The Role of Coping Strategies and Social Competence in Predicting the Social Skills of Single-Child University Students
Keywords:
Social skills, coping strategies, beliefs, differentiation of self, social competence, hopeAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to investigate the role of coping strategies and social competence in predicting the social skills of single-child university students in Isfahan.
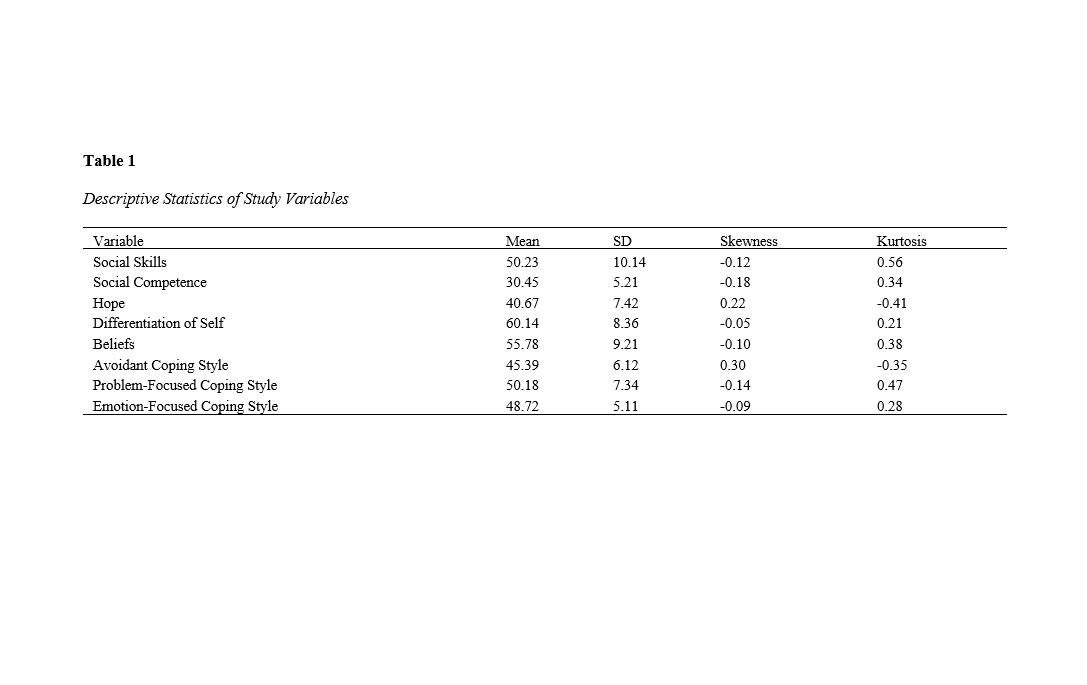
Methods and Materials: This study is categorized as fundamental research and was conducted within the framework of a correlational design using the structural equation modeling (SEM) approach. The statistical population comprised all 18- to 22-year-old university students born into single-child families in Isfahan in 2024, estimated at approximately 520 individuals. To enhance the generalizability of the findings, a total of 250 single-child students were selected for participation. Data were collected using the Social Skills Questionnaire by Inderbitzen and Foster (1992), the Coping with Stressful Situations—Short Form by Kallasbeek et al. (1990), the Revised Differentiation of Self Inventory by Skowron and Schmitt (2003), the Schneider et al. (1991) Questionnaire, the Social Competence Questionnaire by Behini (2007), and the Attitudes and Beliefs Scale by David et al. (2019). Statistical analysis of the data revealed that, in the fitted model, the direct effect of beliefs on social skills was significant at the 0.01 level.
Findings: The direct effect of the avoidant coping style on social skills was not significant. The direct effect of the emotion-focused coping style on social skills was significant at the 0.05 level. The direct effect of differentiation of self on hope was significant at the 0.01 level. The direct effect of the problem-focused coping style on hope was significant at the 0.01 level. The direct effect of the emotion-focused coping style on hope was also significant at the 0.01 level. The direct effect of social competence on social skills was significant at the 0.01 level. Additionally, the direct effect of hope on social skills was significant at the 0.01 level.
Conclusion: Based on these findings, it can be concluded that all first-level variables in the model (i.e., differentiation of self, beliefs, and coping styles) had a significant indirect effect on social skills through the mediating roles of social competence and hope. In other words, social competence and hope played an effective mediating role in the relationship between these variables and social skills.
Downloads
References
Aboui, A., Tavakoli, M., & Nashan, M. S. (2023). To what extent do parental adequacy and social acceptance explain the changes in adolescence and social skills? A study in Yazd. Continuity and Social Change, 2(1), 182-167.
Al-Rawashdah, U. A. U., & Al-Nawaisah, F. A. R. (2024). The Level of Friendship Skills and its Relationship to Hope among Bachelor's Students of Ajloun National University. Jordanian Educational Journal, 9(2), 314-337. https://doi.org/10.46515/jaes.v9i2.671
Alzahrani, M., Alharbi, M., & Alodwani, A. (2019). The Effect of Social-Emotional Competence on Children Academic Achievement and Behavioral Development. International Education Studies, 12(12), 141. https://doi.org/10.5539/ies.v12n12p141
Amini, A. (2008). Social skills of adolescents: Validation of the TISS questionnaire Master's thesis, Islamic Azad University].
Ansari Sadr, A., & Shirazi, M. (2022). The relationship between coping styles with stress and causal attributions with academic achievement in students. Educational Psychology Studies, 19(45), 14-27.
Archetti, C. (2019). No life without family: Film representations of involuntary childlessness, silence and exclusion. International Journal of Media & Cultural Politics, 15(2), 175-196. https://doi.org/10.1386/macp.15.2.175_1
Chae, K. H. (2020). The Mediating Effect of Social Support in the Relationship between Self-Differentiation and Interpersonal Relationship. Journal of the Korea Academia-Industrial Cooperation Society, 21(7), 357-369.
Chen, S., Al-Shaibani, G. K. S., & Lee, S. W. (2024). Examining University Students' Soft Skills in Terms of Problem-Solving and Social Competence: Issues, Causes, and Solutions. Educational Administration: Theory and Practice, 30(4), 2063-2072. https://doi.org/10.53555/kuey.v30i4.1809
Ekström-Bergström, A., Thorstensson, S., & Bäckström, C. (2022). The concept, importance and values of support during childbearing and breastfeeding - A discourse paper. Nursing Open, 9(1), 156-167. https://doi.org/10.1002/nop2.1108
Hu, Y., & Jiang, X. (2022). Hope as an engine mediating the relation between parental attachment and social problem solving skills in adolescents. School Psychology International, 43(3), 237-252. https://doi.org/10.1177/01430343221091991
Kazemi, N., Nemat, L., Yadgari, S. L., & Abdous, F. (2022). Predicting social cognition based on self-differentiation and psychological flexibility in students. Research in Social Psychology, 12(48), 103-116.
Malekzadeh, A., Namvar, H., & Jahromi, F. (2020). A model for predicting social skills in only children based on coping styles with the mediating role of moral intelligence. Journal of Lifestyle with a Focus on Health, 4(4), 23-30.
Medina-Valencia, R. T., Salazar, C. M., Andrade-Sánchez, A. I., Ramos-Carranza, I. G., & Reynoso-Sánchez, L. F. (2023). La recreación, habilidades sociales y estrategias de afrontamiento en adolescentes mexicanos durante la primera etapa del confinamiento por COVID-19. E-balonmano Com, 19(2), 165-178. https://doi.org/10.17398/1885-7019.19.165
Mirzaei, M., Zarei, I., & Sadeqi Fard, M. (2019). The role of self-differentiation and economic factors with the mediation of family conflicts in preventing psychological and social harm. Culture of Counseling and Psychotherapy, 10(37), 143-170.
Morrison, K. E., DeBrabander, K. M., Jones, D. R., Ackerman, R. A., & Sasson, N. J. (2020). Social cognition, social skill, and social motivation minimally predict social interaction outcomes for autistic and non-autistic adults. Frontiers in psychology, 11, 591100. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2020.591100
Rahimi, A. (2021). Examining the relationship between self-differentiation and social adequacy with individual and social adjustment in female students visiting the education counseling center of Marand County.
Sylvest, R., Koert, E., Petersen, K. B., Malling, G. M. H., Hald, F., Nyboe Andersen, A., & Schmidt, L. (2018). Attitudes towards family formation among men attending fertility counselling. Reproductive Biomedicine & Society Online, 6, 1-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbms.2018.06.001
Trombeta, G. (2022). "How Do You See Your Life Now?" A Photo-Elicitation Study Focused on Depression and Social Skills in Adolescence. Psychological studies, 67(2), 228-240. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12646-022-00664-9
Vucenovic, D., Sipek, G., & Jelic, K. (2023). The role of emotional skills (competence) and coping strategies in adolescent depression. European Journal of Investigation in Health, Psychology and Education, 13(3), 540-552. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13030041
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Maryam Fani Mohammadabady (Author); Hooman Namvar (Corresponding Author); Seyed Hamid Atashpour (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








