Cognitive-Affective Disintegration in Women with Complex Developmental Trauma
Keywords:
Complex developmental trauma, cognitive-affective disintegration, alexithymia, emotional dysregulationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to explore the lived experience of cognitive-affective disintegration in women with a history of complex developmental trauma.
Methods and Materials: A qualitative design was employed using a phenomenological approach to capture the subjective experiences of trauma-exposed women. Seventeen adult female participants residing in Hungary were recruited through purposive sampling. Inclusion criteria included a self-reported history of complex developmental trauma and current psychological stability. Data were collected through in-depth semi-structured interviews, each lasting between 60 and 90 minutes. Interviews were transcribed verbatim and analyzed using thematic analysis with the support of NVivo 14 software. The coding process continued until theoretical saturation was achieved.
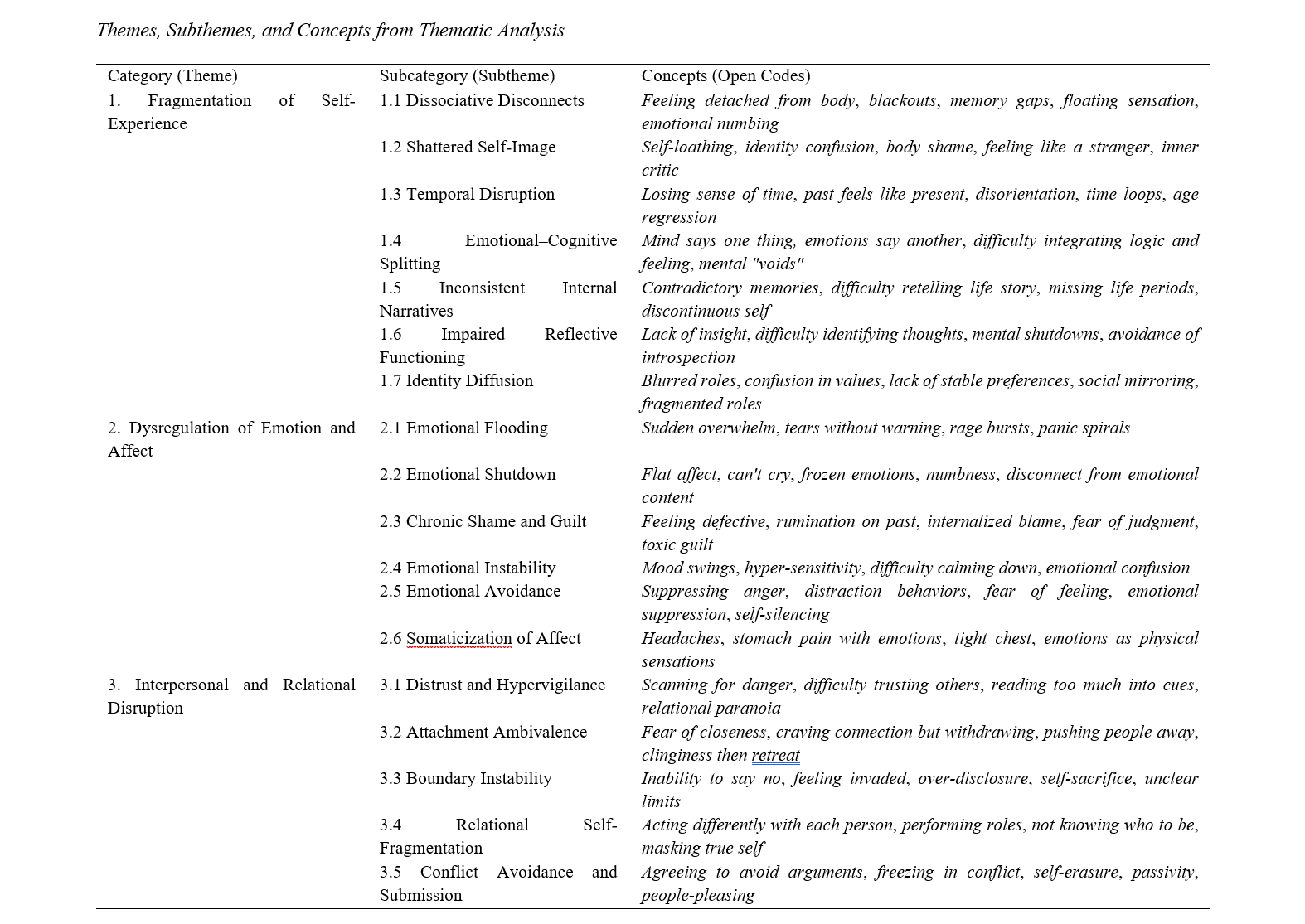
Findings: Three overarching themes emerged: (1) Fragmentation of self-experience, including subthemes such as dissociative disconnects, identity diffusion, and impaired reflective functioning; (2) Dysregulation of emotion and affect, characterized by emotional flooding, shutdown, chronic shame, and somatization of affect; and (3) Interpersonal and relational disruption, which encompassed relational hypervigilance, attachment ambivalence, and conflict avoidance. Participants described a pervasive sense of internal disconnection between thoughts, feelings, and bodily sensations, as well as incoherent self-narratives and unstable relationship patterns. Alexithymia appeared as a central mechanism linking early trauma to cognitive-affective fragmentation. Findings aligned with prior literature on trauma, dissociation, and emotional dysregulation, highlighting the enduring impact of developmental trauma on emotional processing and self-coherence.
Conclusion: The findings underscore the need for trauma-informed therapeutic interventions that target alexithymia, emotion regulation, and narrative integration to restore cognitive-affective coherence and relational stability in trauma survivors.
Downloads
References
Adamowicz, J. L., Sirotiak, Z., & Thomas, E. B. (2024). Childhood Maltreatment and Somatic Symptoms: Examining the Role of Specific Types of Childhood Maltreatment and Alexithymia. Psychological Trauma Theory Research Practice and Policy, 16(Suppl 1), S2-S9. https://doi.org/10.1037/tra0001315
Aghaeimazraji, M., Khosravani, V., Ardestani, S. M. S., Berk, M., & Najafi, M. (2024). The Connections Between Alexithymia, Childhood Maltreatment, Impulsivity and Extreme Sensory Processing Patterns in Relation to Bipolar Symptoms in Inpatients With Bipolar Disorder. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 31(5). https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.3070
Akpinar, B. (2024). Examining the Relationship Between Childhood Traumas, Alexithymia and Emotional Regulation Difficulties in University Students. https://doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.1005138
Akpinar, B., & Demir, Z. (2022). Üniversite Öğrencilerinde Çocukluk Çağı Travmaları, Aleksitimi Ve Duygu Düzenleme Güçlüğü Arasındaki İlişkinin İncelenmesi. International Journal of Social Sciences, 6(26), 509-535. https://doi.org/10.52096/usbd.6.26.33
Anagnostopoulou, T., Kalaitzaki, A., Tsouvelas, G., & Tamiolaki, A. (2024). The Long-Term Effect of Childhood Trauma and Alexithymia on Mental Distress During the COVID-19 Pandemic in Greece. Psychology the Journal of the Hellenic Psychological Society, 29(2), 57-78. https://doi.org/10.12681/psy_hps.28172
Çoban, M. C., & Farajİ, H. (2025). The Mediator Role of Alexithymia Between Childhood Traumas and Fibromyalgia Impact Level of Patients With Fibromyalgia. Interdisciplinary Medical Journal, 16(54), 8-17. https://doi.org/10.17944/interdiscip.1541885
Cooper, H., Jennings, B. J., Kumari, V., Willard, A. K., & Bennetts, R. J. (2024). The Association Between Childhood Trauma and Emotion Recognition Is Reduced or Eliminated When Controlling for Alexithymia and Psychopathy Traits. Scientific reports, 14(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-024-53421-5
Ghogare, A. S., Patil, P. S., & Vankar, G. K. (2021). A Systematic Review of Childhood Psychological Traumas and Alexithymia Among Persons With Alcohol Dependence Syndrome. Annals of Indian Psychiatry, 5(2), 104-115. https://doi.org/10.4103/aip.aip_54_21
Ghogare, A. S., Patil, P. S., & Vankar, G. K. (2022). A Case Series of Study of Childhood Psychological Trauma and Alexithymia Among Persons With Alcohol Dependence Syndrome Attending Inpatient De-Addiction Facility From Central Rural India. Annals of Indian Psychiatry, 6(2), 176-180. https://doi.org/10.4103/aip.aip_37_21
Kahya, Y., & Uluç, S. (2023). Maternal Childhood Trauma and Postpartum Well-Being in a Turkish Sample: The Path From Attachment to Alexithymia. Klinik Psikoloji Dergisi, 7(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.57127/kpd.26024438m000076x
Karaca-Dinç, P., Oktay, S., & Batıgün, A. D. (2021). Mediation Role of Alexithymia, Sensory Processing Sensitivity and Emotional-Mental Processes Between Childhood Trauma and Adult Psychopathology: A Self-Report Study. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-605863/v1
Morie, K. P., Zhai, Z. W., Potenza, M. N., & Mayes, L. C. (2020). Alexithymia, Emotion‐Regulation Strategies, and Traumatic Experiences in Prenatally Cocaine‐Exposed Young Adults. American Journal on Addictions, 29(6), 492-499. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajad.13056
Mullet, N., Hawkins, L. G., Tuliao, A. P., Snyder, H., Holyoak, D., McGuire, K. C., Earl, A. K. K., & McChargue, D. E. (2021). Early Trauma and Later Sexual Victimization in College Women: A Multiple Mediation Examination of Alexithymia, Impulsivity, and Alcohol Use. Journal of interpersonal violence, 37(19-20), NP18194-NP18214. https://doi.org/10.1177/08862605211035876
Quam, A., Biernacki, K., Ross, T. J., Salmeron, B. J., & Janes, A. C. (2024). Childhood Trauma, Emotional Awareness, and Neural Correlates of Long-Term Nicotine Smoking. JAMA Network Open, 7(1), e2351132. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.51132
Rahmati, M., Gholinezhad, H., Jafari, N., Tajik, M., & Zarchi, Z. A. (2024). The Mediating Role of Alexithymia in the Relationship Between Childhood Trauma and Internet Addiction in Adolescents: Emphasizing the Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-Pace) Model. Jarac, 6(2), 135-143. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jarac.6.2.17
Saadi, A., Chibnik, L. B., & Valera, E. M. (2022). Examining the Association Between Childhood Trauma, Brain Injury, and Neurobehavioral Symptoms Among Survivors of Intimate Partner Violence: A Cross-Sectional Analysis. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 37(1), 24-33. https://doi.org/10.1097/htr.0000000000000752
Sharma, P., Sen, M. S., Sinha, U. K., & Kumar, D. (2024). Childhood Trauma, Emotional Regulation, Alexithymia, and Psychological Symptoms Among Adolescents: A Mediational Analysis. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine. https://doi.org/10.1177/02537176241258251
Signorelli, M. S., Fusar‐Poli, L., Arcidiacono, E., Caponnetto, P., & Aguglia, E. (2020). Depression, PTSD and Alexithymia in Victims of Intimate Partner Violence: A Case-Control Study. Archives of Clinical Psychiatry (São Paulo), 47(2), 45-50. https://doi.org/10.1590/0101-60830000000230
Simeon, D., & Abugel, J. (2023). Trauma, Attachment, Emotion, and Cognition. 102-120. https://doi.org/10.1093/oso/9780197622445.003.0007
Sleeuwen, C. v., Zuiden, M. v., Koch, S. B. J., Frijling, J. L., Veltman, D. J., Olff, M., & Nawijn, L. (2023). How Does It Feel? An Exploration of Neurobiological and Clinical Correlates of Alexithymia in Trauma-Exposed Police-Officers With and Without PTSD. European Journal of Psychotraumatology, 14(2). https://doi.org/10.1080/20008066.2023.2281187
Wang, Q. (2024). Childhood Trauma and Non-Suicidal Self-Injury Among Chinese Adolescents: The Chain-Mediated Role of Alexithymia and Rumination. Psychiatry Investigation, 21(7), 726-735. https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2024.0041
Zahmatkesh, Y. Z. (2022). Prediction of Suicidal Thoughts Based on Alexithymia and Childhood Traumas of Divorced Women. PDMD, 1(2), 47-55. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.pdmd.1.2.6
Zahra, K. T., & Ahmad, M. (2025). Childhood Trauma, Alexithymia and Emotional Dysregulation in Adults With Obsessive Compulsive Disorder. Sra, 3(1), 1950-1956. https://doi.org/10.70670/sra.v3i1.504
Zdankiewicz-Ścigała, E., & Ścigała, D. (2020). Attachment Style, Early Childhood Trauma, Alexithymia, and Dissociation Among Persons Addicted to Alcohol: Structural Equation Model of Dependencies. Frontiers in psychology, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2019.02957
Zhang, C., Ge, L., Fan, Z., Tang, X., & Zhang, F. (2020). Psychological Capital Mediating the Relationship Between Childhood Trauma and Alexithymia in Chinese Medical Students: A Cross-Sectional Study. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 13, 1343-1352. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s288647
Zorzella, K. P. M., Muller, R. T., Cribbie, R. A., Bambrah, V., & Classen, C. (2020). The Role of Alexithymia in Trauma Therapy Outcomes: Examining Improvements in PTSD, Dissociation, and Interpersonal Problems. Psychological Trauma Theory Research Practice and Policy, 12(1), 20-28. https://doi.org/10.1037/tra0000433
zusta, z., & evik, A. (2024). The Relationship Between Intimate Partner Violence, Childhood Traumas, Alexithymia and Coping Styles With Stress. Annals of Medical Research, 31(4), 288. https://doi.org/10.5455/annalsmedres.2023.12.347
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Marco Conti (Author); Eszter Kovács

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.