Comparison of the Effectiveness of Brain Gym and Educational Games on the Improvement of Social Skills in 8-10 Year-Old Students
Keywords:
Brain Gym, educational games, social skills, studentsAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to compare the effectiveness of Brain Gym and educational games on improving the social skills of 8-10 year-old students with a two-month follow-up study.
Methods and Materials: The present study was a quasi-experimental research with a pre-test, post-test, and two-month follow-up design, including a control group and two experimental groups. The research population consisted of all 8-10 year-old female students in Ahvaz, among whom 120 were selected as the research sample. Nine students were excluded from the study due to irregular attendance at the educational sessions. In this study, the Matson Social Skills Questionnaire was used to assess social skills at three time points: before the intervention, after the intervention, and during the two-month follow-up. The Brain Gym group underwent 20 sessions, with sessions held twice a week for 20 minutes each. The educational games group participated in an 8-week program, with sessions held twice a week for 30-45 minutes each. The control group did not receive any intervention.
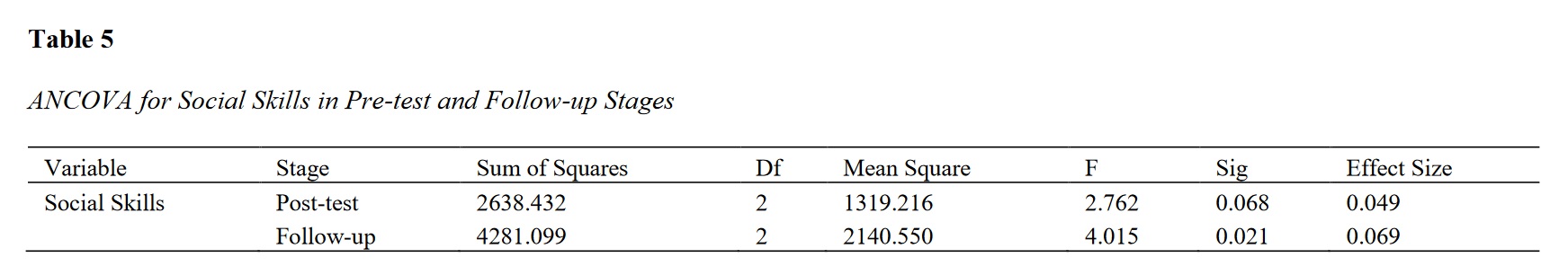
Findings: The results of the Bonferroni post-hoc test showed no significant difference between the effects of Brain Gym and educational games on improving the social skills of 8-10 year-old students (p > 0.05). However, there was a significant difference between the post-test scores and the pre-test scores for each intervention (p < 0.01).
Conclusion: Overall, the results of this study indicate that interventions involving Brain Gym and educational games can be beneficial methods for improving the social skills of elementary school students.
Downloads
References
Andi, P., Dharma, K. K., Purwanto, E., Firdaus, R., & Loriana, R. (2019). The intervention of Brain Gym in increasing the quality of life on The elderly. Asian Community Health Nursing Research, 1(1), 30-35. https://doi.org/10.29253/achnr.2019.12812
Baniasadi, T. (2024). The Effects of a School-based Intervention on the Social and Adaptive Skills among Children with ADHD. Iranian Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 3(1), 1-9. https://maherpub.com/jndd/article/view/45
Battistella, P., & Wangenheim, C. G. (2016). Games for Teaching Computing in Higher Education - A Systematic Review. IEEE Technology and Engineering Education (ITEE) Journal, 9(1), 8-30. http://www.gqs.ufsc.br/files/2020/02/ITEE-Games-for-Teaching-Computing-in-Higher-Education_Vdraft.pdf
Dennison, P. (2010). Brain Gym Teacher's Edition The Companion Guide to Brain Gym: Simple Activities for Whole-Brain Learning. Edu-Kinestetics, Inc. https://www.amazon.com/Brain-Gym-Teachers-Paul-Dennison/dp/0942143027
Domitrovich, C. E., Durlak, J. A., Staley, K. C., & Weissberg, R. P. (2017). Social emotional competence: An essential factor for promoting positive adjustment and reducing risk in school children. Child development, 88(2), 408-416. https://doi.org/10.1111/cdev.12739
Effendy, E., Prasanty, N., & Utami, N. (2019). The effects of brain gym on quality of sleep, anxiety in elderly at nursing home care case Medan. Open Access Macedonian Journal of Medical Sciences, 7, 2595-2598. https://doi.org/10.3889/oamjms.2019.397
Factor, R., Rea, H., Dahiya, A., & Albright, J. (2021). An Initial Pilot Study Examining Child Social Skills, Caregiver Styles, and Family Functioning in the PEERS for Program for Young Autistic Children and their Categivers. Research in Developmental Disabilities, 121(2), 41-52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ridd.2021.104152
Grosse, S. J. (2013). Brain gym in the pool. International Journal of Aquatic Research and Education, 7(1), 72-80. https://doi.org/10.25035/ijare.07.01.07
Hu, B. Y., Li, Y., Wang, C., Wu, H., & Vitiello, G. (2021). Preschool teachers' self-efficacy, classroom process quality, and children's social skills: For kindergarten and first grade students at risk for emotional and behavioral disorders. Journal of School Psychology, 86, 78-99. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/348169895_Preschool_teachers'_self-efficacy_classroom_process_quality_and_children's_social_skills_A_multilevel_mediation_analysis
Karna, W., & Stefaniuk, I. (2024). The Influence of Peer Relationships on the Social Development of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder. Iranian Journal of Neurodevelopmental Disorders, 2(4), 10-18. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.jndd.2.4.2
Kulkarni, C., & Khandale, S. R. (2019). Effect of brain gym exercises on the attention span in young adults. International Journal for Advance Research and Development, 4(4), 71-75. https://www.ijarnd.com/manuscripts/v4i4/V4I4-1159.pdf
Kumari, P., Deepa, S., & Vijayalakshmi, B. (2024). Effect of brain gym and web-based cognitive training intervention on visual attention span and working memory in children with dyslexia. Journal of Research Administration, 6(1).
Masten, A. S., Desjardines, C. D., McCormick, C. M., Kuo, S. I., & Long, J. D. (2010). The significance of childhood competence and problems for adult success in work: A developmental cascade analysis. Development and Psychopathology, 22(3), 679-694. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0954579410000362
Najdi, S., & Sheikh, R. E. (2012). Educational games: Do they make a difference. Procedia - Social and Behavioral Sciences, 47, 48-51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbspro.2012.06.612
Ningrum, A. P., Huda, A., & Praherdhiono, H. (2018). Brain Gym Video Model for Improving the Beginning Writing Abilities of the Autistic Students. Journal of Icsar, 2(2), 175-179. https://doi.org/10.17977/um005v2i22018p175
Sajedi, F., & Barati, H. (2014). The effect of perceptual motor training on motor skills of preschool children. Iranian Rehabilitation Journal, 12(1), 14-17. https://www.sid.ir/fa/Journal/ViewPaper.aspx?ID=577788
Scharfstein, L. A., Beidel, D., Smis, V. K., & Finnell, L. (2011). Social skills deficits and vocal characteristics of children with social phobia or Asperger disorder: A comparative study. Journal of abnormal child psychology, 39, 865-875. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-011-9498-2
Witzel, B., & Mize, M. (2018). Meeting the needs of students with dyslexia and dyscalculia. Journal of Srate, 1(27), 31-39. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/EJ1166703.pdf
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Bahareh Rostaminejad (Author); Negar Arazeshi (Corresponding Author); Keyvan Molanorouzi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














