The Effectiveness of Cognitive Intervention Based on Neurofeedback on Improving Academic Performance and Emotional Regulation in Students with Learning Disabilities
Keywords:
Neurofeedback, Learning Disabilities, Academic Performance, Emotional RegulationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of cognitive intervention based on neurofeedback in improving academic performance and emotional regulation in students with learning disabilities.
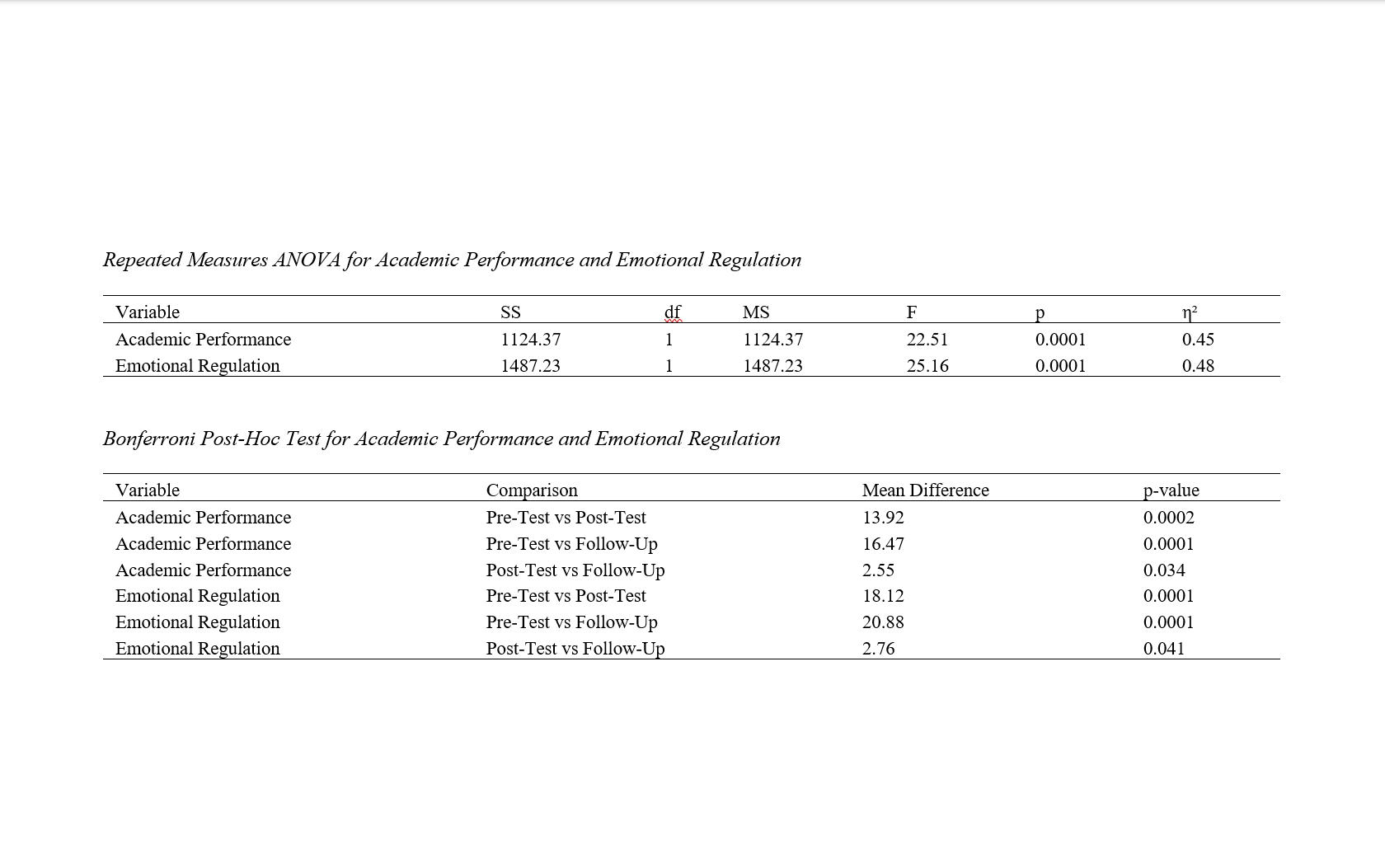
Methods and Materials: The study employed a randomized controlled trial design with 30 students diagnosed with learning disabilities from educational centers in Tehran. Participants were randomly assigned to either an experimental group (n = 15), which received 12 sessions of neurofeedback-based cognitive training over six weeks, or a control group (n = 15), which received no intervention. Assessments were conducted at three time points: pre-test, post-test, and five-month follow-up. Standardized tools were used to measure academic performance and emotional regulation. Data analysis was performed using repeated measures ANOVA and Bonferroni post-hoc tests via SPSS-27.
Findings: The results revealed significant differences between the experimental and control groups over time. For academic performance, the between-group effect was statistically significant (F(1,28) = 22.51, p < 0.001, η² = 0.45), as was the effect for emotional regulation (F(1,28) = 25.16, p < 0.001, η² = 0.48). Bonferroni post-hoc tests indicated significant improvements from pre-test to post-test and from pre-test to follow-up in both outcome variables. Notably, these improvements were sustained at the five-month follow-up, confirming the long-term efficacy of the intervention. The control group showed only marginal improvements across all time points.
Conclusion: The findings suggest that neurofeedback-based cognitive intervention is an effective and durable approach for enhancing academic performance and emotional regulation in students with learning disabilities. The intervention demonstrated both immediate and sustained effects, supporting its application as a non-invasive and practical method within educational and clinical settings.
Downloads
References
Abbasi Fashami, N., Akbari, B., & Hosseinkhanzadeh, A. A. (2020). Comparison of the Effectiveness of Cognitive Rehabilitation and Neurofeedback on Improving the Executive Functions in Children with Dyslexia [Research]. Quarterly Journal of Child Mental Health, 7(2), 294-311. https://doi.org/10.29252/jcmh.7.2.25
Abdian, H., Rezaei, M., Eskandari, Z., Ramezani, S., Pirzeh, R., & Dadashi, M. (2021). The Effect of Quantitative Electroencephalography-Based Neurofeedback Therapy on Anxiety, Depression, and Emotion Regulation in People with Generalized Anxiety Disorder [Original]. Basic and Clinical Neuroscience Journal, 12(2), 281-290. https://doi.org/10.32598/bcn.12.2.2378.1
Alizadeh, G., Kardanoghabi, R., Rashid, K., & Qolizadeh, Z. (2018). The effect of neurofeedback with high-alpha waves on executive functions in female university students at Kurdistan University with academic burnout syndrome and depression symptoms. Journal of Clinical Psychology, 8(30), 163-188. https://jcps.atu.ac.ir/article_8613.html?lang=en
Azizi, A., Mir Derikvand, F., & Sepahvandi, M. A. (2017). Comparing the effects of cognitive rehabilitation training, neurofeedback, and cognitive-behavioral play therapy on visual-motor perception in elementary school students with specific learning disorder. Quarterly Journal of Neuropsychology, 3(8), 103-118. https://civilica.com/doc/1017826/
Baher Talari, M. (2022). The effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in reducing emotional regulation difficulties and cravings in drug users Mohaghegh Ardabili University]. https://jrp.uma.ac.ir/article_2356.html
Cortese, S., Ferrin, M., Brandeis, D., Holtmann, M., Aggensteiner, P., Daley, D., Santosh, P., Simonoff, E., Stevenson, J., Stringaris, A., & Sonuga-Barke, E. J. (2016). Neurofeedback for Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: Meta-Analysis of Clinical and Neuropsychological Outcomes From Randomized Controlled Trials. J Am Acad Child Adolesc Psychiatry, 55(6), 444-455. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaac.2016.03.007
Farid, A., Habibi-Kaleybar, R., & Moshtary E Sahneh, B. (2021). Comparison of the Effectiveness of Play Therapy and Neurofeedback on the Executive Functions of Primary School Female Students with Learning Disabilities. Psychology of Exceptional Individuals, 11(43), 175-206. https://doi.org/10.22054/jpe.2022.60612.2319
Farid, A., Habibi Kaleybar, R., & Moshtari Sahneh, B. (2021). A comparison of the effectiveness of play therapy and neurofeedback on executive functions in elementary school girls with learning disabilities. Exceptional Individuals Psychology Quarterly, 11(43), 177-206. https://jpe.atu.ac.ir/article_13811.html?lang=en
Fernández, T., Harmony, T., Fernández-Bouzas, A., Díaz-Comas, L., Prado-Alcalá, R. A., & Valdés-Sosa, P. (2007). Changes in EEG current sources induced by neurofeedback in learning disabled children. An exploratory study. Applied Psychophysiology and Biofeedback, 32(3), 169-183. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10484-007-9044-8
Ghaemi, H., Mohammadi, N., Sobhani Rad, D., & Yazdani, R. (2016). Investigating the effect of neurofeedback on reading speed and accuracy skills in children with learning disabilities aged 7-10 years. Scientific-Research Quarterly Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine, 5(4), 76-83. https://medrehab.sbmu.ac.ir/article_1100248.html?lang=fa
Huang, W., Wu, W., Lucas, M. V., Huang, H., Wen, Z., & Li, Y. (2023). Neurofeedback Training With an Electroencephalogram-Based Brain-Computer Interface Enhances Emotion Regulation. Ieee Transactions on Affective Computing, 14(2), 998-1011. https://doi.org/10.1109/taffc.2021.3134183
Hyman, S. (2016). The Positive Impact of Neurofeedback in the Management and Treatment of Learning Disabilities in Children. https://scdcentre.com/category/neurofeedback/
Martínez-Briones, B. J., Bosch-Bayard, J., Biscay-Lirio, R. J., Silva-Pereyra, J., Albarrán-Cárdenas, L., & Fernández, T. (2021). Effects of Neurofeedback on the Working Memory of Children with Learning Disorders-An EEG Power-Spectrum Analysis. Brain Sciences, 11, 957. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci11070957
Molavi, P., Aziziaram, S., Basharpoor, S., Atadokht, A., Nitsche, M. A., & Salehinejad, M. A. (2020). Repeated transcranial direct current stimulation of dorsolateral-prefrontal cortex improves executive functions, cognitive reappraisal emotion regulation, and control over emotional processing in borderline personality disorder: A randomized, sham-controlled, parallel-group study. Journal of affective disorders, 274, 93-102. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jad.2020.05.007
Nejati, V., Majidinezhad, M., & Nitsche, M. (2022). The role of the dorsolateral and ventromedial prefrontal cortex in emotion regulation in females with major depressive disorder (MDD): A tDCS study. Journal of psychiatric research, 148, 149-158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpsychires.2022.01.030
Norizadeh, N., Mikaeili Manee, F., Rostami, R., & Sadeghi, V. (2012). The effectiveness of neurofeedback on learning disorder accompanied by attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Learning Disabilities, 2(2), 123-158. https://www.sid.ir/paper/210173/fa
Sajjadi, S. A., Akhoundpour Manteghi, A., & Hashemian, P. (2014). The effect of neurofeedback on the treatment of math learning disorder in third-grade elementary school children. Journal of Mashhad University of Medical Sciences, 57(5), 719-726. https://mjms.mums.ac.ir/article_3422.html
Shari, S., Sedaghat, M., Shoja Kazemi, M., & Moradi, H. (2021). Evaluation of neurofeedback training on executive functioning, cognitive flexibility, and attention in students with learning disorders. Scientific Journal of Ilam University of Medical Sciences, 3(3), 62-74. https://doi.org/10.52547/sjimu.30.3.62
Thatcher, R. W., Biver, C. J., Soler, E. P., Lubar, J., & Koberda, J. L. (2023). Electroencephalogram neuroimaging, brain networks, and neurofeedback protocols. In D. R. Chartier, M. B. Dellinger, J. R. Evans, & H. K. Budzynski (Eds.), Introduction to Quantitative EEG and Neurofeedback (Third Edition) (pp. 143-160). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-323-89827-0.00024-3
Yu, L., Long, Q., Tang, Y., Yin, S., Chen, Z., Zhu, C., & Chen, A. (2021). Improving Emotion Regulation Through Real-Time Neurofeedback Training on the Right Dorsolateral Prefrontal Cortex: Evidence From Behavioral and Brain Network Analyses. Frontiers in human neuroscience, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2021.620342
Zoghipaydar, M., Hasany Khosh, Z., Yar Mohammadi Wasel, M., & Mohagheghi, H. (2022). Comparing of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation (TDCS) and Methadone Maintenance Treatment(MMT) on Emotion Regulation, Distress Tolerance and Decreased Craving in People with Substance Use Disorder(SUD). Neuropsychology, 7(27), 95-109. https://doi.org/10.30473/clpsy.2021.59493.1606
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Niloofar Rezaei (Author); Fereshte Zarei (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








