Prioritizing Pathways Linking Educational Stress to Mental Health Outcomes: A Mixed-Methods Analysis Among Moroccan Students
Keywords:
Educational stress, mental health, academic pressure, coping styles, resilience, Morocco, mixed-method researchAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to identify and prioritize the key pathways through which educational stress influences mental health outcomes among students in Morocco using an integrated qualitative–quantitative framework.
Methods and Materials: A sequential exploratory mixed-method design was employed. In the first phase, a qualitative thematic analysis was conducted through a systematic review of global and regional studies on educational stress and psychological well-being until theoretical saturation was achieved. The data were analyzed using NVivo 14, generating seven major themes: academic pressure, parental expectations, cognitive coping, peer climate, institutional factors, emotional outcomes, and resilience. In the second phase, a quantitative survey was administered to 160 Moroccan participants, including students and educators, who ranked the relative importance of the identified pathways using a five-point Likert scale. Data analysis was performed in SPSS 26, employing descriptive statistics, mean ranking, and Kendall’s coefficient of concordance (W = 0.81, p < 0.001) to assess inter-rater agreement.
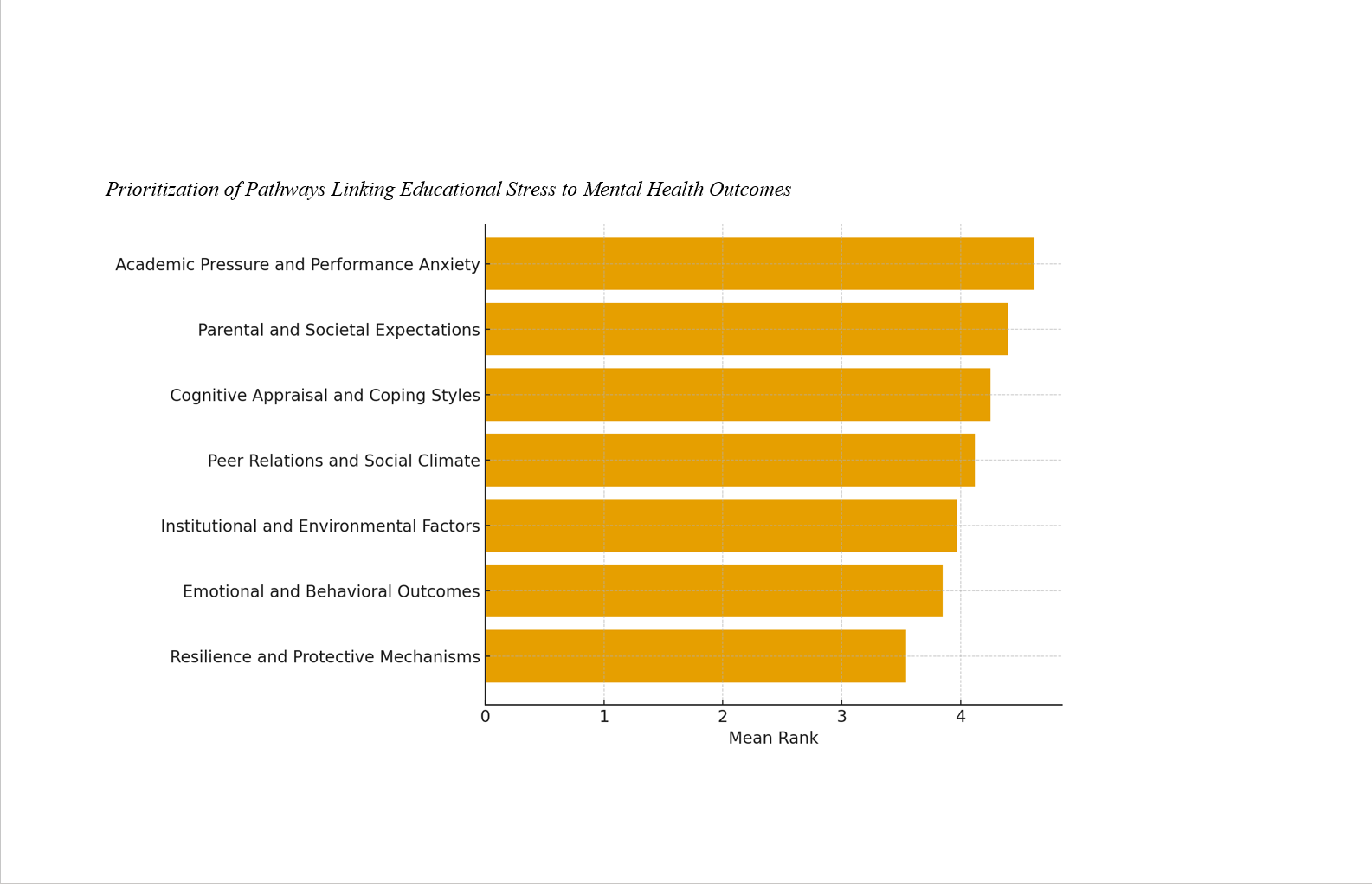
Findings: Results indicated strong consensus among participants regarding the hierarchical influence of stress pathways on mental health. Academic pressure and performance anxiety emerged as the most influential pathway (M = 4.62, SD = 0.48), followed by parental and societal expectations (M = 4.40, SD = 0.55) and cognitive appraisal and coping styles (M = 4.25, SD = 0.59). Peer relations, institutional environment, and emotional outcomes ranked moderately, while resilience and protective mechanisms (M = 3.54, SD = 0.72) were perceived as reactive but essential buffers against stress-induced distress.
Conclusion: Educational stress is a multidimensional construct shaped by academic, familial, cognitive, and institutional dynamics. Addressing these interconnected pathways through targeted interventions—such as resilience training, institutional reform, and family-based awareness—can significantly enhance students’ mental health outcomes and academic sustainability in the Moroccan context.
Downloads
References
Agyemang, S. O., Ninnoni, J. P., & Enyan, N. I. E. (2021). Prevalence and Determinants of Depression, Anxiety and Stress Among Psychiatric Nurses in Ghana: A Cross Sectional Study. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1040468/v1
Ahmed, M. B. M., Ahmed, A. B. M., Gasmalha, M. E. A., Abdalla, O., Ahmed, S., Mohammed, B., Ebrahim, R., Abdeen, M., Babiker, E. M., Ahmed, T. I., Ahmed, A., Ahmed, D., Mubashir, M., & Ahmed, S. (2025). Sudanese Medical Students’ Satisfaction With Online Learning and Its Association With Their Psychological Distress: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Medical Education, 25(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12909-025-07228-1
Al-Qaseer, D. A., Miri, K., Hajiabadi, F., Mazloum, S. R., & Al-fahham, A. A. (2025). The Effectiveness of a Supportive Training Program on Stress, Anxiety, and Depression of Patients With COVID-19 Hospitalized in Najaf Hospitals. BMC psychology, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-025-02490-w
Al‐Maraira, O. A., & Shennaq, S. Z. (2021). Investigation of Depression, Anxiety and Stress Levels of Health-Care Students During COVID-19 Pandemic. Mental Health Review Journal, 26(2), 113-127. https://doi.org/10.1108/mhrj-10-2020-0070
Alfayumi‐Zeadna, S., Touma, L. G., Weinreich, M., & O’Rourke, N. (2022). COVID-19 and Mental Health of Minority Arab Higher-Education Students in Israel: Social, Economic, and Academic Factors. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(20), 13466. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192013466
Bapar, S. H., Raja, R., & Badil. (2022). Frequency and Correlation Between Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among Nursing Students. Liaquat National Journal of Primary Care. https://doi.org/10.37184/lnjpc.2707-3521.4.37
Bilmenoğlu, Ç., Memişoglu, G., Kurt, A., & Çilingir, A. (2023). Correlation of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress With Coping Strategies Among Dentistry Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Eurasian Journal of Family Medicine, 12(1), 11-21. https://doi.org/10.33880/ejfm.2023120102
Costa, R., Machado, J. C., Brandão, T., Pereira, M. G., & Remondes‐Costa, S. (2022). Evaluation of the Effectiveness of a Relaxation Intervention on Distress in University Students: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Análise Psicológica, 40(2), 171-189. https://doi.org/10.14417/ap.1909
Devi, S., Kaushal, S., Agnihotri, G., & Mittal, N. (2023). Stress, Depression, and Anxiety of Female Adolescents of Higher Senior Secondary School: A Cross-Sectional Comparative Study of Humanities, Commerce, and Science Streams. Journal of Pharmacy and Bioallied Sciences, 15(Suppl 2), S1050-S1052. https://doi.org/10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_229_23
Effati-Daryani, F., Zarei, S., Mohammadi, A., Hemmati, E., Yngyknd, S. G., & Mirghafourvand, M. (2020). Depression, Stress, Anxiety and Their Predictors in Iranian Pregnant Women During the Outbreak of COVID-19. BMC psychology, 8(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40359-020-00464-8
Figueira, H. A., Figueira, O., Figueira, A. A., Figueira, J. A., Polo-Ledesma, R. E., Carlos Roberto Lyra da, S., & Dantas, E. H. M. (2023). Impact of Physical Activity on Anxiety, Depression, Stress and Quality of Life of the Older People in Brazil. International journal of environmental research and public health, 20(2), 1127. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20021127
Ghasempour, Z., Abolhassani, M., Gholami, A., Karimi, F., Dokhaei, M., & Rabiee, N. (2024). Training in Child Care and Carrying Out Auriculotherapy Techniques for Mothers of Premature Newborns: Double-Blind Clinical Trial. Revista Brasileira De Saúde Materno Infantil, 24. https://doi.org/10.1590/1806-9304202400000391-en
Hosseini, M. A., Shirzad, F., Ahmadzad-Asl, M., & Hadi, F. (2022). Depression, Anxiety, Stress, and Resiliency in Iranian Families With Autistic Children. Journal of Advances in Medical and Biomedical Research, 30(139), 123-128. https://doi.org/10.30699/jambs.30.139.123
Islam, F., Seemanta, S., Rezina, S., Mehrab, A., Raheem, E., & Hossain, M. S. (2025). Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among Mothers of Children With Thalassemia in Bangladesh: A Cross-Sectional Study. BMC Women S Health, 25(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12905-025-03762-8
Jamal, N. F., Hasan, N. I. A., Baharuddin, M. S., & Suhaimi, S. (2022). Prevalence of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among Undergraduate Students During Open and Distance Learning (ODL). International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 12(8). https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarbss/v12-i8/14383
Kakemam, E., Albelbeisi, A. H., Zavieh, S., Mokhtari, S., Rouhi, A., & Majidi, S. (2020). Prevalence of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Among Iranian Nurses During the COVID-19 Outbreak and Their Related Factors. Israa University Journal for Applied Science, 6(1), 118-138. https://doi.org/10.52865/zpff7715
Landa, J. M. A., García‐Martínez, I., & León, S. P. (2022). Analysis of the Effect of Emotional Intelligence and Coping Strategies on the Anxiety, Stress and Depression Levels of University Students. Psychological Reports, 127(4), 1751-1770. https://doi.org/10.1177/00332941221144603
Laranjeira, C., Dixe, M. d. A., & Querido, A. (2023). Mental Health Status and Coping Among Portuguese Higher Education Students in the Early Phase of the COVID-19 Pandemic. European Journal of Investigation in Health Psychology and Education, 13(2), 429-439. https://doi.org/10.3390/ejihpe13020032
Lu, A. D., Bonder-Smith, S., & Li, X. (2020). The Effects of a Stress Management Group Education Program on Symptoms of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress in People With Comorbid Diabetes and Chronic and/or Recurrent Foot and Ankle Complications. Orthopaedic Nursing, 39(5), 305-314. https://doi.org/10.1097/nor.0000000000000695
Mohammad, S., Almakran, I. W., Al-Montashri, A. S., Mursi, A. M., Al-Harbi, S. M., Pasha, T. S., & Khalid, I. (2020). Depression, Anxiety and Stress and Their Associated Social Determinants in the Saudi College Students. Health Psychology Research, 8(3), 1. https://doi.org/10.4081/hpr.2020.9263
Mohammadbeigi, A., Khavasi, M., Golitaleb, M., & Jodaki, K. (2021). The Effect of Peer Group Education on Anxiety, Stress, and Depression in Older Adults Living in Nursing Homes. Iranian Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Research, 26(3), 252-257. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijnmr.ijnmr_40_20
Moradian, G., Tabarestani, N. D., Dolabi, S. E., Monjazabi, F., Farahanipour, M., & Mojarad, N. (2022). Effect of Self-Care Education on Sleep Quality and Psychological Disorders in Post-Discharged Patients With COVID-19. Journal of Sleep Sciences. https://doi.org/10.18502/jss.v6i(1-2).9289
Muhammad Zakwan Fikhri Bin Mohd, A., & Abdullah, N.-A. (2021). Depression, Anxiety, Stress Ratios and Job Satisfaction in Special Education Schools in Malaysia. International Journal of Academic Research in Progressive Education and Development, 10(1). https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarped/v10-i1/9624
Özdemir, M. A., Topak, D., Turgut, C., Telek, M., & Doğar, F. (2022). Evaluation of Depression, Anxiety, and Stress Status in Parents of Patient With Congenital Clubfoot Treated With Ponseti Method: A Prospective Study. Medicine, 101(44), e31654. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000031654
ÖZyer, Y., & AltaŞ, E. (2023). The Effects of Depression, Anxiety and Stress Levels on Quality of Life of Individuals With Hypertension. Artuklu International Journal of Health Sciences, 3(2), 181-187. https://doi.org/10.58252/artukluder.1288377
Rawi, S. S. A., Jumah, H. A., Ibrahim, A. H., Hamdy, H. A., Hama, H. A., Dogara, A. M., & Effendi, A. B. A. (2022). Depression, Anxiety and Stress Level Among University Students of Class Reentry Post Covid-19 Pandemic. International Journal of Social Sciences and Educational Studies, 9(2). https://doi.org/10.23918/ijsses.v9i2p197
Şanlı, M. E., Yıldız, A., EkİNgen, E., & Yıldırım, M. (2024). Comparison of Stress, Anxiety and Depression Levels of Health, Education and Security Sector Employees: The Effect of Psychological Resilience. Stress and Health, 40(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/smi.3425
Sarbarzeh, P. A., Karimi, S., Jalilian, M., & Mosafer, H. (2020). Depression, Anxiety, Stress and Social Isolation in Hepatitis Patients. SciMedicine Journal, 2(4), 225-233. https://doi.org/10.28991/scimedj-2020-0204-5
Shalaby, A. S., Sadik, S. A. M., & Mahmoud, D. A. M. (2020). Psychiatric Morbidities of Female Obesity Before and After Dieting: An Egyptian Sample. Middle East Current Psychiatry, 27(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s43045-020-00068-3
Song, H., Zhang, M., Wang, Y., Yang, L., Wang, Y., & Li, Y. (2021). The Impact of Resilience on Anxiety and Depression Among Grass-Roots Civil Servants in China. BMC public health, 21(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12889-021-10710-2
Sonia, J., Ali, A., Ali, S., Saghir, T., Sadiq, S., Khan, A. A., & Naz, S. (2022). Depression, Anxiety, Stress and Its Association With Socio-Demographics Characteristics Among Patients Waiting Prior to Elective Coronary Angiography. Saudi Journal of Nursing and Health Care, 5(11), 296-300. https://doi.org/10.36348/sjnhc.2022.v05i11.001
Zhu, M., Chen, H., Wang, Q., Ding, X., & Li, Z. (2025). Comparative Efficacy of Various Interventions to Reduce Perceived Stress Among Older Adults: A Systematic Review and Network Meta‐Analysis. Worldviews on Evidence-Based Nursing, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.70004