Using Artificial Chatbots as Academic Counselors; When Chatgpt Becomes an Academic Counselor (A Case Study of Chatgpt)
Keywords:
academic counsultation, case study, artificial intelligence, ChatGPTAbstract
Objective: This research aimed to investigate the use of artificial intelligence chatbots, particularly ChatGPT, as academic counselors.
Methods and Materials: A qualitative case study design was employed, involving 10 unstructured interview sessions with ChatGPT across three iterative rounds of analysis. Comparative coding with a deductive approach was used to analyze ChatGPT’s responses to academic counseling scenarios.
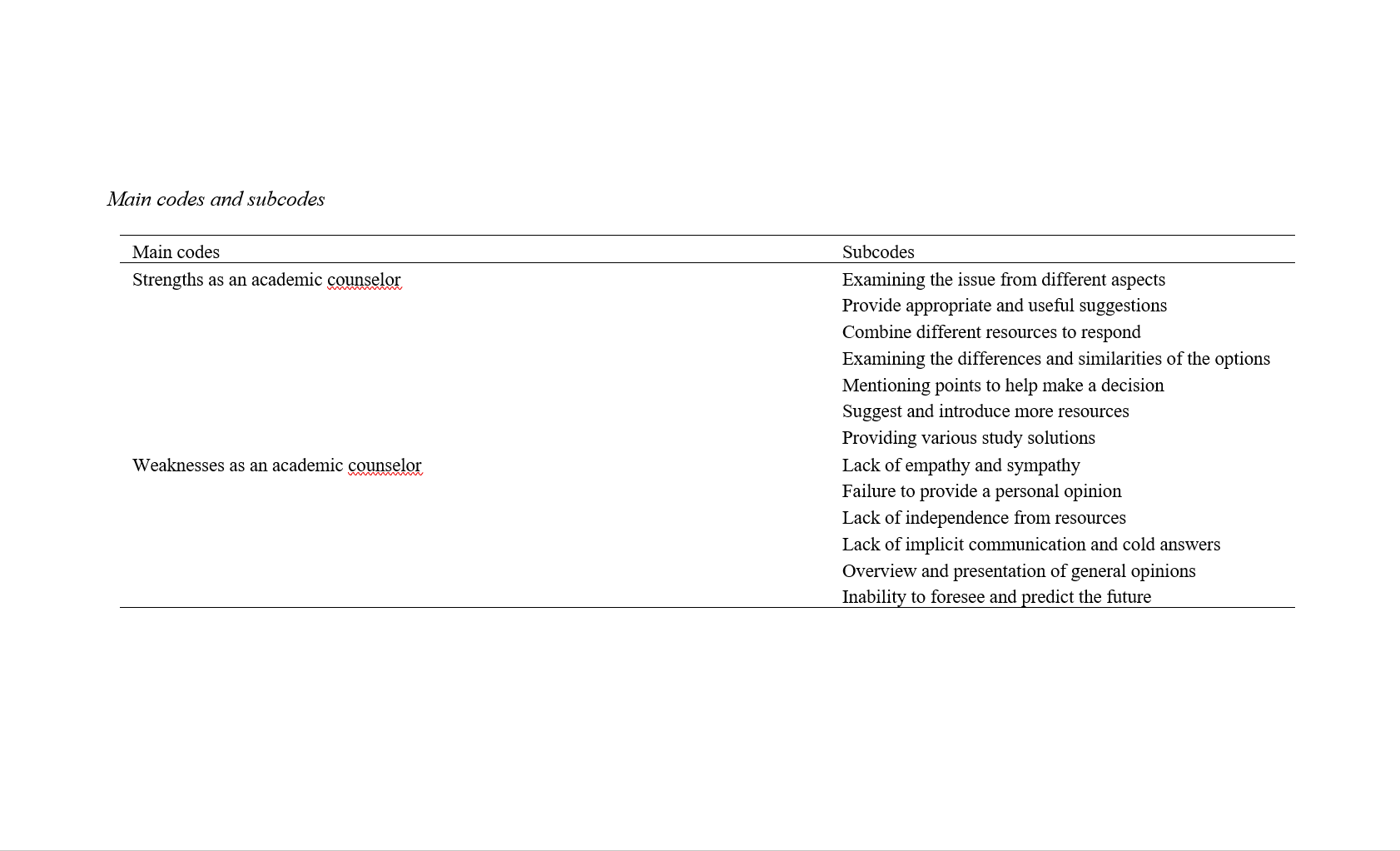
Findings: The findings revealed thirteen subthemes organized under two main themes: strengths and weaknesses. Strengths included providing multifaceted perspectives, suggesting resources, and generating effective study strategies, while weaknesses included a lack of empathy, personal opinion, and foresight.
Conclusion: Although ChatGPT cannot replace professional counselors, results suggest it may function as a semi-professional academic counselor capable of delivering effective guidance in logical, non-emotional contexts. Validity was ensured by comparing ChatGPT’s responses with other AI chatbots, namely Perplexity, Gemini, and Copilot, and ensuring consistency across coding iterations.
Downloads
References
Caratiquit, K., & Caratiquit, J. (2023). ChatGPT as an academic support tool on the academic performance among students: The mediating role of learning motivation. Journal of Social, Humanity, and Education (JSHE), 4(1), 21-23. https://doi.org/10.35912/jshe.v4i1.1558
Firat, M. (2023). What ChatGPT means for universities: Perceptions of scholars and students. Journal of Applied Learning & Teaching, 6(1), 57-63. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.22
Fitria, T. N. (2023). Artificial intelligence (AI) technology in OpenAI ChatGPT application: A review of ChatGPT in writing English essay. ELT Forum: Journal of English Language Teaching, 12(1), 44-58. https://doi.org/10.15294/elt.v12i1.64069
Fuchs, K. (2023). Exploring the opportunities and challenges of NLP models in higher education: is ChatGPT a blessing or a curse? Frontiers in Education, 8, 1-4. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2023.1166682
Inaba, M., Ukiyo, M., & Takamizo, K. (2024). Can Large Language Models be Used to Provide Psychological Counselling? An Analysis of GPT-4-Generated Responses Using Role-play Dialogues. IWSDS 2024,
Kim, H., & Park, J. (2025). AI-driven academic advising: Comparing GPT models with human counselors. Journal of Educational Technology and Research, 15(2), 85-103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jetr.2025.02.004
Liu, C., Zhang, J., & Wang, M. (2023). The Application of ChatGPT-based AI Technology in the Field of Campus Psychological Counseling. Transactions on Social Science, Education, and Humanities Research, 3, 113-120. https://doi.org/10.62051/8a831a77
Liu, J. M., Li, D., Cao, H., Ren, T., Liao, Z., & Wu, J. (2023). ChatCounselor: A Large Language Model for Mental Health Support. PGAI CIKM,
Majjate, H., Bellarhmouch, Y., Jeghal, A., Yahyaouy, A., Tairi, H., & Zidani, K. H. (2023). AI-Powered Academic Guidance and Counseling System Based on Student Profile and Interests. Applied System Innovation, 7(1), 6. https://doi.org/10.3390/asi7010006
Moell, B. (2024). Comparing the Efficacy of GPT-4 and Chat-GPT in Mental Health Care: A Blind Assessment of Large Language Models for Psychological Support. Subject: Artificial Intelligence (cs.AI); Human-Computer Interaction (cs.HC),
Nguyen, L. T. (2025). Emotional limitations of large language models in educational counseling contexts. Computers & Education: Artificial Intelligence, 9(1), 112-127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2025.01.008
OpenAi. (2023). GPT-4 technical report. abs/2303.08774. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2303.08774
Raile, P. (2023). The usefulness of ChatGPT for psychotherapists and patients. Humanities and Social Sciences Communications, 11(47). https://doi.org/10.1057/s41599-023-02567-0
Rudolph, J., Tan, S., & Sh. (2023). ChatGPT: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? Journal of Applied Learning & Teaching, 6(1), 263-342. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.9
Singh Gill, S. e. a. (2023). Transformative effects of ChatGPT on modern education: Emerging Era of AI Chatbots. Internet of Things and Cyber-Physical Systems, 4, 19-23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iotcps.2023.06.002
Tlili, A., Shehata, B., Adarkwah, M., Bozkurt, A., Hickey, D., Huang, R., & Agywmang, B. (2023). What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT is a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learning Environments, 10(15). https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-023-00237-x
Yong, N., & Cao, Y. (2025). Exploring ChatGPT's capabilities, stability, potential and risks in conducting psychological counseling through simulations in school counseling. Mental Health and Digital Technologies, 2(3), 213-239. https://doi.org/10.1108/MHDT-02-2025-0013