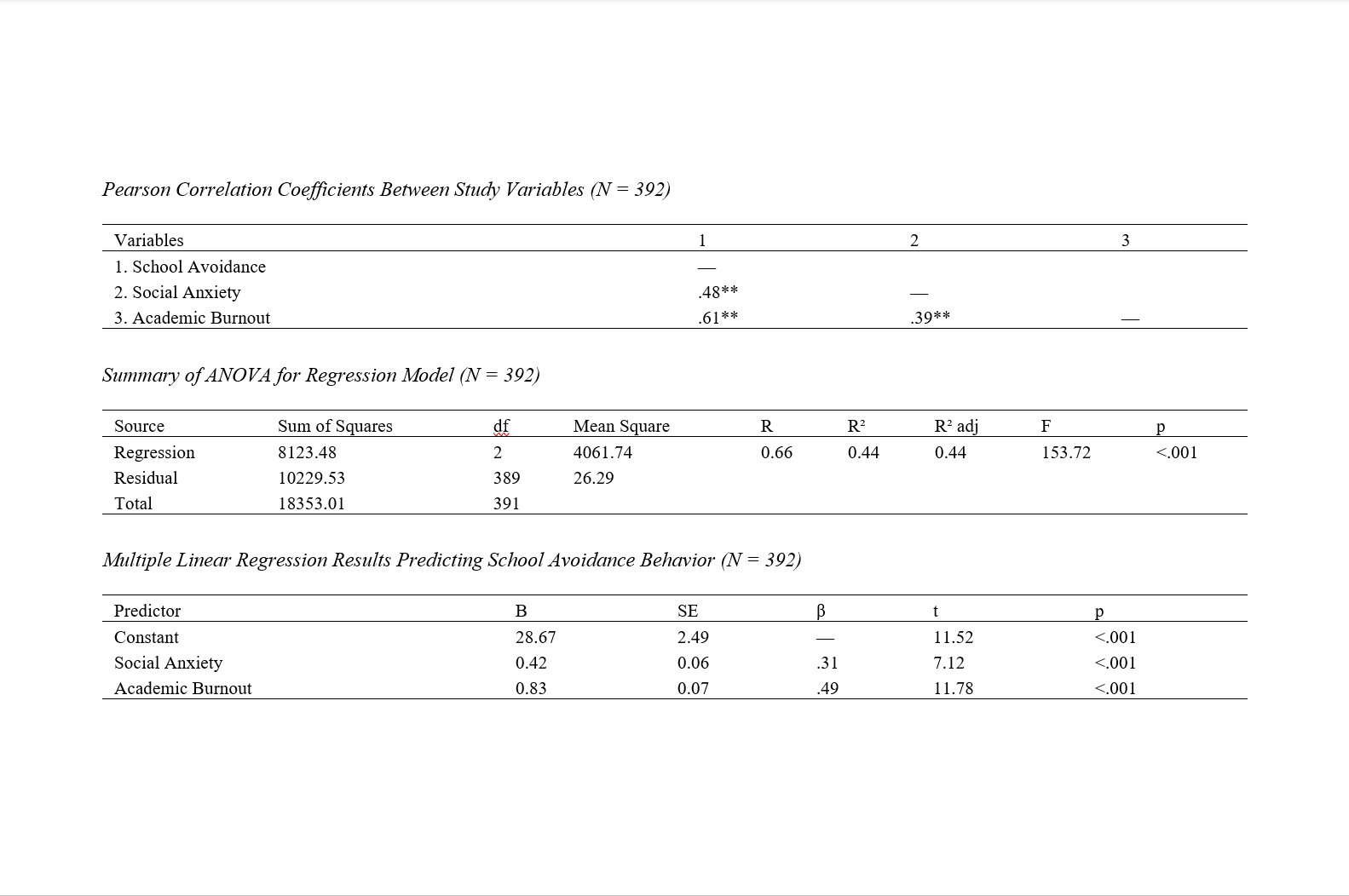
Findings: Results indicated that both social anxiety (r = .48, p < .01) and academic burnout (r = .61, p < .01) were positively and significantly correlated with school avoidance behavior. The regression model was significant, F(2, 389) = 153.72, p < .001, and explained 44% of the variance in school avoidance behavior (R² = .44). Both social anxiety (β = .31, p < .001) and academic burnout (β = .49, p < .001) emerged as significant predictors, with academic burnout exerting a stronger effect.
Conclusion: The findings highlight the crucial role of emotional and psychological factors in predicting school avoidance among adolescents. Academic burnout, more than social anxiety, was identified as the dominant predictor, underscoring the need for educational policies and interventions that address emotional exhaustion and academic stress to reduce absenteeism and disengagement in schools.
Downloads
References
Al-Awad, F. A. (2024). Academic Burnout, Stress, and the Role of Resilience in a Sample of Saudi Arabian Medical Students. Medical Archives, 78(1), 39. https://doi.org/10.5455/medarh.2024.78.39-43
Bazaz, S. M., & Farhadian, A. (2025). Predicting Academic Burnout Based on School Belongingness, Parenting Styles, and Academic Resilience. Jayps, 6(3), 79-86. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.6.3.9
Dehghani, M., Ardakan, A. M., & Moraveji, M. (2024). Comparison of Early Maladaptive Schemas and Difficulty in Emotion Regulation Among Adolescent Boys and Girls With and Without Marijuana Use. Jayps, 5(6), 135-144. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.5.6.15
Gao, B., Chai, X., Shen, Q., Lu, J., & Li, L. (2024). Linking Effort‐reward Imbalance to Academic Burnout Among High School Students: The Roles of School Connectedness and Academic Buoyancy. Psychology in the Schools, 62(1), 202-218. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.23320
Jiang, X., & Wang, K. (2025). Exploring Relationships Between Identities, Dual Career Competency, and Burnout Among Young Talented Athletes. BMC psychology, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-024-02341-0
Kim, M. E. (2022). The Moderating Effect of Grit on the Relationship Between Academic Stress and Academic Burnout in High School Students. Asia Counseling Coaching Soc, 4(2), 1-11. https://doi.org/10.47018/accr.2022.4.2.1
Liu, Y., & Xue, Y. (2022). The Mediating Effect of Grit on the Relationship Between Mindset and Academic Burnout in Chinese High School Students. Korean Soc Cult Converg, 44(12), 1135-1147. https://doi.org/10.33645/cnc.2022.12.44.12.1135
Masruroh, M., Nawafilah, N. Q., & Anggraini, E. (2022). The Analysis of Students’ School Burnout Level and Academic Achievement on the Science Management Subject. Tarbiyah Jurnal Ilmiah Kependidikan, 11(2), 49. https://doi.org/10.18592/tarbiyah.v11i2.7120
Novianty, L., Said, F. M., & Nambiar, N. (2023). The Relationship Between Self-Esteem and School Engagement With Academic Burnout Among Nursing Students in Sukabumi. Kne Social Sciences. https://doi.org/10.18502/kss.v8i14.13847
Oktia, V. (2022). Pengaruh Academic Burnout Dan Academic Engagament Terhadap School Well-Being Santri Pesantren. Nusant. J. Behav. And. Soc. Sci, 1(3), 89-94. https://doi.org/10.47679/202213
Park, H. (2025). The Effects of Academic Achievement Pressure of Parents and Parent-Adolescent Communication on Academic Burnout and School Life Adjustment of High School Students. Korean Assoc Learner-Centered Curric Instr, 25(1), 653-670. https://doi.org/10.22251/jlcci.2025.25.1.653
Peng, L., Chen, H., Peng, J., Liang, W., Li, M., & Wang, F. (2025). The Influence of Parental Burnout on Middle School Students’ Academic Achievement: Moderated Mediation Effect. Frontiers in psychology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1530289
Putri, A. A., & Magistarina, E. (2024). Perbedaan Tingkat Academic Burnout Pada Siswa Ditinjau Dari Jenis Sekolah SMA/SMK/MA. Masaliq, 4(3), 760-768. https://doi.org/10.58578/masaliq.v4i3.3072
Rahman, A., & Djamhoer, T. (2023). Hubungan Antara Academic Self Efficacy Dengan Academic Burnout. Bandung Conference Series Psychology Science, 3(1). https://doi.org/10.29313/bcsps.v3i1.5275
Supriyanto, A., Imtinan, S., Arikunto, S., Handaka, I. B., & Hartini, S. (2024). Academic Burnout Conditions in Indonesian Students: Physical, Mental, and Emotional. Edu, 80-86. https://doi.org/10.59397/edu.v2i2.26
Wang, Y., Gao, Y., Zhang, X., Shen, J., Wang, Q., & Wang, Y. (2022). The Relationship Between Effort-Reward Imbalance for Learning and Academic Burnout in Junior High School: A Moderated Mediation Model. Behavioral Sciences, 13(1), 28. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13010028
Xiaoling, T. (2024). The Impact of School Climate on Academic Burnout of Chinese Students: The Mediating Effect of Psychological Capital. Frontiers in Education, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1346347
Xue, S., Lu, A., Chen, W., Liang, Y., Li, X., Liu, W. C., Zhu, Y. C., Wang, X. J., & Zeng, S. (2025). How to Alleviate Students' Academic Burnout? Using Latent Profile Analysis and Network Analysis to Explore the Positive Impact of School Climate and Achievement Goal Orientation. Psychology in the Schools, 62(6), 1704-1715. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.23424
Yongmei, H., & Dan, W. (2022). The Influence of Academic Stress on Academic Burnout Among Middle School Students in Guangdong. Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal, 9(9), 404-411. https://doi.org/10.14738/assrj.99.13113
Zhang, Z., Wang, Y., Wu, H., Zhou, Y., & Peng, C. (2024). Direct and Indirect Effects of Father-Child Attachment on Academic Burnout in College Students. Frontiers in psychology, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2024.1345590
Zhao, H., Han, M., Wang, Z., & Liu, B. (2024). School Connectedness and Academic Burnout in Middle School Students: A Multiple Serial Mediation Model. Behavioral Sciences, 14(11), 1077. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs14111077
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








