The Impact of Organizational and Situational Factors on the Relationship Between Disclosure Triangle Elements and Auditors' Whistleblowing Motivation
Keywords:
Disclosure Triangle, Auditors' Whistleblowing, Organizational Factors, Situational FactorsAbstract
Objective: This study aims to investigate the impact of organizational and situational factors on the relationship between disclosure triangle elements and internal auditors' whistleblowing motivation.
Methodology: The research employs a descriptive survey method, using a cross-sectional design and structural equation modeling to analyze data collected from a sample of 384 internal auditors through a questionnaire.
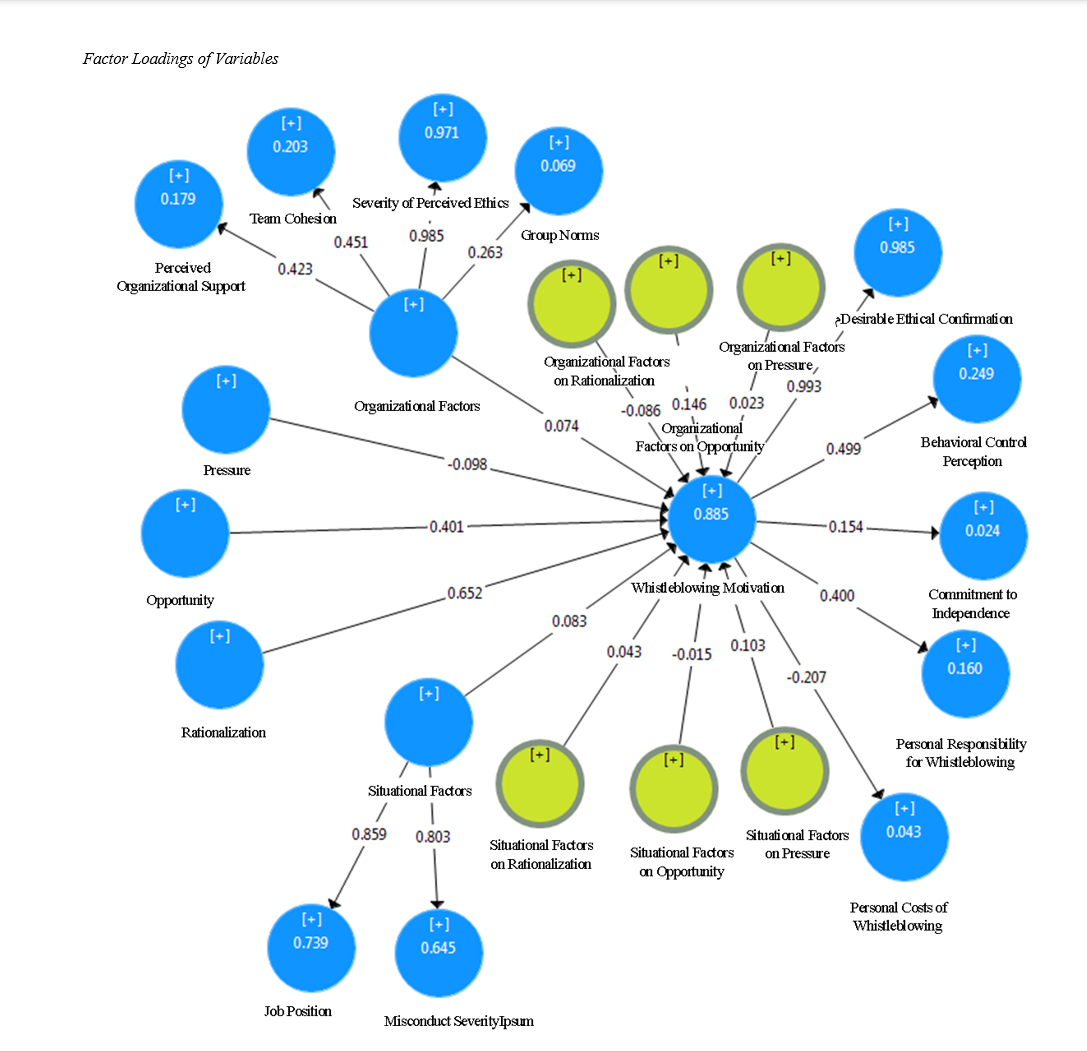
Findings: The results reveal that the disclosure triangle elements, specifically opportunity and rationalization, positively influence whistleblowing motivation, while pressure does not have a significant effect. Additionally, organizational and situational factors do not moderate the relationship between disclosure triangle elements and whistleblowing motivation.
Conclusion: Whistleblowing motivation is significantly driven by opportunity and rationalization, but organizational and situational factors fail to exert a moderating influence, emphasizing the need for ethical support and rational justification mechanisms within organizations to encourage whistleblowing behavior.
Downloads
References
Ahmad, S., Smith, G., & Ismail, Z. (2013). Internal whistleblowing intentions by internal auditors: A prosocial behaviour perspective. Malaysian Accounting Review, 12(1), 145-181. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/260427493_Internal_Whistleblowing_Intentions_by_Internal_Auditors_A_Prosocial_Behaviour_Perspective
Al-Ahdal, W. M., & Hashim, H. A. (2021). Impact of audit committee characteristics and external audit quality on firm performance: Evidence from India. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society. https://doi.org/10.1108/CG-09-2020-0420
Alleyne, P., & Chandler, M. (2018). Examining the Potential Impact of Whistleblowing on Corruption in the Caribbean's Financial Sector. In Corruption Scandals and Their Global Impacts (pp. 34-56). Routledge. https://doi.org/10.4324/9781315142722-3
Alleyne, P., Charles-Soverall, W., Broome, T., & Pierce, A. (2017). Perceptions, predictors and consequences of whistleblowing among accounting employees in Barbados. Meditari Accountancy Research, 25, 241-267. https://doi.org/10.1108/MEDAR-09-2016-0080
Alleyne, P., Hudaib, M., & Pike, R. (2013). Towards a conceptual model of whistle-blowing intentions among external auditors. The British Accounting Review, 45(1), 10-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bar.2012.12.003
Bani Mahd, B., & Gol Mohammadi, A. (2017). Examining the Relationship Between Ethical Climate and Whistleblowing on Fraud Through the Voluntary Reporting Model in Iran's Auditing Profession. Value and Behavioral Accounting, 2(3), 61-86. https://doi.org/10.29252/aapc.2.3.61
Brink, A. G., Lowe, D. J., & Victoravich, L. M. (2017). The Public Company Whistleblowing Environment: Perceptions of a Wrongful Act and Monetary Attitude. Accounting and the Public Interest, 17(1), 1-30. https://doi.org/10.2308/apin-51681
Brown, J. O., Hays, J., & Stuebs Jr, M. T. (2016). Modeling accountant whistleblowing intentions: Applying the theory of planned behavior and the fraud triangle. Accounting and the Public Interest, 16(1), 28-56. https://doi.org/10.2308/apin-51675
Defiantoro, D., Tinangon, J. J., & Gamaliel, H. G. (2023). The Whistleblowing Diamond: Considering Four Elements of Whistleblowing Intention. Accounting and Finance Studies, 3(1), 63-82. https://doi.org/10.47153/afs31.6252023
Eghbali Far, N., Talebnia, G., & Vakili Fard, H. (2020). The Impact of Organizational Ethical Care Tools on Whistleblowing Regarding Financial Corruption in Auditing Firms. Ethical Research, 11(1), 47-70. https://www.noormags.ir/view/en/articlepage/1684143/%D8%AA%D8%A7%D8%AB%DB%8C%D8%B1-%D8%A7%D8%A8%D8%B2%D8%A7%D8%B1%D9%87%D8%A7%DB%8C-%D9%85%D8%B1%D8%A7%D9%82%D8%A8%D8%AA-%D8%A7%D8%AE%D9%84%D8%A7%D9%82%DB%8C-%D8%B3%D8%A7%D8%B2%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%86-%D8%A8%D8%B1-%D9%87%D8%B4%D8%AF%D8%A7%D8%B1-%D8%AF%D9%87%DB%8C-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D9%85%D9%88%D8%B1%D8%AF-%D9%81%D8%B3%D8%A7%D8%AF-%D9%85%D8%A7%D9%84%DB%8C-%D8%AF%D8%B1-%D9%85%D9%88%D8%B3%D8%B3%D8%A7%D8%AA-%D8%AD%D8%B3%D8%A7%D8%A8%D8%B1%D8%B3%DB%8C
Goldoust, M., Talebnia, G., Esmailzadeh Mogheri, A., Rahnamaye Roodposhti, F., & Royayi, R. (2019). Analyzing the Relationship Between Ethical Perception and Ethical Judgment Among Public Sector Accountants Regarding Financial Misconduct Whistleblowing (Case Study: Gilan Province). Biannual Journal of Public Sector Accounting, 5(1), 85-98. https://gaa.journals.pnu.ac.ir/article_6121.html?lang=en
Holtzblatt, M. A., Foltin, C., & Tschakert, N. (2020). Learning from ethical violations in public accounting: a South African audit scandal and a firm's transformation. Issues in Accounting Education, 35(2), 37-63. https://doi.org/10.2308/issues-19-062
Jayanti, Y. D., Maharani, S. N., & Handayati, P. (2021). Personal and organizational factors on Whistleblowing intention with religiosity as a moderating variable. South East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business, Economics and Law, 24(4), 22-34. https://seajbel.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/06/SEAJBEL24_707.pdf
Keil, M., Park, E. H., & Ramesh, B. (2017). Violations of health information privacy: The role of attributions and anticipated regret in shaping whistle-blowing intentions. Information Systems Journal, 28, 818-848. https://doi.org/10.1111/isj.12168
King, G. (1999). The Implications of an Organization's Structure on Whistleblowing. Journal of Business Ethics, 20(4), 315-326. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1006028417000
Kroll, A. (2017). Global fraud and risk report: building resilience in a volatile world. Kroll. www.kroll.com/-/media/kroll/pdfs/news/press-assets-2016-17/kroll-global-fraud-report-2016-2017.pdf
Latan, H., Chiappetta Jabbour, C. J., & Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, A. B. (2019). To blow or not to blow the whistle: The role of rationalization in the perceived seriousness of threats and wrongdoing. Journal of Business Ethics. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-019-04287-5
Latan, H., Chiappetta Jabbour, C. J., & Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, A. B. (2020). Social Media as a Form of Virtual Whistleblowing: Empirical Evidence for Elements of the Diamond Model. Journal of Business Ethics, 174(3), 529-548. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-020-04598-y
Latan, H., Ringle, C. M., & Jabbour, C. J. C. (2017). Whistleblowing Intentions Among Public Accountants in Indonesia: Testing for the Moderation Effects. Journal of Business Ethics, 152, 573-588. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-016-3318-0
MacGregor, J., & Stuebs, M. (2014). The Silent Samaritan Syndrome: Why the Whistle Remains Unblown. Journal of Business Ethics, 120, 149-164. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10551-013-1639-9
May-Amy, Y. C., Han-Rashwin, L. Y., & Carter, S. (2020). Antecedents of company secretaries' behaviour and their relationship and effect on intended whistleblowing. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society, 20(5), 837-861. https://doi.org/10.1108/CG-10-2019-0308
Molaei, A. (2024). Organizational Environment and Whistleblowing Mindset Among Internal Auditors. Quarterly Journal of New Research Approaches in Management and Accounting, 8(92), 1996-2011. https://majournal.ir/index.php/ma/article/view/2630
Momenifar, F., Raji, A., YarAhmadi, J., & Aziziyan Kohn, N. (2023). The Relationship Between Interpersonal Skills and Organizational Whistleblowing Mediated by Ethical Intelligence Among Employees of the Ministry of Sports and Youth. Quarterly Journal of Ethics in Science and Technology, 18(1), 78-86. https://ethicsjournal.ir/article-1-2940-en.html
Murphy, P. R., & Free, C. (2015). Broadening the Fraud Triangle: Instrumental Climate and Fraud. Behavioral Research in Accounting, 28, 41-56. https://doi.org/10.2308/bria-51083
Near, J. P., & Miceli, M. P. (1985). Organizational dissidence: The case of whistleblowing. Journal of Business Ethics, 4(1), 1-16. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00382668
Nuswantara, D. A. (2022). Reframing whistleblowing intention: an analysis of individual and situational factors. Journal of Financial Crime. https://doi.org/10.1108/JFC-11-2021-0255
Shahabi, S. S., Beni Mahd, B., & Rezaei, F. (2021). Organizational Justice and Ethical Whistleblowing of Misconduct in the Auditing Profession. Ethics in Science and Technology, 16(2), 156-161. https://ethicsjournal.ir/article-1-2300-en.html
Tavan Gar Ranjbar, M., Alvani, S. M., & Mehrmanesh, H. (2022). A Model for Implementing Whistleblowing Policy in Iranian Public Organizations. Basij Strategic Studies Quarterly, 25(2), 99-126. https://www.bsrq.ir/article_168046.html?lang=en
Tsahuridu, E. (2011). Whistleblowing management is Risk management. International Whistleblowing Research Network. https://www.academia.edu/4192260/Whistleblowing_Management_is_Risk_Management
Tuan Mansor, T. M., Mohamad Ariff, A., & Hashim, H. A. (2020). Whistleblowing by auditors: the role of professional commitment and independence commitment. Managerial Auditing Journal, 35(8), 1033-1055. https://doi.org/10.1108/MAJ-11-2019-2484
Tuan Mansor, T. M., Mohamad Ariff, A., Hashim, H. A., & Ngah, A. H. (2022). External whistleblowing intentions of auditors: a perspective based on stimulus-organism-response theory. Corporate Governance, 22(4), 871-897. https://doi.org/10.1108/CG-03-2021-0116
Yadegari, K., Salehi, E. K., Amiri, H., & Khanifar, H. (2022). Developing an Auditor Whistleblowing Model Using Grounded Theory. Experimental Accounting Research, 12(45), 199-230. https://jera.alzahra.ac.ir/article_6528.html?lang=en
Young, R. F. (2017). Blowing the whistle: individual persuasion under perceived threat of retaliation. Behavioral Research in Accounting, 29(2), 97-111. https://doi.org/10.2308/bria-51729
Yousaf, W., Hussain, S., Aqdas, M., Zaman, Q., & Rana, F. (2020). The Nexus of Whistle-blowing Triangle and Whistle-blowing Intentions on the Pakistani Organizations: Moderating Role of Perceived Organizational Support. International Journal of Psychosocial Rehabilitation, 23(1), 6294-6304. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/344374436_The_Nexus_of_Whistle-blowing_Triangle_and_Whistle-blowing_Intentions_on_the_Pakistani_Organizations_Moderating_Role_of_Perceived_Organizational_Support
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Zahra Akbari (Author); Arezoo Aghaei chadegani (Corresponding Author); Ehsan Karami (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















