Moral Disengagement and Aggression: The Mediating Role of Empathy Deficits
Keywords:
Aggression, Moral Disengagement, Empathy DeficitsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to investigate the mediating role of empathy deficits in the relationship between moral disengagement and aggression among young adults.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational design was employed, involving 399 participants from Taiwan, selected based on the Morgan and Krejcie sample size table. Participants completed validated self-report measures: the Aggression Questionnaire (AQ), the Moral Disengagement Scale (MDS), and the Basic Empathy Scale (BES). Pearson correlation analysis was conducted using SPSS-27 to examine bivariate relationships among the variables, and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was employed via AMOS-21 to test the hypothesized mediation model. Model fit indices and standardized path coefficients were calculated to assess the strength and validity of the relationships.
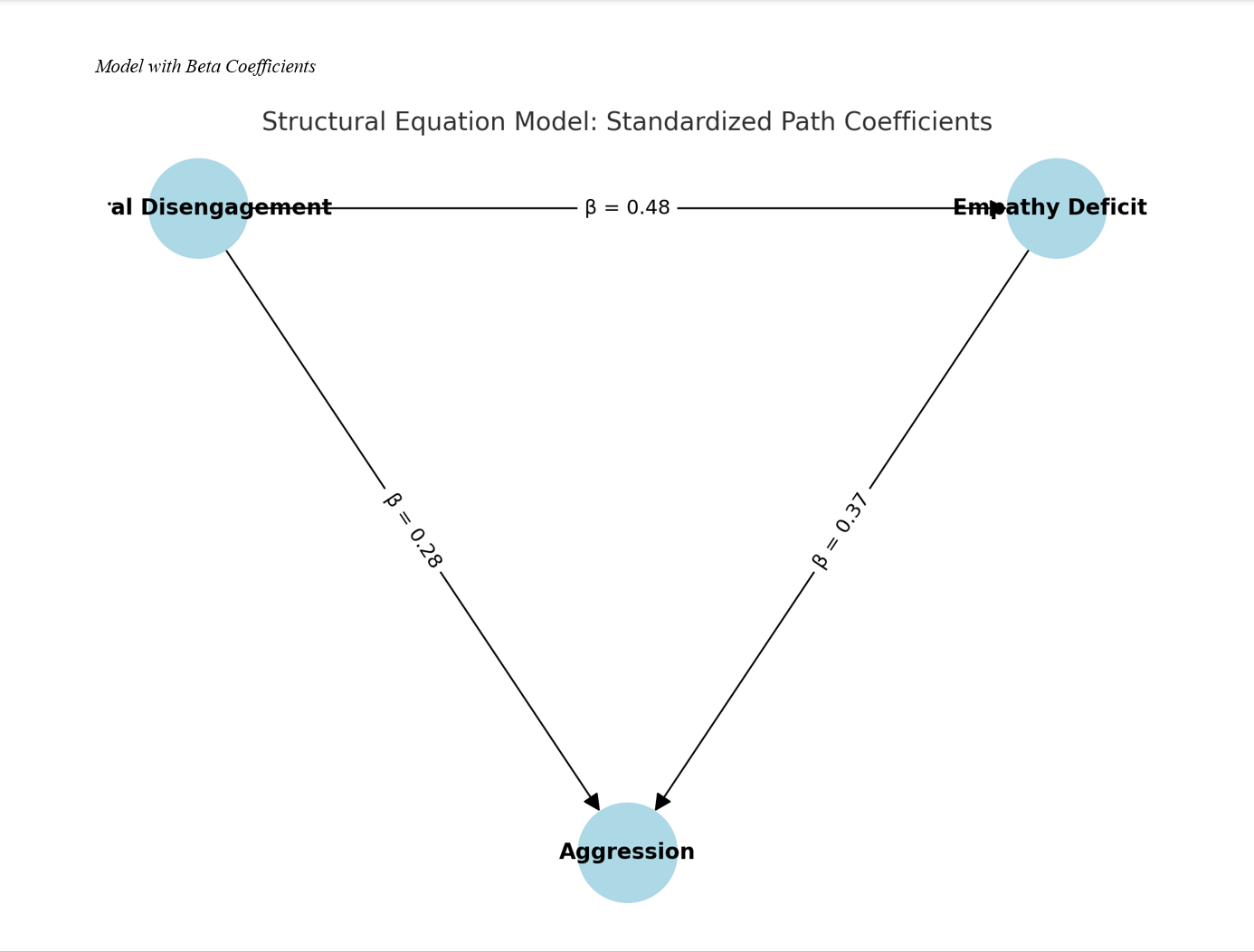
Findings: Results revealed that moral disengagement was positively correlated with aggression (r = .48, p < .001) and empathy deficits (r = .59, p < .001), while empathy deficits also correlated significantly with aggression (r = .55, p < .001). The SEM analysis confirmed that the model had acceptable fit indices (χ²/df = 2.06; CFI = .96; RMSEA = .052). Moral disengagement had a significant direct effect on aggression (β = .28, p < .001), as well as an indirect effect through empathy deficits (β = .18, p < .001), resulting in a total effect of β = .46 (p < .001). Empathy deficits also directly predicted aggression (β = .37, p < .001).
Conclusion: The findings support a mediational model in which empathy deficits partially explain the relationship between moral disengagement and aggression. These results highlight the cognitive and emotional mechanisms underlying aggressive behavior and underscore the importance of targeting both moral reasoning and empathic responsiveness in intervention efforts.
Downloads
References
Anselmo, A., Lucifora, C., Rusconi, P., Martino, G., Craparo, G., Salehinejad, M. A., & Vicario, C. M. (2022). Can We Rewire Criminal Mind via Non-Invasive Brain Stimulation of Prefrontal Cortex? Insights From Clinical, Forensic and Social Cognition Studies. Current Psychology, 42(24), 20765-20775. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12144-022-03210-y
Atadjikova, Y. A., & Ениколопов, С. Н. (2019). Some Concerns About Antisocial Behavior in Children and Adolescents: Psychopathy and Callous-Unemotional Traits. Journal of Modern Foreign Psychology, 8(3), 16-28. https://doi.org/10.17759/jmfp.2019080302
Bosch, R., Chakhssi, F., & Hummelen, K. (2020). Inpatient Aggression in Forensic Psychiatric Patients With Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Role of Risk and Protective Factors. Journal of Intellectual Disabilities and Offending Behaviour, 11(2), 93-100. https://doi.org/10.1108/jidob-05-2019-0008
Čekić, E. (2025). Redefining Evil: An Interdisciplinary Perspective on Psychological Traits and Societal Perceptions. International journal of psychology, 10(1), 72-108. https://doi.org/10.47604/ijp.3222
Claro, R., Vieira, J. B., Terburg, D., & Klaus, J. (2025). Parsing the Role of Basolateral and Central Amygdala Nuclei on Facial Emotion Recognition in Psychopathy: A Systematic Review. https://doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/m38qr_v1
Couette, M., Mouchabac, S., Bourla, A., Nuss, P., & Ferreri, F. (2019). Social Cognition in Post‐traumatic Stress Disorder: A Systematic Review. British Journal of Clinical Psychology, 59(2), 117-138. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjc.12238
Cristofani, C., Sesso, G., Cristofani, P., Fantozzi, P., Inguaggiato, E., Muratori, P., Narzisi, A., Pfanner, C., Pisano, S., Polidori, L., Ruglioni, L., Valente, E., Masi, G., & Milone, A. (2020). The Role of Executive Functions in the Development of Empathy and Its Association With Externalizing Behaviors in Children With Neurodevelopmental Disorders and Other Psychiatric Comorbidities. Brain Sciences, 10(8), 489. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci10080489
Derish, F. V. (2021). The Dark Tetrad of Personality: Review of Recent Research. Вестник Пермского Университета Философия Психология Социология(2), 222-235. https://doi.org/10.17072/2078-7898/2021-2-222-235
Frick, P. J., & Kemp, E. C. (2021). Conduct Disorders and Empathy Development. Annual Review of Clinical Psychology, 17(1), 391-416. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-clinpsy-081219-105809
Galán, C. A., & Mazefsky, C. A. (2022). Autism Spectrum Disorder Versus Conduct Problems. 86-C85.P81. https://doi.org/10.1093/med-psych/9780197516881.003.0005
Godfrey, D. A., Kehoe, C. M., Bastardas-Albero, A., & Babcock, J. C. (2020). Empathy Mediates the Relations Between Working Memory and Perpetration of Intimate Partner Violence and Aggression. Behavioral Sciences, 10(3), 63. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs10030063
Gong, M., Yao, L., Ge, X., Liu, Z., Zhang, C., Yang, Y., Amdanee, N., Wang, C., & Zhang, X. (2023). Empathy Deficit in Male Patients With Schizophrenia and Its Relationships With Impulsivity and Premeditated Violence. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1160357
Hernández, E. D. N. (2025). Escala De Comportamiento Asertivo Entre Pares. Know and Share Psychology, 6(1), 52-70. https://doi.org/10.25115/kasp.v6i1.9770
Heym, N., Firth, J., Kibowski, F., Sumich, A., Egan, V., & Bloxsom, C. (2019). Empathy at the Heart of Darkness: Empathy Deficits That Bind the Dark Triad and Those That Mediate Indirect Relational Aggression. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2019.00095
Kimonis, E. R., & Prasad, A. H. (2020). Callous and Unemotional Traits in Childhood. 1-12. https://doi.org/10.1002/9781119171492.wecad163
Mg, Y., Reddy, K. J., & Bennet, C. N. (2025). Social Intelligence Deficits and Aggression in Children in Conflict With the Law: A Comparative Study With Typically Developing Adolescents. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-6161190/v1
Neo, B., Fleming, G. E., Kaouar, S., Chan, M. E., Huang, N. N., Hawes, D. J., Eapen, V., Briggs, N., & Kimonis, E. R. (2023). Clinical Utility of Diagnosing Limited Prosocial Emotions in Young Children Using the Clinical Assessment of Prosocial Emotions (CAPE). Psychological assessment, 35(12), 1085-1097. https://doi.org/10.1037/pas0001279
Tyler, P. M., White, S. F., Thompson, R. W., & Blair, J. (2018). Applying a Cognitive Neuroscience Perspective to Disruptive Behavior Disorders: Implications for Schools. Developmental Neuropsychology, 44(1), 17-42. https://doi.org/10.1080/87565641.2017.1334782
Waller, R., & Hyde, L. W. (2018). Callous-Unemotional Behaviors in Early Childhood: The Development of Empathy and Prosociality Gone Awry. Current opinion in psychology, 20, 11-16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2017.07.037
Wardani, N. D., Widiastuti, M. I., Sudiyanto, A., Hardian, H., Lukman, P. R., Subagio, H. W., & Tugasworo, D. (2023). Clinical Practice Supportive Psychotherapy for Borderline Personality Disorder. Bali Medical Journal, 12(3), 2435-2439. https://doi.org/10.15562/bmj.v12i3.4614
Дучимінська, Т., & Mahdysiuk, L. (2022). Features of Aggressive Behavior in Preschool Children: Psychodiagnostics and Correction. Psychological studies(1), 15-19. https://doi.org/10.32782/psych.studies/2022.1.3
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














