Relational Aggression and Depressive Symptoms: The Mediating Role of Social Exclusion Perception
Keywords:
Relational aggression, Social exclusion, Depressive symptoms, AdolescentsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the mediating role of social exclusion perception in the relationship between relational aggression and depressive symptoms among Malaysian adolescents.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational design was employed with a sample of 383 secondary school students in Malaysia, selected based on Krejcie and Morgan’s sample size determination table. Data were collected using standardized self-report instruments measuring relational aggression, social exclusion perception, and depressive symptoms. Descriptive statistics and Pearson correlation analyses were performed using SPSS-27. Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was conducted using AMOS-21 to assess the hypothesized mediation model and evaluate model fit through indices such as CFI, TLI, RMSEA, and χ²/df.
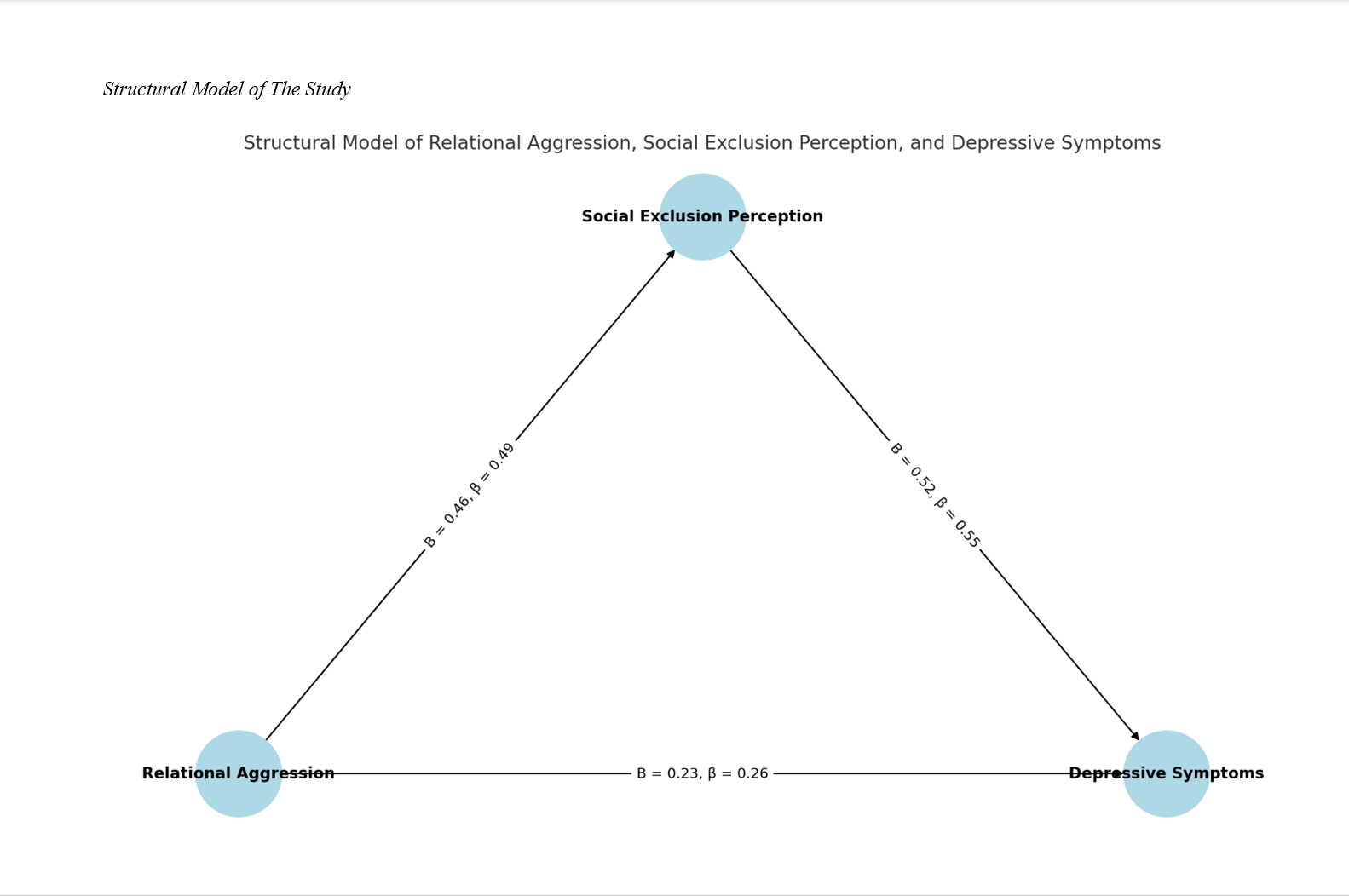
Findings: Results indicated that relational aggression was significantly and positively correlated with both social exclusion perception (r = .49, p < .001) and depressive symptoms (r = .42, p < .001), while social exclusion perception was also strongly correlated with depressive symptoms (r = .55, p < .001). SEM analysis demonstrated an acceptable model fit (χ²/df = 2.34, CFI = 0.96, RMSEA = 0.058), supporting the proposed mediational model. Path analysis revealed that relational aggression had a significant direct effect on depressive symptoms (β = 0.26, p < .001), as well as an indirect effect through social exclusion perception (β = 0.27, p < .001), with a total effect of β = 0.53. These results support the role of perceived social exclusion as a partial mediator in the association between relational aggression and depressive symptomatology.
Conclusion: The findings underscore the importance of perceived social exclusion as a psychological mechanism linking relational aggression to depressive symptoms in adolescents. Addressing exclusion experiences in peer interactions may be critical in designing effective interventions to reduce depression and promote emotional well-being among youth.
Downloads
References
Bratu, I. (2023). Academic Stress and Aggression. The Moderating Role of Social Support. Studia Doctoralia, 14(2/2023), 96-105. https://doi.org/10.47040/sdpsych.v14i2.165
Çelikkaleli, Ö., & TÜMtaŞ, M. S. (2017). Üni̇versi̇te Öğrenci̇leri̇nde Sosyal Dişlanma İle Saldirganlik Arasindaki̇ İli̇şki̇de Sosyal Yabancilaşmanin Araci Rolü1. Mehmet Akif Ersoy Üniversitesi Eğitim Fakültesi Dergisi, 0(43), 156. https://doi.org/10.21764/efd.14945
Deason, D. L., Dahlen, E. R., Madson, M. B., & Bullock‐Yowell, E. (2019). Five-Factor Model of Personality, Social Anxiety, and Relational Aggression in College Students. Journal of College Student Development, 60(1), 110-114. https://doi.org/10.1353/csd.2019.0007
Hames, J. L., Rogers, M. L., Silva, C., Ribeiro, J. D., Teale, N. E., & Joiner, T. E. (2017). A Social Exclusion Manipulation Interacts With Acquired Capability for Suicide to Predict Self-Aggressive Behaviors. Archives of Suicide Research, 22(1), 32-45. https://doi.org/10.1080/13811118.2017.1304309
He, C., Mao, J., Yang, Q., Yuan, J., & Yang, J. (2022). Trait Acceptance Buffers Aggressive Tendency by the Regulation of Anger During Social Exclusion. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(22), 14666. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192214666
Klanienė, I., Skališienė, R., & Lidžiūtė, S. (2024). Social Exclusion Among Peers as a Form of Expression of Bullying in a Pre-School Education Group. Society Integration Education Proceedings of the International Scientific Conference, 1, 710-723. https://doi.org/10.17770/sie2024vol1.7802
Lee, S. H., Smith, P. K., & Monks, C. P. (2015). Participant Roles in Peer‐victimization Among Young Children in South Korea: Peer‐, Self‐, and Teacher‐nominations. Aggressive Behavior, 42(3), 287-298. https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.21623
Lent, M. C., Perry, K. J., Blakely‐McClure, S. J., Buck, C., Murray‐Close, D., & Ostrov, J. M. (2022). Autonomic Nervous System Reactivity and Preschoolers’ Social Dominance. Developmental Psychobiology, 64(8). https://doi.org/10.1002/dev.22336
Marcos‐Vidal, L., Gil-Buitrago, H., Cisma, I., Hendricks, R. C., Atran, S., & Pretus, C. (2025). When Group Grievances Become Personal: The Neural Correlates of Group and Personal Rejection. Cognitive Affective & Behavioral Neuroscience, 25(3), 799-813. https://doi.org/10.3758/s13415-024-01257-x
Martínez-Martínez, A., Sánchez, M. C., Rodríguez-Fernández, S., Ortega, F. Z., Cuberos, R. C., & Garcés, T. E. (2018). Violent Behaviour, Victimization, Self-Esteem and Physical Activity of Spanish Adolescents According to Place of Residence: A Structural Equation Model / Conducta Violenta, Victimización, Autoestima Y Actividad Física De Adolescentes Españoles en Función Del Lugar De Residencia: Un Modelo De Ecuaciones Estructurales. International Journal of Social Psychology Revista De Psicología Social, 33(1), 111-141. https://doi.org/10.1080/02134748.2017.1385242
Moon, C. (2022). Narcissism and Aggression: The Moderating Role of Social Exclusion. https://doi.org/10.17605/osf.io/b2s9m
Murray‐Close, D., Nelson, D. A., Ostrov, J. M., Casas, J. F., & Crick, N. R. (2016). Relational Aggression: A Developmental Psychopathology Perspective. 1-63. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119125556.devpsy413
Qiu, Y., Chen, L., Xu, C., He, X., Zong, Q., Chen, W., & Liu, F. (2025). The Impact of Social Exclusion on Aggressive Behavior: The Role of Self-Control and Attribution. Personality and individual differences, 243, 113231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2025.113231
Quan, F., Zhou, J., Gou, Y., Gui, M., Wang, L., & Zhang, S. (2024). The Mediating Role of Hostile Attribution Bias in Social Exclusion Affecting Aggressive Behavior. Aggressive Behavior, 50(4). https://doi.org/10.1002/ab.22169
Riva, P., Lauro, L. J. R., DeWall, C. N., Chester, D. S., & Bushman, B. J. (2014). Reducing Aggressive Responses to Social Exclusion Using Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation. Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience, 10(3), 352-356. https://doi.org/10.1093/scan/nsu053
Stenseng, F., Belsky, J., Skalická, V., & Wichstrøm, L. (2014). Preschool Social Exclusion, Aggression, and Cooperation. Personality and Social Psychology Bulletin, 40(12), 1637-1647. https://doi.org/10.1177/0146167214554591
Teffelen, M. W. v., Vancleef, L. M., & Lobbestael, J. (2021). Provoked Aggression, Psychopathy and Narcissism: Comparing the Impact of Social Exclusion and Insult. Psychology of violence, 11(1), 82-91. https://doi.org/10.1037/vio0000340
Tong, L., Jiang, Y., Cao, W., & Wang, H. (2024). How Does Social Exclusion Lead to Emerging Adult Relational Aggression? Potential Mechanisms of Action of Relative Deprivation and Hostile Attribution Bias. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4191073/v1
Troop‐Gordon, W., & Ranney, J. D. (2014). Popularity Among Same-Sex and Cross-Sex Peers: A Process-Oriented Examination of Links to Aggressive Behaviors and Depressive Affect. Developmental Psychology, 50(6), 1721-1733. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0036417
Wang, T., Xiao, Q., Wang, H., Hu, Y., & Xiang, J. (2024). Self‐compassion Defuses the Aggression Triggered by Social Exclusion. PsyCh Journal, 13(6), 1014-1025. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.774
Winter, B., & Burholt, V. (2018). The Impact of Social Exclusion From Social Relations on Belonging and Social Cohesion. Innovation in Aging, 2(suppl_1), 593-594. https://doi.org/10.1093/geroni/igy023.2204
Yamamoto, N., & Moriguchi, Y. (2025). Hostile Cognitions and Aggressive Responses Toward Excluders in Young Children. Journal of interpersonal violence. https://doi.org/10.1177/08862605251336346
Yang, X., Zou, Y., Yin, H., Jiang, R., Wang, Y., & Wang, F. (2023). Differences in Aggressive Behavior of Individuals With Different Self-Construal Types After Social Exclusion in the Same Cultural Background. Behavioral Sciences, 13(8), 623. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13080623
Zhao, J., Chen, S., Hua, W., & Hu, Y. (2025). Social Exclusion and Online Aggressive Behavior: Mediation Through Ego Depletion and Moderation Through Mindfulness. Behavioral Sciences, 15(3), 346. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15030346
Downloads
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.








