Identifying Key Psychological Predictors of Mind–Body Health Discrepancy
Keywords:
Mind–body discrepancy, emotional dysregulation, cognitive appraisal, health perceptionAbstract
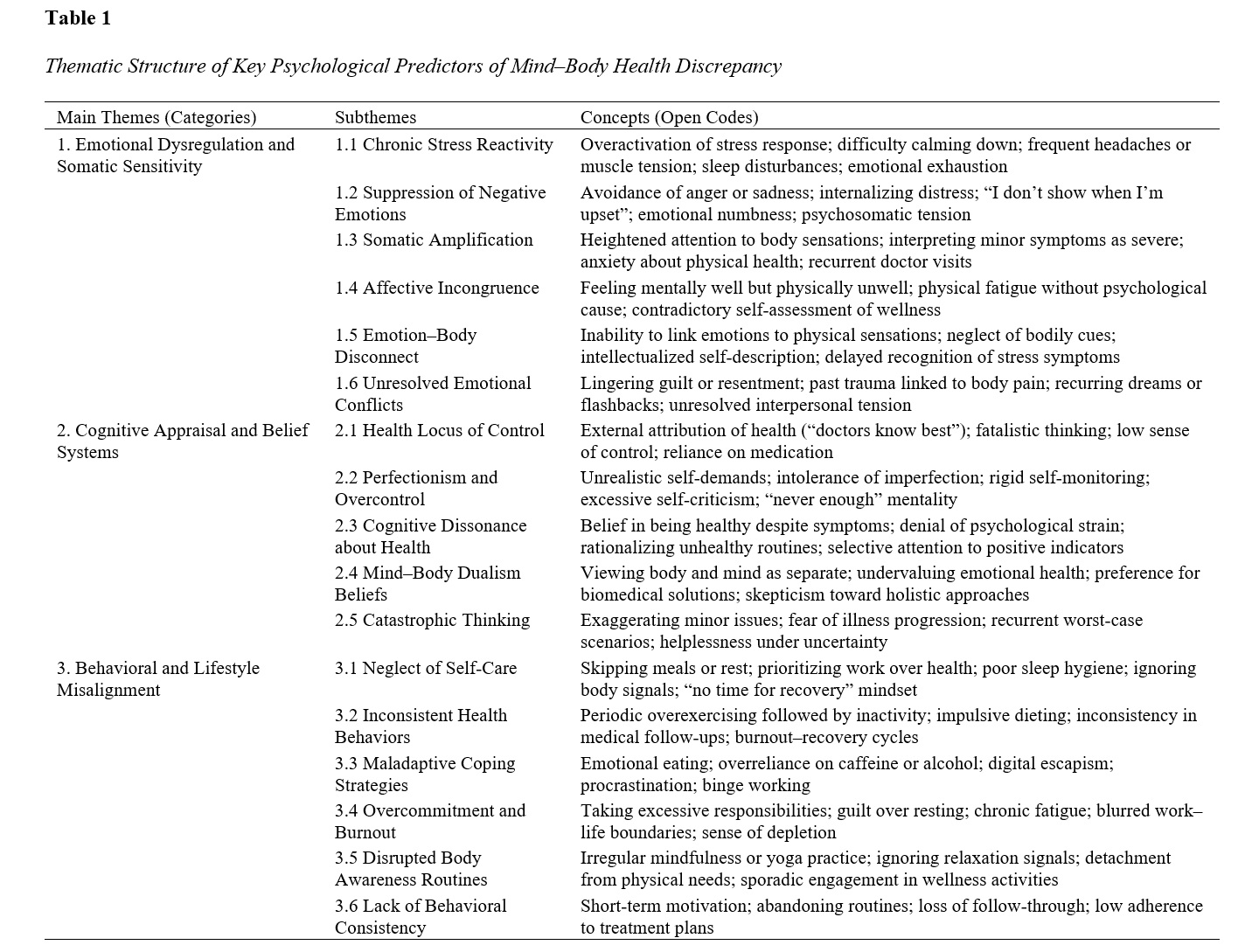
This study aimed to identify the key psychological predictors that contribute to discrepancies between perceived mental well-being and physical health among adults in Singapore. A qualitative research design with an interpretive phenomenological approach was adopted to explore the psychological mechanisms underlying mind–body health incongruence. A total of 21 adult participants (12 females, 9 males; aged 26–54 years) were recruited through purposeful sampling based on self-reported differences between their psychological and physical health experiences. Data were collected through semi-structured, in-depth interviews lasting 60–90 minutes and analyzed using Braun and Clarke’s thematic analysis framework with the aid of NVivo 14 software. Theoretical saturation was achieved after the 21st interview. Rigor was ensured through member checking, audit trails, and peer debriefing. The analysis revealed four major psychological domains explaining the mind–body health discrepancy: (1) Emotional dysregulation and somatic sensitivity, reflecting the translation of unprocessed emotions into bodily symptoms; (2) Cognitive appraisal and belief systems, indicating that maladaptive health beliefs, perfectionism, and mind–body dualism contribute to misaligned health perceptions; (3) Behavioral and lifestyle misalignment, showing inconsistent self-care and maladaptive coping strategies that sustain perceptual dissonance; and (4) Interpersonal and sociocultural determinants, encompassing social expectations, family communication patterns, and cultural norms that reinforce emotional suppression and health misperception. Collectively, these themes suggest that subjective health perception is shaped more by cognitive–emotional regulation and social context than by biological status. The study underscores that mind–body health discrepancy arises from the convergence of emotional, cognitive, behavioral, and sociocultural factors. Enhancing emotional regulation, cognitive flexibility, and social support systems may reduce such incongruence and promote holistic well-being. These findings provide a conceptual foundation for integrative psychological and medical interventions.
Downloads
References
Aizlewood, E. G., Jones, F. W., & Whatmough, R. (2023). Paediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease and Parental Mental Health: Prevalence and Predictors. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry, 28(3), 1024-1037. https://doi.org/10.1177/13591045231164866
Ampuero-Tello, N. L., Zegarra-López, A., Padilla-López, D. A., & Venturo-Pimentel, D. S. (2022). Academic Self-Efficacy as a Protective Factor for the Mental Health of University Students During the COVID-19 Pandemic. Interacciones Revista De Avances en Psicología, e289. https://doi.org/10.24016/2022.v8.289
Bazen, L., Bree, E. d., Boer, M. v. d., & Jong, P. F. d. (2022). Perceived Negative Consequences of Dyslexia: The Influence of Person and Environmental Factors. Annals of Dyslexia, 73(2), 214-234. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11881-022-00274-0
Benavides, A. M., Finn, J. A., Tang, X., Ropacki, S., Brown, R., Smith, A. N., Stevens, L. F., Rabinowitz, A. R., Juengst, S. B., Johnson‐Greene, D., & Hart, T. (2021). Psychosocial and Functional Predictors of Depression and Anxiety Symptoms in Veterans and Service Members With TBI: A VA TBI Model Systems Study. Journal of Head Trauma Rehabilitation, 36(6), 397-407. https://doi.org/10.1097/htr.0000000000000647
Bérard, A., Gorgui, J., Tchuente, V., Lacasse, A., Gomez, Y.-H., Côté, S. M., King, S., Muanda, F. T., Mufike, Y., Boucoiran, I., Nuyt, A. M., Quach, C., Ferreira, E., Kaul, P., Winquist, B., O'Donnell, K., Eltonsy, S., Château, D., Zhao, J. P., . . . Zaphiratos, V. (2022). The COVID-19 Pandemic Impacted Maternal Mental Health Differently Depending on Pregnancy Status and Trimester of Gestation. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1167874/v1
Biermann, M., Vonderlin, R., Mier, D., Witthöft, M., & Bailer, J. (2021). Predictors of Psychological Distress and Coronavirus Fears in the First Recovery Phase of the Coronavirus Disease 2019 Pandemic in Germany. Frontiers in psychology, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2021.678860
Fjermestad, K. W., Norum, F. Ø., Brask, H. S., Kodal, A., Silverman, W. K., Heiervang, E., & Wergeland, G. J. (2024). Anxiety Symptom Trajectories Predict Depression Symptom Trajectories Up to Four Years After CBT for Youth Anxiety Disorders. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 52(10), 1503-1513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-024-01214-9
García‐Rudolph, A., Cegarra, B., Opisso, E., Tormos, J. M., & Saurí, J. (2021). Relationships Between Functionality, Depression, and Anxiety With Community Integration and Quality of Life in Chronic Traumatic Spinal Cord Injury. American Journal of Physical Medicine & Rehabilitation, 100(9), 840-850. https://doi.org/10.1097/phm.0000000000001773
Lee, J., Jung, H. Y., Lee, S. I., Youn, H., & Kim, S. G. (2021). Smartphone Addiction Proneness Is Associated With Subjective-Objective Sleep Discrepancy in Patients With Insomnia Disorder. Psychiatry Investigation, 18(11), 1035-1043. https://doi.org/10.30773/pi.2020.0360
Lee, J., Wilson, J. M., Oosterhoff, B., & Shook, N. J. (2024). Self-Quarantining, Social Distancing, and Mental Health During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Multi Wave, Longitudinal Investigation. PLoS One, 19(2), e0298461. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0298461
Luiz Antônio Alves de, M.-J., Moura, S. S. d., Machado-Coelho, G. L. L., & Meireles, A. L. (2024). How Anxiety and Depression Mediate the Link Between Sleep Quality and Health Perception During Crisis Periods. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-4606216/v1
McBride, N. L., Bates, G., Elphinstone, B., & Whitehead, R. (2022). Self‐compassion and Social Anxiety: The Mediating Effect of Emotion Regulation Strategies and the Influence of Depressed Mood. Psychology and Psychotherapy Theory Research and Practice, 95(4), 1036-1055. https://doi.org/10.1111/papt.12417
Méndez-López, F., Olivan‐Blázquez, B., García, M. D., Hoyo, Y. L. d., Tamayo‐Morales, O., & Magallón-Botaya, R. (2023). Depressive and Anxious Symptoms Increase With Problematic Technologies Use Among Adults: The Effects of Personal Factors Related to Health Behavior. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 16, 2499-2515. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s412013
Salimi, H., Griffiths, M. D., & Alimoradi, Z. (2023). Prevalence of Anxiety and Depression Among Pregnant Women With Diabetes and Their Predictors in Qazvin Province, Iran. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3302118/v1
Schlechter, P., Hellmann, J. H., & Morina, N. (2022). Self-Discrepancy, Depression, Anxiety, and Psychological Well-Being: The Role of Affective Style and Self-Efficacy. Cognitive therapy and research, 46(6), 1075-1086. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-022-10314-z
Sun, S., Yu-ping, H., Qian, J., Wang, F., Sun, Y.-P., & Yu, X. (2022). Incidence and Predictors of Paternal Anxiety and Depression Following Fetal Abnormalities Requiring Pregnancy Termination: A Cross-Sectional Study in China. BMC Pregnancy and Childbirth, 22(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12884-022-04739-3
Tafolla, M., & Lord, C. (2024). Longitudinal Analyses of Mental Health in Autistic Individuals: A Systematic Review. Brain Sciences, 14(10), 1033. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci14101033
Thapa, A., Kang, J., Chung, M. L., Wu, J.-R., Biddle, M., Cha, G., & Moser, D. K. (2025). Self-Care, Perceived Social Support, and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients With Heart Failure. Nursing research, 74(4), 258-265. https://doi.org/10.1097/nnr.0000000000000820
Thomas, G., Riegler, K. E., Bradson, M. L., O’Shea, D. U., & Arnett, P. A. (2022). Subjective Report, Objective Neurocognitive Performance, and “Invisible Symptoms” in Multiple Sclerosis. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 38(2), 169-181. https://doi.org/10.1093/arclin/acac086
Thomas, T., & Johnco, C. (2025). Biased Perceptions of Physiological Arousal in Social Anxiety: Understanding the Role of Objective and Subjective Physiological Arousal in the Discrepancy Between Self and Observer Perceptions of Social Performance. Cognitive therapy and research, 49(4), 824-834. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10608-025-10583-4
Toci, G. R., Lambrechts, M. J., Karamian, B. A., Mao, J. Z., Heinle, J., Bhatt, S., Harlamova, D., Canseco, J. A., Kaye, I. D., Woods, B. I., Hilibrand, A. S., Kepler, C. K., Vaccaro, A. R., & Schroeder, G. D. (2022). Depression Increases Posterior Cervical Decompression and Fusion Revision Rates and Diminishes Neck Disability Index Improvement. Spine, 47(18), 1287-1294. https://doi.org/10.1097/brs.0000000000004371
Visser, L., Pat‐El, R., Lataster, J., Lankveld, J. v., & Jacobs, N. (2024). Beyond Difference Scores: Unlocking Insights With Polynomial Regression in Studies on the Effects of Implicit-Explicit Congruency. Psychologica Belgica, 64(1), 5-23. https://doi.org/10.5334/pb.1246
Zad, Z. N., Bakhshayesh, A., & Abarghoui, M. S. (2022). The Role of Personality Traits and Lifestyle in Predicting Anxiety and Depression During the Covid-19 Pandemic: A Web-Based Cross-Sectional Study. Journal of Guilan University of Medical Sciences, 31(2), 84-101. https://doi.org/10.32598/jgums.31.2.1883.1
Виноградова, В. В., Ķīvīte‐Urtāne, A., Vrubļevska, J., & Rancāns, E. (2022). Anxiety Screening Among the General Population of Latvia and Associated Factors. Medicina, 58(9), 1163. https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina58091163