Identifying Generational Gaps in Emotional Expression among Youth and Parents
Keywords:
Emotional expression, intergenerational communication, youth, parents, cultural norms, emotional literacyAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to identify and interpret generational differences in emotional expression between youth and parents, focusing on how social, cognitive, and cultural factors influence emotional communication patterns across generations.
Methods and Materials: This qualitative research employed an exploratory design grounded in the interpretivist paradigm to capture the lived experiences of emotional communication within families. The study involved 20 participants from Canada, comprising 10 youth (aged 18–25) and 10 parents (aged 40–60), selected through purposive sampling to ensure diversity in gender, culture, and socioeconomic background. Semi-structured interviews were conducted in person and online, each lasting 45–70 minutes, until theoretical saturation was reached. Data were transcribed verbatim and analyzed thematically using NVivo 14 software. Thematic analysis followed Braun and Clarke’s six-step framework, with codes and categories refined through constant comparison and reflexive journaling to ensure credibility and consistency.
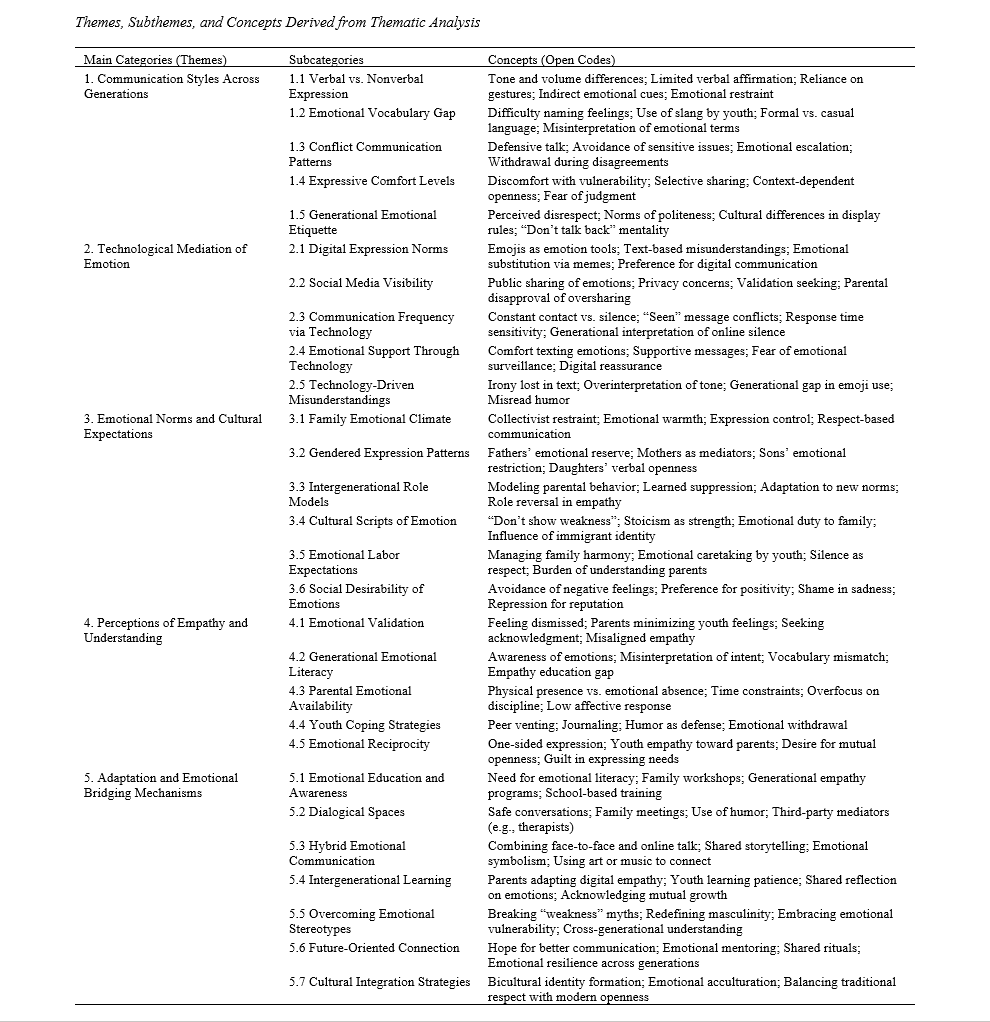
Findings: Five major themes emerged: (1) Communication Styles Across Generations, reflecting youth’s verbal openness versus parental restraint; (2) Technological Mediation of Emotion, highlighting digital communication as both a bridge and barrier; (3) Emotional Norms and Cultural Expectations, emphasizing the impact of cultural scripts and gendered expression; (4) Perceptions of Empathy and Understanding, revealing emotional misattunement and validation gaps; and (5) Adaptation and Emotional Bridging Mechanisms, showing efforts toward intergenerational empathy and emotional literacy. The findings indicated that differences in emotional vocabulary, digital fluency, and cultural norms contribute to misinterpretations and emotional distance, while reflective dialogue and hybrid communication foster improved understanding.
Conclusion: Generational gaps in emotional expression arise from interwoven social, cultural, and cognitive mechanisms that shape emotion socialization within families. Promoting emotional literacy, reciprocal empathy, and adaptive communication practices can enhance intergenerational cohesion and emotional well-being.
Downloads
References
Bailey, K., & Im‐Bolter, N. (2024). Social Cognitive Processes in Children With Specific Learning Disorder: The Importance of Language. Learning Disability Quarterly, 48(4), 215-226. https://doi.org/10.1177/07319487241288531
Bennett, L., Moreau, S., & Matthews, B. L. (2024). Factors Contributing to Identity Confusion in Adolescents From Immigrant Families. Jayps, 5(1), 142-150. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.5.1.17
Chiang, S. C., & Bai, S. (2024). Testing Family-of-Origin Sensitization: Parent-Adolescent Conflict, Emotional Reactivity, and Adolescent Internalizing Psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 37(4), 2172-2180. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0954579424001779
Espinosa, F., Blanco, I., Romero, N., & Sánchez-López, Á. (2025). Cognitive Biases and Emotional Symptomatology as Predictors of Changes in Peer Victimization: A Longitudinal Structural Equation Modeling Study. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 53(9), 1325-1337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-025-01337-7
Gottschlich, D., Turner, S., & Anderson, M. (2025). Internalized Shame as a Mediator Between Emotional Neglect and Self-Harming Behavior. Jarac, 7(1), 240-249. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jarac.7.1.28
Grech, L., Martins, C., & Capitão, L. (2025). A Novel Vignette Measure for Assessing Adolescent Responses to Positive, Negative, Neutral and Constructive Peer Feedback. https://doi.org/10.31234/osf.io/7qawv_v1
Guo, M., Lu, Y., Zhai, R., & Tian, L. (2024). Does Cognitive Control Mediate the Relationship Between Peer Presence and Adolescent Risk‐taking? An ERP Study. Psychophysiology, 61(12). https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.14675
Lievore, R., Cardillo, R., & Mammarella, I. C. (2025). Anxiety in Youth With and Without Specific Learning Disorders: Exploring the Relationships With Inhibitory Control, Perfectionism, and Self-Conscious Emotions. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience, 19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2025.1536192
Moore, J. A., Tam, L. Y. C., & Allen, J. L. (2024). When Being Bad Feels Good: A Systematic Review of the Relationship Between Positive Emotion and Antisocial Behavior in Children and Adolescents. Clinical Child and Family Psychology Review, 27(3), 832-862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10567-024-00493-4
Muntamah, B. S., & Pratama, M. F. (2025). Peer Attachment With Emotion Regulation: The Influence of Affective and Cognitive Empathy as Moderators. Psikologia Jurnal Pemikiran Dan Penelitian Psikologi, 20(1), 18-27. https://doi.org/10.32734/psikologia.v20i1.19972
Petrov, G., & Dimitrov, I. (2024). Exploring the Indicators of Self-Silencing in Adolescent Romantic Relationships. Jayps, 5(3), 159-169. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.5.3.17
Quiroga-Garza, A., & Cavalera, C. (2024). The Resilience Factor: Examining Its Potential to Alleviate Shame and Guilt in School Bullying. Journal of interpersonal violence, 40(15-16), 3548-3572. https://doi.org/10.1177/08862605241270075
Romano, G., Piskorz-Ryń, O., & Ríos, J. (2025). Parental Rejection and Child Emotion Dysregulation: The Mediating Role of Shame. Aftj, 6(2), 172-181. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.aftj.6.2.18
Tsuritani, M., & Jikihara, Y. (2024). Moderating Effects of Coping With Interparental Conflict, Emotional Insecurity in the Interparental Relationship, and Adolescents’ Adjustment. The Japanese Journal of Psychology, 95(3), 153-163. https://doi.org/10.4992/jjpsy.95.22049
Uddenberg, C., Everaert, J., Joormann, J., Kober, H., & Polack, R. G. (2025). Networks of Guilt, Shame, Pride, and Disordered Eating in Youths Show Stability Over Time. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 35(2). https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.70019
Yan, P., Jiang, Z.-X., Wang, Y., Zhang, A., Wang, L., & Zhang, G. (2024). The Impact of Shame on the Dual Harm in Adolescents: The Role of Cognitive Flexibility. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4813234/v1
Yunita, R., & Isnawati, I. A. (2024). Adolescent Verbal Violent Behavior and Emotional Intelligence: A Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Nursing Science Update (Jnsu), 12(1), 53-61. https://doi.org/10.21776/ub.jik.2024.012.01.07
Zulvia, L., & Aviani, Y. I. (2025). Studi Fenomenologis: Psychological Burden Remaja Laki-Laki Dengan Ibu Yang Mengalami Skizofrenia. JPM, 3(4), 326-332. https://doi.org/10.61132/obat.v3i4.1569