Social Media Addiction as a Predictor of Academic Burnout: The Mediating Role of Sleep Quality in Adolescents
Keywords:
Social media addiction, Academic burnout, Sleep quality, AdolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the predictive relationship between social media addiction and academic burnout among adolescents, with sleep quality examined as a mediating variable.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational design was employed with a sample of 399 Indonesian adolescents, determined using the Morgan and Krejcie table for adequate statistical power. Standardized instruments were used to assess social media addiction, sleep quality, and academic burnout. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 27 for descriptive and correlational analyses and AMOS version 21 for Structural Equation Modeling (SEM). Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to test bivariate associations, and SEM was applied to evaluate the mediating role of sleep quality. Model fit indices, including χ²/df, CFI, TLI, and RMSEA, were used to assess the adequacy of the proposed model.
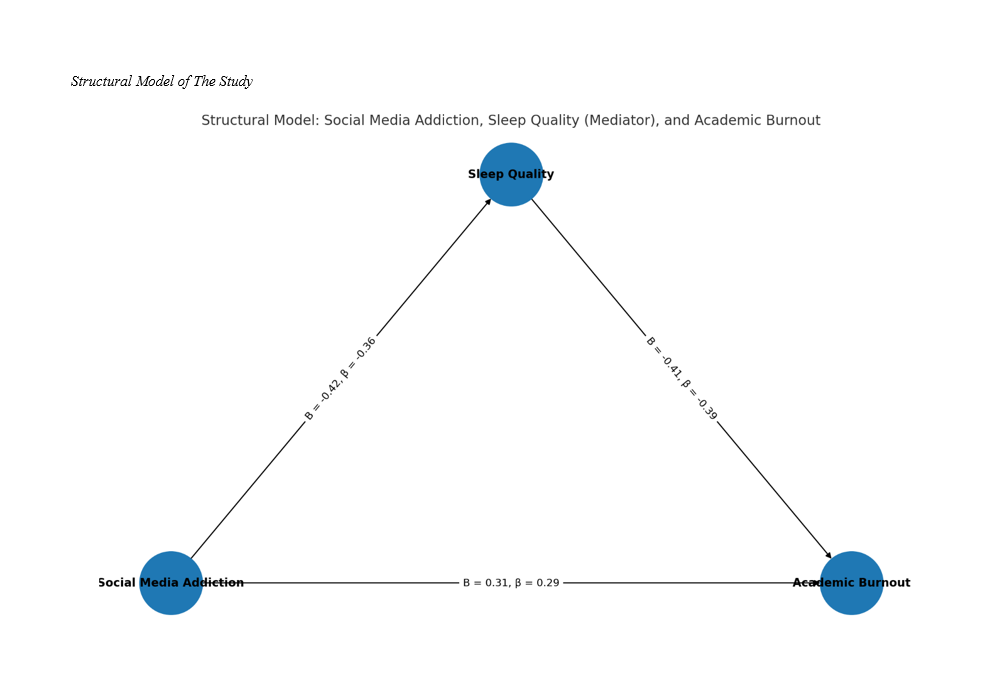
Findings: Inferential results showed a significant positive correlation between social media addiction and academic burnout (r = .41, p < .001). Sleep quality was found to be negatively correlated with both social media addiction (r = –.36, p < .001) and academic burnout (r = –.39, p < .001). SEM analysis confirmed that social media addiction significantly predicted academic burnout both directly (β = .29, p < .001) and indirectly through sleep quality (β = .15, p < .01), indicating a partial mediation effect. Model fit indices demonstrated acceptable values (χ²/df = 2.44, CFI = 0.94, TLI = 0.92, RMSEA = 0.061), supporting the validity of the hypothesized model.
Conclusion: The findings highlight that social media addiction is a significant predictor of academic burnout in adolescents, with poor sleep quality acting as an important mediating factor. These results underscore the necessity of interventions targeting both responsible social media use and sleep hygiene practices to mitigate academic burnout among adolescents.
Downloads
References
Aydın, D., & GÖNcÜ, H. B. (2025). From Childhood Experiences to Social Media Addiction: Unraveling the Impact on Adolescents. Children, 12(3), 385. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12030385
Aydın, K. Y., Aydın, N., & Özçırpıcı, B. (2021). Social Media Use, Addiction and Burnout Levels of Hospital Employees, Effective Factors: A Cross Sectional Study. International Neuropsychiatric Disease Journal, 34-41. https://doi.org/10.9734/indj/2021/v15i330157
Badri, H. M., Aboalshamat, K., Abdouh, I., Quronfulah, B. S., Mahmoud, M. A., Rajeh, M., Badawoud, A. M., & Alzhrani, A. M. (2023). The Effect of Social Media Addiction on Burnout Among Health-Care Students and Professionals in Saudi Arabia. International Journal of Academic Medicine, 9(1), 11-17. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijam.ijam_72_22
Chen, J. (2023). Social Media Addiction and Consequences in Adolescents. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media, 7(1), 291-296. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7048/7/20220823
Cheng, X., & Lin, H. (2023). Mechanisms From Academic Stress to Subjective Well-Being of Chinese Adolescents: The Roles of Academic Burnout and Internet Addiction. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 16, 4183-4196. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s423336
Ernawati, D. R. I., Rizal, A., & Suryadi, B. (2021). Tingkat Pengetahuan Orang Tua Dan Tingkat Ketergantungan Gadget Pada Anak Usia Sekolah. Indonesian Scholar Journal of Nursing and Midwifery Science (Isjnms), 1(04), 118-124. https://doi.org/10.54402/isjnms.v1i04.79
Evers, K., Chen, S., Rothmann, S., Dhir, A., & Pallesen, S. (2020). Investigating the Relation Among Disturbed Sleep Due to Social Media Use, School Burnout, and Academic Performance. Journal of adolescence, 84(1), 156-164. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2020.08.011
Gao, J., Tian, X., & Wu, H. (2025). Exploring the Mediating Role of Social Support in Sports Participation and Academic Burnout Among Adolescent Students in China. Frontiers in psychology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1591460
He, Q. (2022). The Relationship Between Family and Social Media. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.220704.058
Hietajärvi, L., Maksniemi, E., Lonka, K., Hakkarainen, K., Alho, K., & Salmela‐Aro, K. (2022). Digital Engagement, School Burnout and Academic Performance: Longitudinal Within-Student Relations. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/a2bk7
Horozoğlu, M. A., & Gündüz, G. (2024). Investigation of the Relationship Between Social Media Addiction, Social Media Burnout and Exercise Commitment in Individuals Actively Engaged in Fitness. Akdeniz Spor Bilimleri Dergisi, 7(2), 351-364. https://doi.org/10.38021/asbid.1482661
Iskajyan, A. (2024). The Influence of Social Media Addiction on Mental Health and Academic Performance. Sush Scientific Proceedings, 291-302. https://doi.org/10.54151/27382559-24.2pb-291
Jiang, Y., Lü, L., & Hu, R. H. (2023). Parental Phubbing and Academic Burnout in Adolescents: The Role of Social Anxiety and Self-Control. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1157209
Kara, F. M., Sarol, H., Gürbüz, B., & Gürkan, R. K. (2023). Boreout at the Office: The Role of Leisure Boredom in Predicting Job Burnout and Social Media Addiction. Journal of Education and Recreation Patterns, 4(2), 400-414. https://doi.org/10.53016/jerp.v4i2.178
Karakoç, E., Öğüt, N., & Aslan, A. (2024). The Effect of Burnout Syndrome on Social Media Addiction: The Case of Healthcare Workers. Mehmet Akif Ersoy Üniversitesi İktisadi Ve İdari Bilimler Fakültesi Dergisi. https://doi.org/10.30798/makuiibf.1282212
Khan, R. S. U. (2025). Social Media Problematic Use and Academic Procrastination: a Correlational Quantitative Study of Adolescents in Pakistan. J. Asian Dev. Studies, 14(2), 494-498. https://doi.org/10.62345/jads.2025.14.2.39
Kudubeş, A. A., & Efe, Y. S. (2023). The Predictive Power of Game Addiction and Social Media Addiction on Adolescents' Lifestyle. Psychology in the Schools, 61(3), 1000-1017. https://doi.org/10.1002/pits.23096
Kuilong, H. (2025). Unveiling the Complex Mechanism of Short Video Addiction on English Learning Engagement and Burnout Among College EFL Students. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-5885393/v1
Layrtthon Carlos de Oliveira, S., & Alves, M. M. (2023). Social Media Burnout and Internet Addiction: The Role of Extroversion and Social Self-Concept in a Brazilian Sample. Psychological Reports, 128(3), 1356-1370. https://doi.org/10.1177/00332941231174390
Liu, C. (2023). The Unique Role of Smartphone Addiction and Related Factors Among University Students: A Model Based on Cross-Sectional and Cross-Lagged Network Analyses. BMC psychiatry, 23(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12888-023-05384-6
Mu, H.-L., Jiang, Q., Xu, J., & Chen, S. (2022). Drivers and Consequences of Short-Form Video (SFV) Addiction Amongst Adolescents in China: Stress-Coping Theory Perspective. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(21), 14173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192114173
Naffisa, T., & Dwatra, F. D. (2024). The Relationship Between Academic Burnout and Social Media Addiction Among College Students at Universitas Negeri Padang in Writing Undergraduate Theses. In Trend, 1(4), 139-145. https://doi.org/10.62260/intrend.v1i4.280
Priani, P. (2024). Mengatasi Kecanduan Media Sosial Pada Remaja Melalui Layanan Bimbingan Konseling. Bikoling, 1(1), 19-24. https://doi.org/10.70134/bikoling.v1i1.207
Taş, İ. (2021). The Relationship Between Social Ignore and Social Media Addiction Among Adolescents: Mediator Effect of Satisfaction With Family Life. Youth & Society, 55(4), 708-729. https://doi.org/10.1177/0044118x211055210
Vashishtha, S., Ahuja, S., & Sharma, M. R. (2021). Impact of Facebook Addiction Disorder (Fad) on Study Habits and Academic Achievement of Adolescents. Mier Journal of Educational Studies Trends & Practices, 195-207. https://doi.org/10.52634/mier/2017/v7/i2/1422
Wang, F., Huang, M. L., & Jian-guo, Q. U. (2023). The Effect of Internet Addiction on Mind Wandering: Resilience and Academic Burnout as Mediators Among Chinese Adolescents. Social Behavior and Personality an International Journal, 51(2), 1-13. https://doi.org/10.2224/sbp.12097
Yam, F. C., Yildirim, O., & Köksal, B. (2024). The Mediating and Buffering Effect of Resilience on the Relationship Between Loneliness and Social Media Addiction Among Adolescent. Current Psychology, 43(28), 24080-24090. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-024-06148-5
Yang, Z. (2023). Why Adolescents Are Addicted to Social Media. Journal of Education Humanities and Social Sciences, 8, 1430-1436. https://doi.org/10.54097/ehss.v8i.4498
Yayman, E., & Bilgin, O. (2020). Relationship Between Social Media Addiction, Game Addiction and Family Functions. International Journal of Evaluation and Research in Education (Ijere), 9(4), 979. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijere.v9i4.20680
Zani, B. N., Said, F. M., Nambiar, N., & Sholihat, S. (2024). The Relationship Between Social Media Dependency, Mental Health, and Academic Performance Among Adolescents in Indonesia. Jurnal Keperawatan Komprehensif, 10(4), 410-417. https://doi.org/10.33755/jkk.v10i4.699
Zhang, W. (2024). An Analysis of Social Media Addiction in Adolescents. Lecture Notes in Education Psychology and Public Media, 52(1), 86-90. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7048/52/20241537
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








