Emotion Suppression and Aggressive Behavior: Frustration Tolerance as a Mediator in Young Adults
Keywords:
Emotion suppression, Frustration tolerance, Aggressive behaviorAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the mediating role of frustration tolerance in the relationship between emotion suppression and aggressive behavior among young adults.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational research design was employed with a sample of 400 young adults aged 18–30 from Georgia, selected based on the Morgan and Krejcie sample size table. Participants completed standardized self-report instruments: the Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (Suppression Subscale), the Frustration Discomfort Scale, and the Buss–Perry Aggression Questionnaire. Data were analyzed using SPSS-27 for descriptive and Pearson correlation analyses, and AMOS-21 for structural equation modeling (SEM). Assumptions for normality, linearity, and multicollinearity were confirmed prior to model testing.
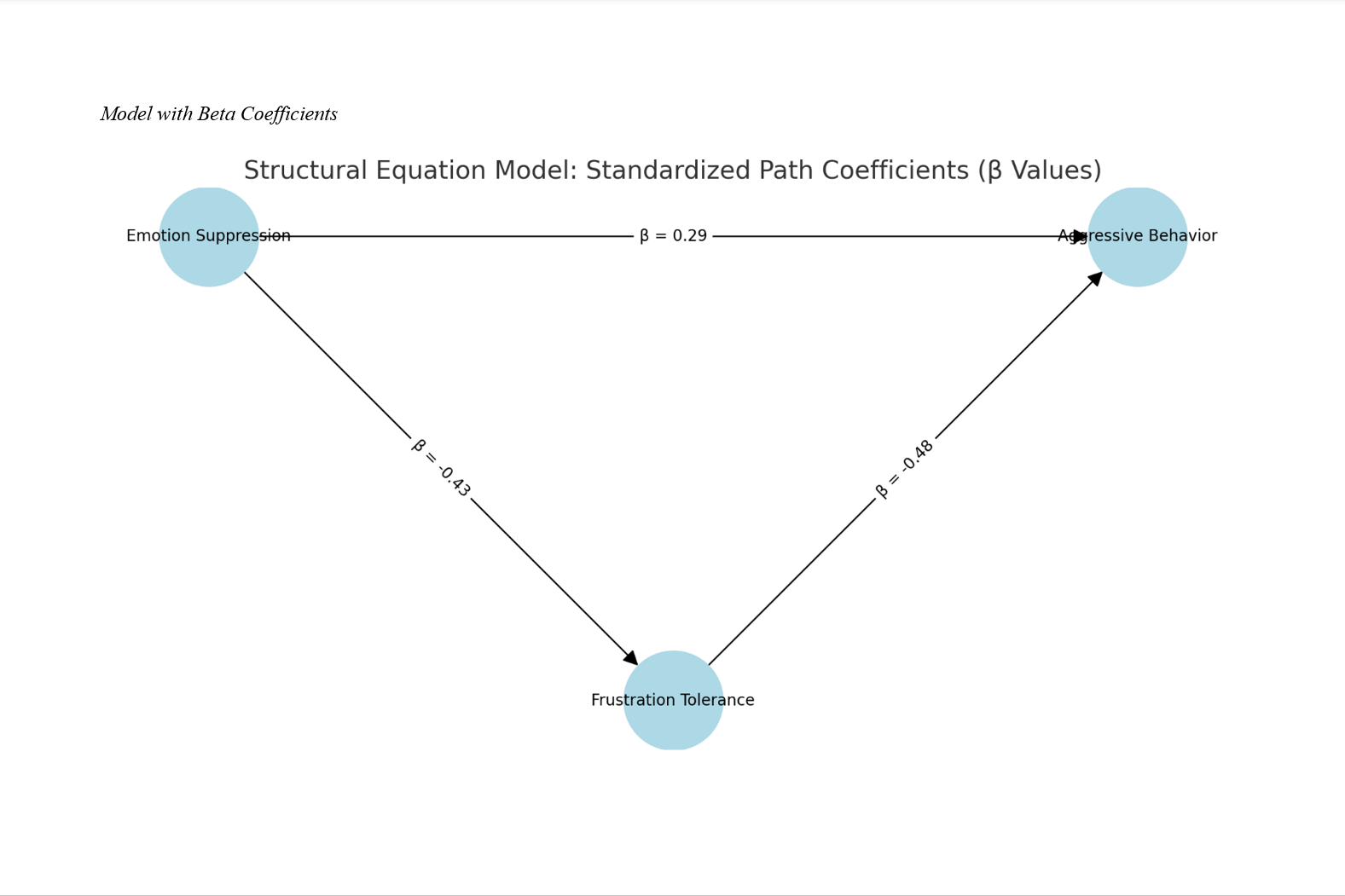
Findings: Emotion suppression was significantly and negatively correlated with frustration tolerance (r = −.43, p < .001) and positively correlated with aggressive behavior (r = .48, p < .001). Frustration tolerance was also negatively correlated with aggressive behavior (r = −.52, p < .001). SEM results indicated good model fit (χ²/df = 2.22; CFI = 0.96; RMSEA = 0.056). Emotion suppression had a significant direct effect on aggression (β = 0.29, p < .001), as well as an indirect effect via frustration tolerance (β = 0.21, p < .001), confirming partial mediation. The total effect of emotion suppression on aggressive behavior was strong (β = 0.50, p < .001).
Conclusion: The findings suggest that frustration tolerance partially mediates the relationship between emotion suppression and aggressive behavior in young adults. Individuals who suppress their emotions tend to exhibit lower frustration tolerance, which increases their likelihood of aggressive responses. Interventions aimed at enhancing emotional expression and frustration management may reduce aggression in this population.
Downloads
References
Abdullah, M. T., Al-Zorfi, F., Jassim, H., & Al-Ibrahimi, M. (2020). Assessment of Aggression Among High Schools Students. Indian Journal of Forensic Medicine & Toxicology. https://doi.org/10.37506/ijfmt.v14i3.10540
Batic, D. (2022). Aggressive Behaviour Among Convicts in the Prisons in Macedonia. 189-199. https://doi.org/10.20544/icp.3.6.22.p19
Bertsch, K., Back, S. N., Flechsenhar, A., Neukel, C., Krauch, M., Spieß, K., Panizza, A., & Herpertz, S. C. (2021). Don't Make Me Angry: Frustration-Induced Anger and Its Link to Aggression in Women With Borderline Personality Disorder. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.695062
Breuer, J., Scharkow, M., & Quandt, T. (2015). Sore Losers? A Reexamination of the Frustration–aggression Hypothesis for Colocated Video Game Play. Psychology of Popular Media Culture, 4(2), 126-137. https://doi.org/10.1037/ppm0000020
Cornejo-Babida, P. L. (2020). Aggressive Behavior and Suicidal Ideation of Adolescents With High and Low Level of Frustration Intolerance. Ajehd, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.69566/ajehd.v1i1.17
DiBlasi, T., Keenan, K., Pisano, C., Tumbarello, G., Engel, V., Vincent, B., & Loiacono, A. (2024). Examining Cognitions in an Anger Episode With and Without Physical Aggression. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-5060203/v1
Gurtovaya, M. I. (2020). Studying of an Aggressive Component in Interaction of Teenagers. Scientific Notes of v I Vernadsky Crimean Federal University Sociology Pedagogy Psychology, 6(72)(3), 77-85. https://doi.org/10.37279/2413-1709-2020-6-3-77-85
Ivanov, V. I., & Perevozkina, Y. M. (2022). Approaches to Understanding Frustration. Smalta(4), 32-43. https://doi.org/10.15293/2312-1580.2204.04
Kwon, M., & Lee, J. S. (2025). Influence of Negative Parenting Behavior Perceived by School-Aged Children on Aggression: Mediating Effects of Basic Psychological Needs Frustration. Soc Cognitive Enhancement Intervention, 16(1), 69-83. https://doi.org/10.21197/jcei.16.1.4
Ling, K. C., Ling, C. P., Wang, Z., Hung, K. K., & Leong, L. H. (2017). The Impacts of Reactive Aggression and Friendship Quality on Cyberbullying Behaviour. International Journal of Cyber Behavior Psychology and Learning, 7(2), 49-71. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijcbpl.2017040105
Nordman, J., & Adcock, J. (2022). Addressing Low Frustration Tolerance in Students With Learning Disabilities. Intervention in School and Clinic, 59(2), 133-137. https://doi.org/10.1177/10534512221140490
Nugroho, W., & Reza, I. F. (2022). Frustration as a Forming Factor of Aggressive Behavior in Moslem Adolescents in Playing Online Games. Indonesian Journal of Multidisciplinary Sciences (Ijoms), 1(1), 50-66. https://doi.org/10.59066/ijoms.v1i1.50
Popa, E. (2024). Research Results on the Impact of Reintegration Programs on the Behavioral Dimensions of Prisoners. 89-96. https://doi.org/10.54481/pcss2023.09
Rijlaarsdam, J., Tiemeier, H., Ringoot, A. P., Ivanova, M. Y., Jaddoe, V. W. V., Verhulst, F. C., & Roza, S. J. (2015). Early Family Regularity Protects Against Later Disruptive Behavior. European Child & Adolescent Psychiatry, 25(7), 781-789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00787-015-0797-y
Rodriguez, J. A. P. (2020). Psychological Actions to Increase Tolerance to Frustration in Pitchers: Category 15-16 Years. International journal of health sciences. https://doi.org/10.29332/ijhs.v4n1.377
Sriwahyuningsih, V., Yusuf, A. M., & Daharnis, D. (2016). Hubungan Prasangka Dan Frustrasi Dengan Perilaku Agresif Remaja. Jppi (Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Indonesia), 2(2), 38-51. https://doi.org/10.29210/02016146
Sugian, A. A., Fatimah, S., & Pahlevi, R. (2021). Gambaran Perilaku Agresif Ditinjau Dari Perspektif Usia Dan Tingkat Kelas Bagi Peserta Didik SMK. Fokus (Kajian Bimbingan & Konseling Dalam Pendidikan), 4(5), 392. https://doi.org/10.22460/fokus.v4i5.7486
Toxanbayeva, N., Tokhtarov, A., Naubaeva, K., Orazbekova, D., & Altaeva, G. (2024). The Study of the Influence of Internal and External Frustration on the Psychological Self-Defense of a Person. The Journal of Psychology and Sociology, 89(2), 51-60. https://doi.org/10.26577/jpss.2024.v89.i2.05
Zeigler‐Hill, V., & Shackelford, T. K. (2020). Emotional Suppression. 1342-1342. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-24612-3_300808
Zhang, M., Jiang, Z., Zhao, K., Zhang, Y. H., Xu, M., & Xu, X. (2023). Effects of Polygenes, Parent–child Relationship and Frustration on Junior High School Students' Aggressive Behaviors. PsyCh Journal. https://doi.org/10.1002/pchj.717
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














