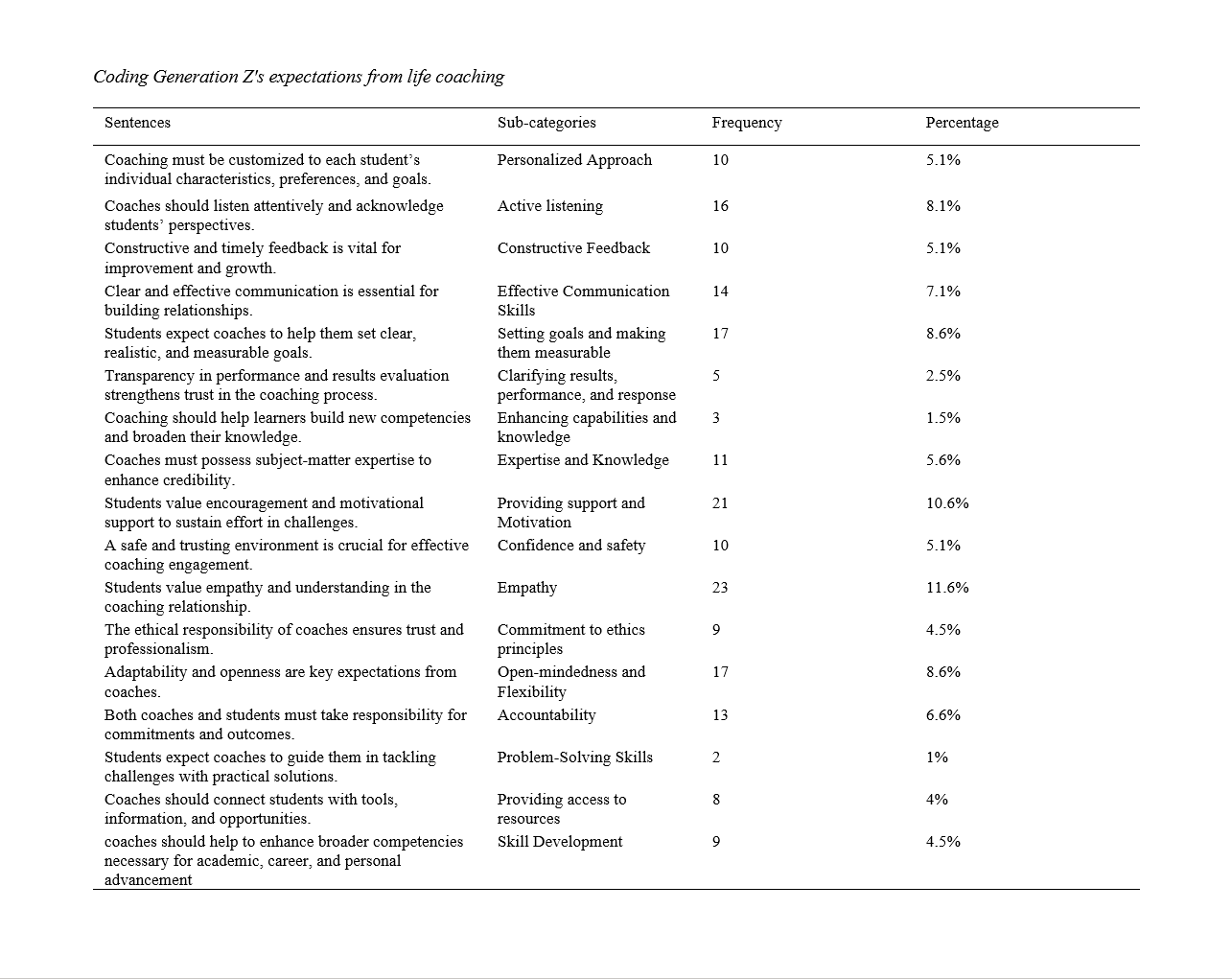
Generation Z's expectations from coaching
Keywords:
Coaching, Life Coaching, Generation Z, IraqAbstract
Downloads
References
Aboalshamat, K., Al-Zaidi, D., Jawa, D., Al-Harbi, H., Alharbi, R., & Al-Otaibi, S. (2020). The effect of life coaching on psychological distress among dental students: an interventional study. BMC psychology, 8(1), 106. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-020-00475-5
Aboujaoude, E. (2020). Where life coaching ends and therapy begins: Toward a less confusing treatment landscape. Perspectives on Psychological Science, 15(4), 973-977. https://doi.org/10.1177/1745691620904962
Al-Twal, A., Jarrar, D. M., Bedevian, V., & Eblan, M. (2025). Unlocking potential: examining Generation Z's vision for career growth in the Jordanian context. International Journal of Organizational Analysis. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJOA-10-2024-4887
Álvarez González, J. A. (2024). Prediction of Clients of "The Career Coach Company" based on Customer Profiling: Leveraging Machine Learning for marketing strategies optimization Dublin Business School].
Anderson, S. J., Chintagunta, P. K., & Vilcassim, N. (2024). Virtual collaboration technology and international business coaching: Examining the impact on marketing strategies and sales. Marketing Science, 43(3), 637-672. https://doi.org/10.1287/mksc.2019.0121
Arsova, M., & Temjanovski, R. (2019). Strategy for market segmentation and differentiation: contemporary marketing practice. Journal of Economics, 4(1), 27-35. https://doi.org/10.46763/JOE227.1027a
Banda, J. H. (2025). A critical analysis of pedagogical strategies for fostering ethical decision-making, integrity, and social responsibility in Generation Z: addressing the impact of modern societal challenges on moral development. Journal of Trends in Arts and Humanities, 2(1), 15-25. https://doi.org/10.61784/jtah3035
Baykal, B. (2020). Generational differences in Omnichannel experience: rising new segment: Gen Z. In Managing Customer Experiences in an Omnichannel World: Melody of Online and Offline Environments in the Customer Journey (pp. 117-132). Emerald Publishing Limited. https://doi.org/10.1108/978-1-80043-388-520201011
Cox, E., Clutterbuck, D. A., & Bachkirova, T. (2023). The complete handbook of coaching. SAGE Publications. https://doi.org/10.4135/9781036233556
Cronin, L. D., & Allen, J. (2018). Examining the relationships among the coaching climate, life skills development, and well-being in sport. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching, 13(6), 815-827. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747954118787949
Csobanka, Z. E. (2016). The Z generation. Acta Educationis Generalis, 6(2), 63-76. https://doi.org/10.1515/atd-2016-0012
Czinkota, M. R., Kotabe, M., Vrontis, D., & Shams, S. R. (2021). Marketing management: Past, present, and future. Springer Nature. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-66916-4
Daoud, M. K., Al-Qeed, M., Ahmad, A. Y. B., & Al-Gasawneh, J. A. (2023). Mobile marketing: Exploring the efficacy of user-centric strategies for enhanced consumer engagement and conversion rates. International Journal of Membrane Science and Technology, 10(2), 1252-1262. https://doi.org/10.15379/ijmst.vi.1425
DiGirolamo, J. (2015). Coaching for professional development. SHRM-SIOP Science of HR White Paper Series (pp. 1-26).
Ebner, K., Schulte, E. M., Soucek, R., & Kauffeld, S. (2018). Coaching as stress-management intervention: The mediating role of self-efficacy in a framework of self-management and coping. International Journal of Stress Management, 25(3), 209. https://doi.org/10.1037/str0000058
George, A. S. (2024). Trendsetters: How Gen Z Defined 2024. Partners Universal Innovative Research Publication, 2(3), 92-103. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/381430260_Trendsetters_How_Gen_Z_Defined_2024
Gould, D., Nalepa, J., & Mignano, M. (2020). Coaching Generation Z athletes. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology, 32(1), 104-120. https://doi.org/10.1080/10413200.2019.1581856
Grant, A. M. (2003). The impact of life coaching on goal attainment, metacognition and mental health. Social Behavior and Personality: an international journal, 31(3), 253-263. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.2003.31.3.253
Hammad, H. (2025). Teaching the Digital Natives: Examining the Learning Needs and Preferences of Gen Z Learners in Higher Education. Transcultural Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences, 6(2), 214-242. https://doi.org/10.21608/tjhss.2025.346098.1303
Horn, T. S., Lox, C., & Labrador, F. (2001). The self-fulfilling prophecy: When coaches' expectations become reality. In Applied sport psychology: Personal growth to peak performance (Vol. 4, pp. 63-81). https://library.stlawu.edu/node/761
Hysa, B. (2016). Zarządzanie różnorodnością pokoleniową. Zeszyty Naukowe Politechniki Śląskiej, seria Organizacja i Zarządzanie, 97(1964), 385-398. https://www.google.com/url?sa=t&source=web&rct=j&opi=89978449&url=https://bibliotekanauki.pl/articles/325393.pdf&ved=2ahUKEwjujIuKub2QAxWXVKQEHcqPNdwQFnoECCYQAQ&usg=AOvVaw1W3oVix3DSPDqCOfuc9bc9
Landman, M., Grobbelaar, H., & Kraak, W. (2024). Coach perspectives on coach-athlete relationships and characteristics of Generation Z academy-level rugby union players from South Africa. Frontiers in Sports and Active Living, 6, 1461951. https://doi.org/10.3389/fspor.2024.1461951
Lindroos, L. (2023). Importance of Market Segmentation in New Markets: Southwestern Consulting's Entry into the Finnish Market Hame University of Applied Science]. Finland. https://www.theseus.fi/bitstream/handle/10024/815011/Lindroos_Leevi.pdf;jsessionid=18BBF0A473AAB39CC05B1C3E6EB1B203?sequence=2
Luisa, Z. (2025). The Coaching Industry Market Size in 2025.
Narojczyk, S., & Nowak, D. (2024). Entrepreneurship from the perspective of Generation Z (Gen Z). Management, 28(2). https://doi.org/10.58691/man/200057
Parsakia, K., Rostami, M., Darbani, S. A., Saadati, N., & Navabinejad, S. (2023). Explanation of the concept of generation disjunction in studying generation z. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS), 4(2), 136-142. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.4.2.15
Parsakia, K., Rostami, M., Saadati, N., & Navabinejad, S. (2023). Analyzing the causes and factors of the difference between the girls of the generation Z and the previous generations in Iran from the perspective of social psychology. Psychology of Woman Journal, 4(1), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.pwj.4.1.1
Świerkosz-Hołysz, M. (2016). Pokolenie Z wkracza na rynek pracy. Społeczeństwo i Edukacja. Międzynarodowe Studia Humanistyczne(2 (21)), 439-447.
Tee, D., Misra, K., Roderique-Davies, G., & Shearer, D. (2022). A systematic review of coaching client characteristics. International Coaching Psychology Review, 17(1), 50-74. https://doi.org/10.53841/bpsicpr.2022.17.1.50
Wajdi, M., Susanto, B., Sumartana, I. M., Sutiarso, M. A., & Hadi, W. (2024). Profile of Generation Z characteristics: Implications for contemporary educational approaches. Kajian Pendidikan, Seni, Budaya, Sosial dan Lingkungan, 1(1), 33-44. https://doi.org/10.58881/kpsbsl.v1i1.8
Wu, H. H., & Pan, W. R. (2009). An integrated approach of the Kano model and ANOVA technique in market segmentation-a case of a coach company. Journal of Statistics and Management Systems, 12(4), 679-691. https://doi.org/10.1080/09720510.2009.10701415