Examining the Role of Family and Social Environment in Social Media Use Among Youth
Keywords:
social media, family, social support, attachment youth, systematic reviewAbstract
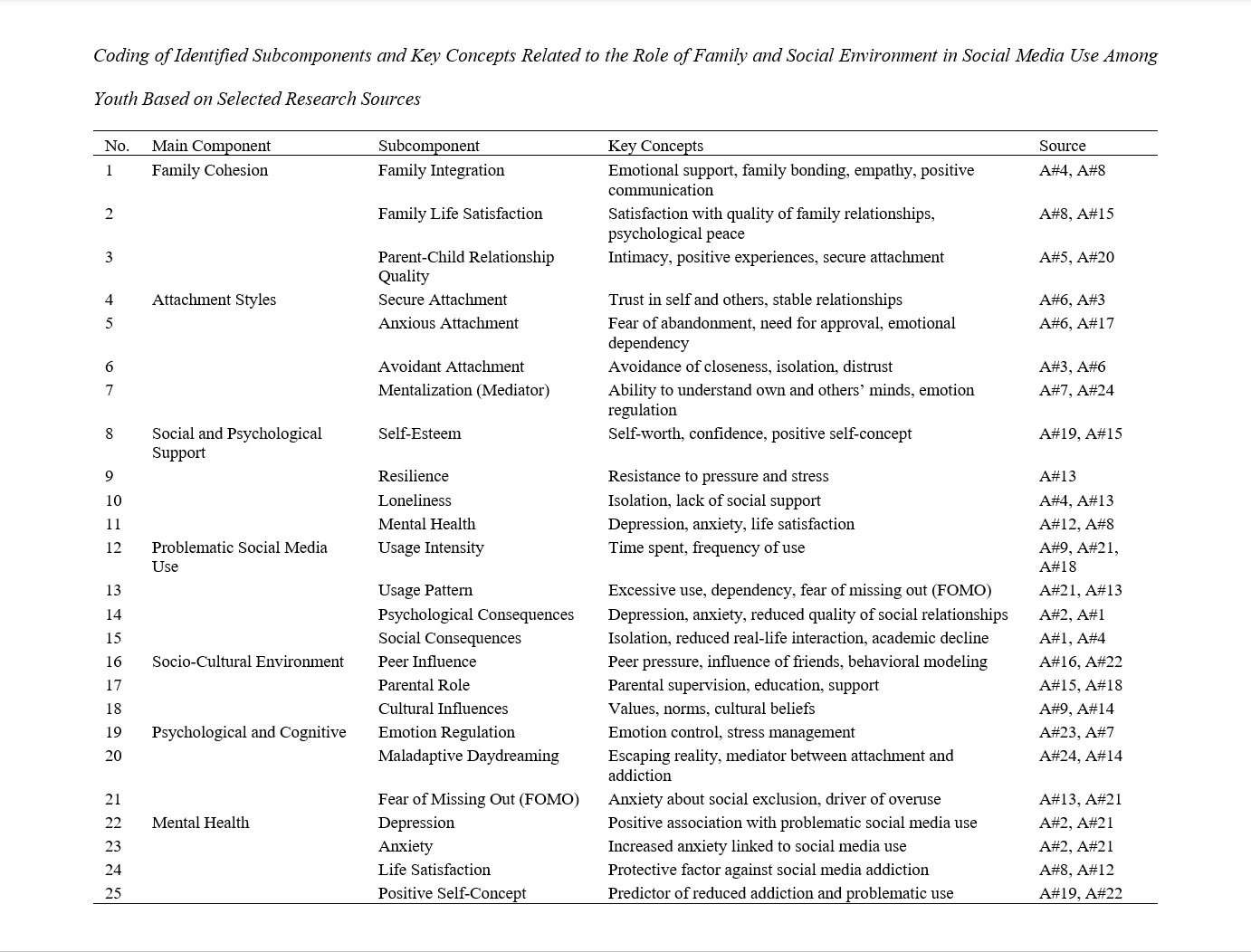
Given the increasing use of social media among youth and the resulting psychological, social, and cognitive consequences, this study aimed to identify and analyze the familial and social components associated with social media use in this age group. This research was conducted using a systematic review approach by analyzing 25 scholarly articles published between 2012 and 2024. The selected articles were extracted from reputable academic databases including PubMed, Scopus, ScienceDirect, and Google Scholar. The article selection process was carried out based on predefined inclusion and exclusion criteria. Data were systematically extracted using qualitative content analysis, and a coding table was developed accordingly. The results indicated that factors such as family cohesion, satisfaction with family relationships, attachment styles, social support, self-esteem, resilience, peer pressure, emotion regulation, fear of missing out (FoMO), and cognitive characteristics significantly influence excessive or problematic social media use. Moreover, the mediating role of psychological variables such as mentalization and mental health in the relationship between family and social environment with youths' online behavior was emphasized. Based on the findings of this study, designing preventive and promotive interventions centered on family education, strengthening emotion regulation skills, and enhancing resilience can help reduce the harms associated with maladaptive social media use among youth.
Downloads
References
Amin, S., Haroon Rashidi, H., & Kazemian Moghaddam, K. (2022). Investigating the Relationship between Parenting Styles and Family Communication Patterns with Addiction to Virtual Networks: The Mediating Role of Social Competence. Cultural-Educational Journal of Women and Family, 17(58), 133-157. https://cwfs.ihu.ac.ir/article_207166.html
Aref, A., & Kashani, M. (2022). The Impact of Social Networks (Cyberspace) on the Social Vitality of Teachers in Tehran in 2020. Strategic Communication Studies, 2(1), 87-100. https://rcc.soore.ac.ir/article_253276_7e03a2ee2d735f40bb9af2c18ec9cd72.pdf
Arıkan, G., Acar, I. H., & Üstündağ-Budak, A. M. (2022). A two-generation study: The trans- mission of attachment and young adults' de- pression, anxiety, and social media addiction. Addictive behaviors, 124, 107109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.107109
Austermann, M. I., Thomasius, R., & Paschke, K. (2021). Assessing problematic social me- dia use in adolescents by parental ratings: De- velopment and validation of the social media disorder Scale for parents (SMDS-P). Journal of clinical medicine, 10(4), 617. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10040617
Avari, N., Alaei, Z., & Attar Toosi, S. M. (2022). A Comparative Study of Self-Efficacy and Social Acceptance in Mothers of Hyperactive Children with Marital Satisfaction. New Advances in Psychology, Educational Sciences and Education, 5(48), 44-55. https://jonapte.ir/fa/showart-
Bayraktar, M., & Çelik, S. B. (2023). Relationship between attachment styles, social media addiction, and contingencies of self-worth. Bağımlılık Dergisi, 24(3), 294-304. https://doi.org/10.51982/bagimli.1163299
Bilgin, M., Şahin, İ., & Togay, A. (2020). Social media addiction in adolescents and parentadolescent relationship. Education & Science, 45(202), 263-281. https://doi.org/10.15390/EB.2020.8202
Blackwell, D., Leaman, C., Tramposch, R., & Osborne, M. (2017). Extraversion, neuroticism, attachment style and fear of missing out as predictors of social media use and addiction. Personality and individual differences, 116, 69-72. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2017.04.039
Boursier, V., Gioia, F., & Griffiths, M. D. (2020). Do selfie-expectancies and social appearance anxiety predict adolescents' problematic social media use? Computers in human Behavior, 110, 106395. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106395
Brand, M., Young, K. S., Laier, C., Wölfling, K., & Potenza, M. N. (2016). Integrating psychological and neurobiological considerations regarding the development and maintenance of specific Internet-use disorders: An Interaction of Person-Affect-Cognition-Execution (I-PACE) model. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 71, 252-266. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2016.08.033
Chen, A. (2019). From attachment to addiction: The mediating role of need satisfaction on social networking sites. Computers in human Behavior, 98, 80-92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2019.03.034
Cheng, C., Lau, Y. C., Chan, L., & Luk, J. W. (2021). Prevalence of social media addiction across 32 nations: Meta-analysis with subgroup analysis of classification schemes and cultural values. Addictive behaviors, 117, 106845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2021.106845
Conway, C. A., Falconier, M. K., & Kim, J. (2024). The relationships among parents' anxious and avoidant attachment, emotion dysregulation, and parenting. Contemporary Family Therapy, 46(3), 294-311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10591-023-09681-w
Costanzo, A., Santoro, G., Russo, S., Cassarà, M. S., Midolo, L. R., Billieux, J., & Schimmenti, A. (2021). Attached to virtual dreams: The mediating role of maladaptive daydreaming in the relationship between attachment styles and problematic social media use. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 209(9), 656-664. https://doi.org/10.1097/NMD.0000000000001356
D'Arienzo, M. C., Boursier, V., & Griffiths, M. D. (2019). Addiction to social media and attachment styles: a systematic literature review. International journal of mental health and addiction, 17, 1094-1118. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-019-00082-5
Ehtemam, H., Taghipour, F., & Korang Beheshti, S. (2024). Strategies for Using Social Networks to Enhance Vitality in the Family. Strategic Studies of Culture Quarterly, 4(4), 87-124. https://scsj.ricac.ac.ir/article_207846.html
Ercengiz, M., & Bayraktar, M. (2025). Social media use disorder in adolescents: Relationship to attachment styles and family harmony. An approach based on structural equation modeling. Československá Psychologie, 69(2), 96-117. https://doi.org/10.51561/cspsych.69.2.96
Fabris, M. A., Marengo, D., Longobardi, C., & Settanni, M. (2020). Investigating the links between fear of missing out, social media addiction, and emotional symptoms in adolescence: The role of stress associated with neglect and negative reactions on social media. Addictive behaviors, 106, 106364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2020.106364
Gökçearslan, Ş., Yildiz Durak, H., Berikan, B., & Saritepeci, M. (2021). Smartphone addic- tion, loneliness, narcissistic personality, and family belonging among university students: A path analysis. Social Science Quarterly, 102(4), 1743-1760. https://doi.org/10.1111/ssqu.12949
Li, Y., Wang, X., Lin, X., & Hajli, M. (2018). Seeking and sharing health information on social media: A net valence model and crosscultural comparison. Technological Forecast- ing and Social Change, 126, 28-40. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.techfore.2016.07.021
Liu, X., Huang, J., Yu, N. X., Li, Q., & Zhu, T. (2020). Mediation effect of suicide-related social media use behaviors on the associa- tion between suicidal ideation and suicide attempt: Cross-sectional questionnaire study. Journal of medical Internet research, 22(4), e14940. https://doi.org/10.2196/14940
Livingstone, S., Nandi, A., Banaji, S., & Stoilo- va, M. (2017). Young adolescents and digital media: uses, risks and opportunities in lowand middle-income countries: a rapid evidence review. Gage. https://eprints.lse.ac.uk/83753
Mohammadi, M., & Dimehkar Haghighi, F. (2024). Out-of-Rule Behaviors of Students in the Education System - A Meta-Synthesis Model of Theorizing. Applied Sociology, 35(4), 121-158. https://jas.ui.ac.ir/article_29027_en.html
Monacis, L., De Palo, V., Griffiths, M. D., & Sinatra, M. (2017). Social networking addiction, attachment style, and validation 114 / Výzkumné studie of the Italian version of the Bergen social media addiction scale. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 6(2), 178-186. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.6.2017.023
O'Reilly, M., Dogra, N., Hughes, J., Reilly, P., George, R., & Whiteman, N. (2019). Potential of social media in promoting mental health in adolescents. Health Promotion International, 34(5), 981-991. https://doi.org/10.1093/heapro/day056
Pezoa-Jares, R. E., Espinoza-Luna, I. L., & Vasquez-Medina, J. A. (2012). Internet addiction: a review. J. Addict. Res. Therapy, 6(004). https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6105.s6-004
Pontes, H. M., Kuss, D. J., & Griffiths, M. D. (2015). Clinical psychology of Internetaddic-tion: a review of its conceptualization, preva- lence, neuronal processes, and implications for treatment. Neurosci. Neuroecon, 4, 11-23. https://doi.org/10.2147/NAN.S60982
Pourrezaei, S., & Naderi, M. (2016). The Role of Virtual Networks and the Internet as One of the Social Harms in Families and Its Role as a Harm Among Adolescents and Youth.
Raeisi, S. M., Ansari, H., & Mousaei, M. (2021). Investigating the Impact of Virtual Social Networks on Family Member Interactions. National Security, 11(41), 339-370. https://ns.sndu.ac.ir/article_1593.html
Rom, E., & Alfasi, Y. (2014). The role of adult attachment style in online social network affect, cognition, and behavior. Journal of Psychology, 1(1), 24-34. https://doi.org/10.12974/2313-1047.2014.01.01.3
Ruhl, H., Dolan, E. A., & Buhrmester, D. (2015). Adolescent attachment trajectories with mothers and fathers: The importance of parent-child relationship experiences and gender. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 25(3), 427-442. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12144
Salehi, E., Fallahchai, R., & Griffiths, M. (2023). Online addictions among adolescents and young adults in Iran: The role of attachment styles and gender. Social Science Computer Review, 41(2), 554-572. https://doi.org/10.1177/08944393221111242
Salehi, M. (2024). A Systematic Review of Studies on Child and Adolescent Suicide in Iran between 2006-2023. Iranian Journal of Social Problems, 15(3), 163-218. https://doi.org/10.61186/jspi.15.3.163
Santoro, G., Costanzo, A., Franceschini, C., Lenzo, V., Musetti, A., & Schimmenti, A. (2024). Insecure minds through the looking glass: the mediating role of mentalization in the relationships between adult attachment styles and problematic social media use. International journal of environmental research and public health, 21(3), 255. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph21030255
Sattar, S., Younas, F., & Tariq, S. (2025). FAMILY ENVIRONMENT AND SOCIAL NETWORKING USAGE IN EMERGING ADULTS: A COMPREHENSIVE STUDY. https://www.researchgate.net/profile/Faiz-Younas/publication/388743080_FAMILY_ENVIRONMENT_AND_SOCIAL_NETWORKING_USAGE_IN_EMERGING_ADULTS_A_COMPREHENSIVE_STUDY/links/67a47c09645ef274a4714bf4/FAMILY-ENVIRONMENT-AND-SOCIAL-NETWORKING-USAGE-IN-EMERGING-ADULTS-A-COMPREHENSIVE-STUDY.pdf
Savci, M., Akat, M., Ercengiz, M., Griffiths, M. D., & Aysan, F. (2020). Problematic social media use and social connectedness in adolescence: The mediating and moderating role of family life satisfaction. International journal of mental health and addiction, 1-17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11469-020-00410-0
Savci, M., & Aysan, F. (2017). Technological addictions and social connectedness: predic- tor effect of internet addiction, social media addiction, digital game addiction and smart- phone addiction on social connectedness. Dusunen Adam: Journal of Psychiatry & Neu- rological Sciences, 30(3), 202-216. https://doi.org/10.5350/dajpn2017300304
Sawyer, S. M., Azzopardi, P. S., Wickremarathne, D., & Patton, G. C. (2018). The age of adolescence. The Lancet Child & Ado- lescent Health, 2(3), 223-228. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2352-4642(18)30022-1
Shannon, H., Bush, K., Villeneuve, P. J., Hel- lemans, K. G., & Guimond, S. (2022). Prob- lematic social media use in adolescents and young adults: systematic review and metaanalysis. Mental Health, 9(4), e33450. https://doi.org/10.2196/33450
Spada, M. M. (2014). An overview of problematic internet use. Addict. Behav, 39, 3-6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.addbeh.2013.09.007
Tadpatrikar, A., Sharma, M. K., & Viswanath, S. S. (2021). Influence of technology usage on family communication patterns and functioning: A systematic review. Asian Journal of Psychiatry, 58, 102595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajp.2021.102595
Taibi, D., Scifo, L., Bruno, N., & Fulantelli, G. (2023). Social Media Literacy to Support a Conscious Use of Social Media in Adolescents and Improve Their Psychological WellBeing: A Pilot Study. Sustainability, 15(17), 12726. https://doi.org/10.3390/su151712726
Tariq, A., Muñoz Sáez, D., & Khan, S. R. (2022). Social media use and family connectedness: A systematic review of quantitative literature. New Media & Society, 24(3), 815-832. https://doi.org/10.1177/14614448211016885
Van Den Eijnden, R., Koning, I., Doornwaard, S., Van Gurp, F., & Ter Bogt, T. (2018). The impact of heavy and disordered use of games and social media on adolescents' psychological, social, and school functioning. Journal of Behavioral Addictions, 7(3), 697-706. https://doi.org/10.1556/2006.7.2018.65
Vannucci, A., Simpson, E. G., Gagnon, S., & Ohannessian, C. M. (2020). Social media use and risky behaviors in adolescents: A meta-analysis. Journal of adolescence, 79, 258-274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adoles- cence.2020.01.014
Wang, P., Wang, X., Wu, Y., Xie, X., Wang, X., Zhao, F., Ouyang, M., & Lei, L. (2018). So- cial networking sites addiction and adolescent depression: A moderated mediation model of rumination and self-esteem. Personality and individual differences, 127, 162-167. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.paid.2018.02.008
Wang, S., Bi, Y., & Qi, X. (2024). Harmony at home, everything goes well: the cross-domain influence mechanism of family harmony on employees' innovative behaviour in China. Asia Pacific Business Review, 1-24. https://doi.org/10.1080/13602381.2024.2319597
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Esmaeil Hamzeh (Corresponding Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







