Comparison of the Effectiveness of Relapse Prevention Therapy Based on Neurofeedback and Cognitive Rehabilitation on Clinical Symptoms in Women Using Methamphetamine
Keywords:
Neurofeedback, Cognitive Rehabilitation , Methamphetamine , PainAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to compare the effectiveness of neurofeedback-based relapse prevention and cognitive rehabilitation on pain perception and momentary craving in women with a history of methamphetamine use.
Methods and Materials: The study employed a quasi-experimental design with a pre-test, post-test, and follow-up assessment. Participants included 86 women aged 20 to 40 years with a history of methamphetamine addiction who had undergone treatment and participated in recovery support programs. They were randomly assigned to the neurofeedback group (n = 43) or the cognitive rehabilitation group (n = 43). The interventions were conducted over five weeks, with neurofeedback training focusing on sensorimotor rhythm (SMR) and alpha-theta protocols, while cognitive rehabilitation targeted executive functions such as working memory, attention, and response inhibition. The McGill Pain Questionnaire (MPQ) and the Desire for Drug Questionnaire (DDQ) were administered at baseline, post-intervention, and follow-up. Data analysis was conducted using analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) and multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA).
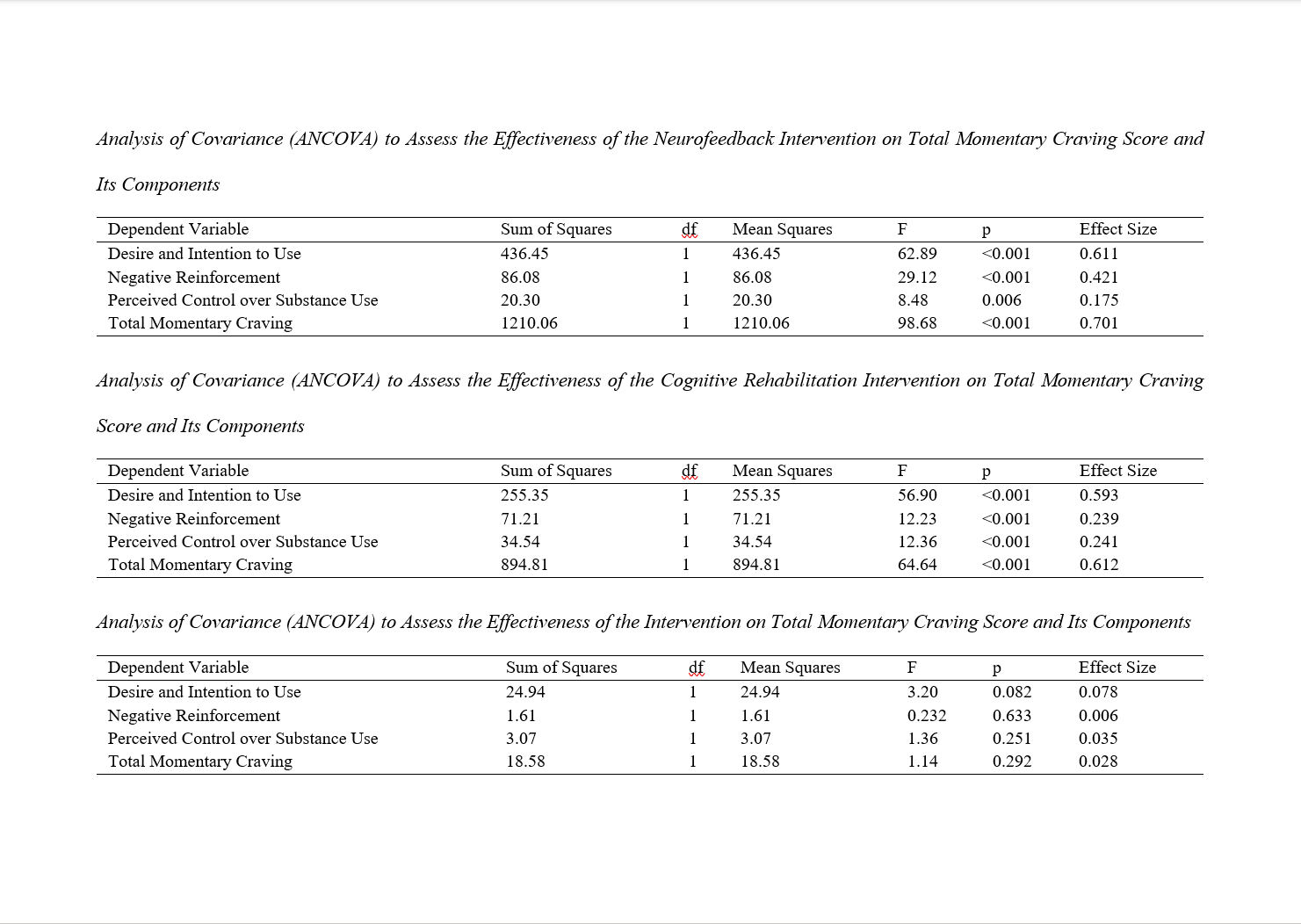
Findings: The cognitive rehabilitation intervention significantly reduced total pain scores (F = 4.57, p = 0.039, η² = 0.100) and affective perception of pain (F = 4.94, p = 0.032, η² = 0.115), whereas the neurofeedback intervention did not show significant effects on pain (p > 0.05). Both interventions significantly reduced total momentary craving (Neurofeedback: F = 98.68, p < 0.001, η² = 0.701; Cognitive Rehabilitation: F = 64.64, p < 0.001, η² = 0.612) and its components, including desire and intention to use, negative reinforcement, and perceived control over substance use (p < 0.05). There was no significant difference in treatment effects between the two interventions (p > 0.05).
Conclusion: Cognitive rehabilitation was effective in reducing pain, particularly affective pain perception, while both neurofeedback and cognitive rehabilitation significantly reduced momentary craving. These findings suggest that cognitive rehabilitation may be a more suitable intervention for pain management, while both interventions can be effective for craving reduction in individuals recovering from methamphetamine addiction.
Downloads
References
Alizadehgoradel, J., Imani, S., Nejati, V., Vanderhasselt, M. A., Molaei, B., Salehinejad, M. A., & Taherifard, M. (2021). Improved executive functions and reduced craving in youths with methamphetamine addiction: Evidence from combined transcranial direct current stimulation with mindfulness treatment. Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience, 19(4), 653. https://doi.org/10.9758/cpn.2021.19.4.653
Baher Talari, M. (2022). The effectiveness of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) in reducing emotional regulation difficulties and cravings in drug users Mohaghegh Ardabili University]. https://jrp.uma.ac.ir/article_2356.html
Barati, A., Safarzadeh Sirzar, R., Pakroyan, N., & Salehi, F. (2023). The relationship between obsession and addiction relapse with the mediation of sensation seeking in methamphetamine dependent patients. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS), 4(9), 70-78. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jayps.4.9.8
Behroozi, N., Mohammadi, F., & Omidian, M. (2018). Social Support, Metacognitive Beliefs, Mental Health and Vitality of Normal and Delinquent Adolescent Boys in Correction and Rehabilitation Centers of Ahvaz. Strategic Research on Social Problems, 7(1), 81-96. https://doi.org/10.22108/ssoss.2018.103836.1072
Cascarilla, E. A. (2009). Chronic Pain-Related Distress & Disability: An Empirical Investigation of a Modern Behavioral Theory of Acceptance of Chronic Pain University of Akron]. http://rave.ohiolink.edu/etdc/view?acc_num=akron1257472306
Castro, E., & Hill, R. W. (2002). Getting Rid of Ritalin: How Neurofeedback Can Successfully Treat Attention Deficit Disorder without Drugs. Hampton Roads. https://books.google.com/books/about/Getting_Rid_of_Ritalin.html?id=CiUBAAAACAAJ
Christie, D., Hood, D., & Griffin, A. (2006). Thinking, Feeling and Moving: Drama and Movement Therapy as an Adjunct to a Multidisciplinary Rehabilitation Approach for Chronic Pain in Two Adolescent Girls. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 11(4), 569-577. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359104506067878
DosSantos, M. F., Love, T. M., Martikainen, I. K., Nascimento, T. D., Fregni, F., Cummiford, C., Deboer, M. D., Zubieta, J. K., & DaSilva, A. F. (2012). Immediate Effects of tDCS on the μ-Opioid System of a Chronic Pain Patient [Clinical Case Study]. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2012.00093
Hine, R., Ward, B., Kippen, R., Sutton, K., Duncan, Z., Quinn, B., Powell, A., & Dietze, P. (2023). Prevalence and correlates of panic attacks among people who primarily smoke methamphetamine. International journal of mental health and addiction, 1-19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-023-01042-w
Luikinga, S. J., Kim, J. H., & Perry, C. J. (2018). Developmental perspectives on methamphetamine abuse: exploring adolescent vulnerabilities on brain and behavior. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 87(Pt A), 78-84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pnpbp.2017.11.010
Melzack, R. (2017). The McGill Pain Questionnaire. Pain, 1(3), 277-299. https://doi.org/10.1016/0304-3959(75)90044-5
Nooripour, R., Hosseinian, S., Afrouz, G. A., & Bakhshani, N.-M. (2018). Effectiveness of Neurofeedback on Executive Functions and Tendency Toward High-Risk Behaviors in Adolescents With Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. International Journal High Risk Behaviors & Addiction, 7(4). https://doi.org/10.5812/ijhrba.82012
Nooripour, R., Sikström, S., Ghanbari, N., Hosseinian, S., Hassani-Abharian, P., & Ilanloo, H. (2021). Neurofeedback rehabilitation reduces anxiety in methamphetamine abusers. NeuroRegulation, 8(3), 128-128. https://www.neuroregulation.org/article/view/21599
Pourasghar, M., Raisi, M., & Kord, M. (2022). Comparing the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy of the matrix model with and without hypnosis on the anxiety and depression of methamphetamine-dependent patients. Journal of new developments in psychology, educational sciences and education, 5(49), 310-319.
Pourjaberi, B., Shirkavand, N., & Ashoori, J. (2023). The Effectiveness of Cognitive Rehabilitation Training on Prospective Memory and Cognitive Flexibility in Individuals with Depression. International Journal of Education and Cognitive Sciences, 4(3), 45-53. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.ijecs.4.3.5
Roshandel, Z., Ghaffari, A., Kazemi, R., & Nadermohammadi, M. (2022). Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment based Therapy on Pain Severity, Fatigue, and Alexithymia in Female Patients with Rheumatic Diseases. Applied Family Therapy Journal (AFTJ), 3(5), 84-100. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.aftj.3.5.6
Safikhani, F. (2022). The effectiveness of grammatical mental imagery with cognitive processing on self-efficacy, emotional processing and spirituality in mothers of students with autism spectrum disorder. International Journal of Education and Cognitive Sciences, 3(2), 12-22. https://doi.org/10.22034/injoeas.2022.160609
Shojaei, B. (2024). Reducing Symptoms of Attention Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) in Elementary Students: The Effectiveness of Neurofeedback. Annals of medicine and surgery, 86(5), 2651-2656. https://doi.org/10.1097/ms9.0000000000001861
Siefried, K. J., Acheson, L. S., Lintzeris, N., & Ezard, N. (2020). Pharmacological Treatment of Methamphetamine/Amphetamine Dependence: A Systematic Review. CNS Drugs, 34(4), 337-365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40263-020-00711-x
Simons, J. S., Dvorak, R. D., & Batien, B. D. (2018). Methamphetamine use in a rural college population: Associations with marijuana use, sensitivity to punishment, and sensitivity to reward. Psychology of Addictive Behaviors, 22(3), 444. https://doi.org/10.1037/0893-164X.22.3.444
Stellern, J., Xiao, K. B., Grennell, E., Sanches, M., Gowin, J. L., & Sloan, M. E. (2023). Emotion regulation in substance use disorders: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Addiction, 118(1), 30-47. https://doi.org/10.1111/add.16001
Sunder, K., & Bohnen, J. L. (2017). The Progression of Neurofeedback: An Evolving Paradigm in Addiction Treatment and Relapse Prevention. Moj Addiction Medicine & Therapy, 3(3). https://doi.org/10.15406/mojamt.2017.03.00037
Turan, Ç., Ünal, S., Şenormancı, G., & Şenormancı, Ö. (2023). Posttraumatic Growth in Family Members of Individuals With Methamphetamine Use Disorder. The European Research Journal, 9(5), 984-991. https://doi.org/10.18621/eurj.1276458
Wu, C., Wu, D., Fang, Y., & Song, H. (2024). Efficacy of Integrated Neurofeedback and Virtual Reality Training in Children with ADHD: A Randomized Controlled Trial. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/379892579_Efficacy_of_Integrated_Neurofeedback_and_Virtual_Reality_Training_in_Children_with_ADHD_A_Randomized_Controlled_Trial
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Bahareh Zeif'dini (Author); Fatemeh Mohammadi Shirmahale (Corresponding Author); Arezo Tari moradi, Mohammadreza Belyad (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.