Parental Smartphone Addiction and Child Behavioral Problems: The Mediating Role of Parenting Quality
Keywords:
Parental smartphone addiction, Parenting quality, Child behavioral problemsAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the direct and indirect effects of parental smartphone addiction on child behavioral problems, with parenting quality as a mediating variable.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational design was employed with a sample of 410 parents from Malaysia, determined according to the Morgan and Krejcie sample size table. Participants were recruited through schools and community centers and completed standardized measures assessing smartphone addiction, parenting quality, and child behavioral problems. Data were analyzed using SPSS-27 for descriptive statistics and Pearson correlations, and AMOS-21 for structural equation modeling (SEM). Model fit indices, including χ²/df, GFI, AGFI, CFI, TLI, and RMSEA, were used to assess model adequacy.
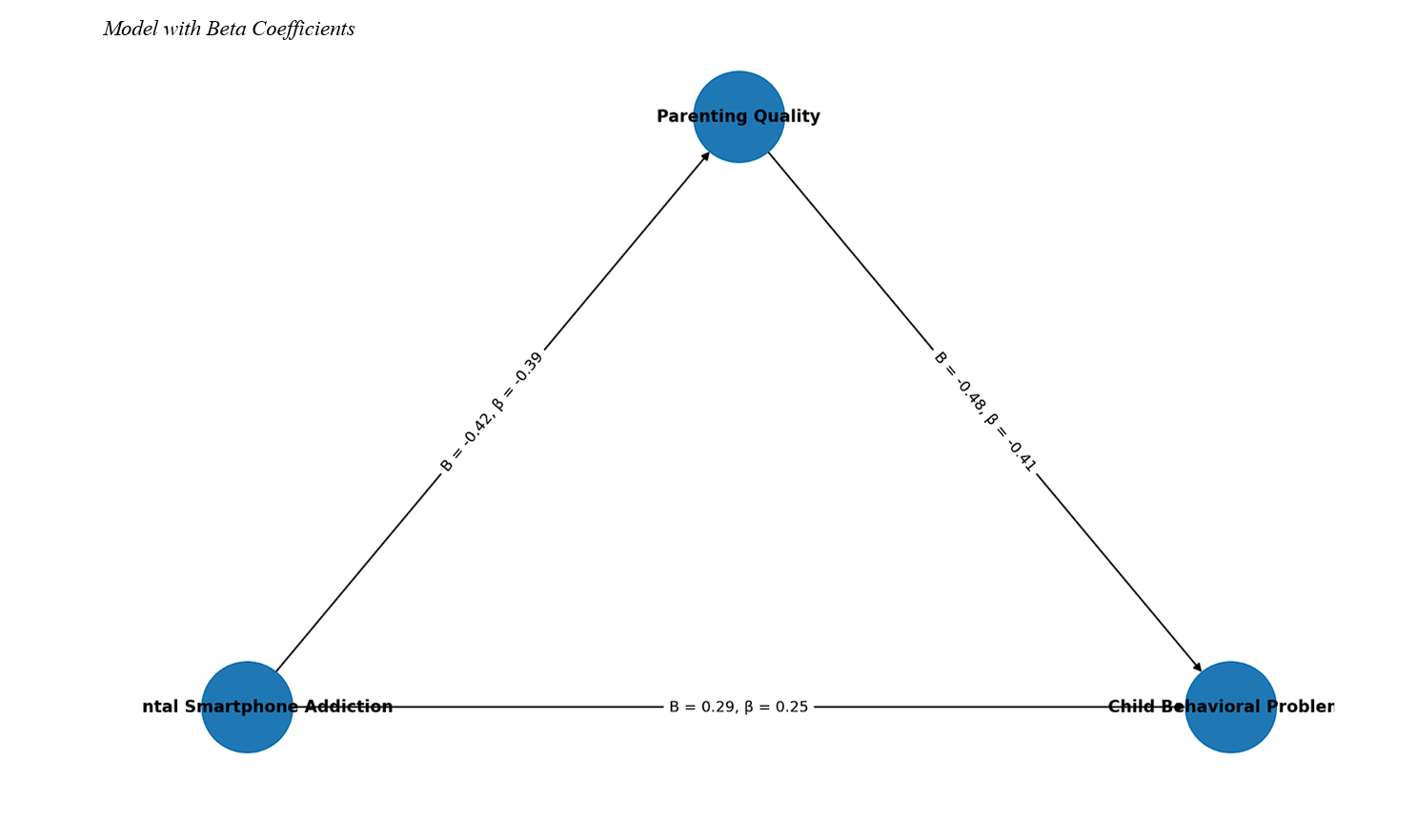
Findings: Descriptive statistics revealed moderate levels of parental smartphone addiction (M = 32.47, SD = 6.81), relatively high parenting quality (M = 74.26, SD = 9.54), and mild to moderate child behavioral problems (M = 18.63, SD = 5.72). Correlation analyses showed that parental smartphone addiction was positively correlated with child behavioral problems (r = .36, p < .001) and negatively correlated with parenting quality (r = –.41, p < .001). Parenting quality was negatively correlated with child behavioral problems (r = –.44, p < .001). SEM confirmed partial mediation: parental smartphone addiction negatively predicted parenting quality (β = –.39, p < .001), which in turn negatively predicted child behavioral problems (β = –.41, p < .001). The direct path from parental smartphone addiction to child behavioral problems remained significant (β = .25, p = .001), while the indirect effect through parenting quality was also significant (β = .16, p < .001).
Conclusion: The study highlights that parental smartphone addiction increases child behavioral problems both directly and indirectly through reduced parenting quality. Interventions should target reducing parental smartphone addiction and enhancing parenting practices to safeguard children’s behavioral health.
Downloads
References
Amiraliev, S. N. (2020). Influence of Computer Technologies on Development and Children's Well-Being. Scientific Work, 58(9), 52-55. https://doi.org/10.36719/2663-4619/58/52-55
Chen, L. (2023). Smartphone Dependency and Mental Health Among Chinese Rural Adolescents: The Mediating Role of Cognitive Failure and Parent–child Relationship. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1194939
Chen, S., Qiu, D., Li, X., & Zhao, Q. (2023a). Discrepancies in Adolescent–Parent Perceptions of Parental Phubbing and Their Relevance to Adolescent Smartphone Dependence: The Mediating Role of Parent–Child Relationship. Behavioral Sciences, 13(11), 888. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs13110888
Chen, S., Qiu, D., Li, X., & Zhao, Q. (2023b). Discrepancies in Adolescent–Parent Perceptions of the Parental Phubbing and Their Relevance to Adolescent Smartphone Dependence: The Mediating Role of Parent-Child Relationship. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202309.0708.v1
Doo, E. Y., & Kim, J. (2022). Parental Smartphone Addiction and Adolescent Smartphone Addiction by Negative Parenting Attitude and Adolescent Aggression: A Cross-Sectional Study. Frontiers in Public Health, 10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2022.981245
Ertemel, A. V., & Arı, E. (2020). A Marketing Approach to a Psychological Problem: Problematic Smartphone Use on Adolescents. International journal of environmental research and public health, 17(7), 2471. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17072471
Extremera, N., Quintana‐Orts, C., Sánchez‐Álvarez, N., & Rey, L. (2019). The Role of Cognitive Emotion Regulation Strategies on Problematic Smartphone Use: Comparison Between Problematic and Non-Problematic Adolescent Users. International journal of environmental research and public health, 16(17), 3142. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph16173142
Flamant, N., Haerens, L., Vansteenkiste, M., Laporte, N., Mabbe, E., & Soenens, B. (2022). A Daily Examination of the Moderating Role of Adolescents’ Coping in Associations Between Psychologically Controlling Parenting and Adolescents’ Maladjustment. Journal of youth and adolescence, 52(2), 287-305. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-022-01685-3
Goldstein, M. A., & Goldstein, M. C. (2024). Problematic Internet Use. 145-160. https://doi.org/10.1093/med/9780197640739.003.0010
Kabbaro, H., Wulan, N., & Hamiyati. (2023). Status of Living With Parents, Smartphone Addiction, and Problematic Eating Behavior in Adolescents. Journal of Family Sciences, 8(2), 264-283. https://doi.org/10.29244/jfs.v8i2.51068
KarataŞ, B. K., Ayhan, E., Beyazıt, U., & Ayhan, A. B. (2024). The Relationship Between Social Media Use and Smartphone Addiction in Adolescents and Parental Neglect During the Pandemic. Socialsciencesconf, 1(1), 14-25. https://doi.org/10.33422/socialsciencesconf.v1i1.352
Kim, J.-H. (2022). Parental Support and Problematic Smartphone Use: A Serial Mediating Model of Self-Esteem and Fear of Missing Out. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(13), 7657. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137657
Kim, J. H., Song, H. Y., & Jung, G. H. (2024). Relationship Between Positive Parenting and Cyberbullying Perpetration Among Adolescents: Role of Self-Esteem and Smartphone Addiction. Frontiers in psychology, 14. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1252424
Lathiifah, D. A., Qodariah, L., & Abidin, F. A. (2023). Problematic Smartphone Use in Adolescents: Parental Structure and Parental Psychological Control as Predictors. Jurnal Ilmu Keluarga Dan Konsumen, 16(1), 50-60. https://doi.org/10.24156/jikk.2023.16.1.50
Loleska, S., & Pop‐Jordanova, N. (2021). Is Smartphone Addiction in the Younger Population a Public Health Problem? Prilozi, 42(3), 29-36. https://doi.org/10.2478/prilozi-2021-0032
Marini, L., Hendriani, W., & Wulandari, P. Y. (2023). Optimizing the Role of the Family in Prevention Teen Smartphone Addiction Through Psychoeducation Smartphone Addiction to Parents. Dinamisia Jurnal Pengabdian Kepada Masyarakat, 7(4), 930-941. https://doi.org/10.31849/dinamisia.v7i4.15217
Merkaš, M., Selak, M. B., & Žulec, A. (2024). Problematic Smartphone Use and Communication in Families With Adolescents. Adolescents, 4(1), 107-119. https://doi.org/10.3390/adolescents4010008
Mico, R. (2022). Pengaruh Smartphone Pada Remaja Di Sd Karya Bhakti Helvetia Medan Ditinjau Dari Perspektif Islam. Jurnal Syiar-Syiar, 2(2), 67-84. https://doi.org/10.36490/syiar.v2i2.370
Oh, S., & Park, S. (2022). Smartphone Usage Patterns and Their Physical, Psychological, and Cyber‐Behavioral Predictors Among Adolescents in South Korea. Journal of School Health, 92(11), 1096-1105. https://doi.org/10.1111/josh.13198
Omede, J. (2023). Levels of Knowledge and Involvements in Behavioral Problems Associated With Use of Smartphone by in-School Christian Adolescents in North Central Nigeria. Advances in Social Sciences Research Journal, 10(6), 108-123. https://doi.org/10.14738/assrj.106.14667
Proborini, R., & Septania, S. (2021). Adiksi Smartphone Ditinjau Dari Attachment Orang Tua – Remaja Dan Regulasi Emosi. Insight Jurnal Pemikiran Dan Penelitian Psikologi, 17(1), 74-87. https://doi.org/10.32528/ins.v17i1.3798
Rahmah, A. A., Mustikawati, I. F., Septianawati, P., & Immanuel, G. (2024). Analysis of Factor Causing Nomophobia in Adolescents: A Meta- Analysis Study. Jurnal Syntax Admiration, 5(4), 237-244. https://doi.org/10.46799/jhs.v5i4.1258
Sahithya, B. R., & Raman, V. (2021). Parenting Style, Parental Personality, and Child Temperament in Children With Anxiety Disorders—A Clinical Study From India. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, 43(5), 382-391. https://doi.org/10.1177/0253717620973376
Silvanasari, I. A., Sustini, F., & Has, E. M. M. (2018). Smartphone Usage and Parent Role Correlated With Risky Dating Behaviour in Adolescent. Indonesian Journal of Health Research, 1(2), 27-36. https://doi.org/10.32805/ijhr.2018.1.2.10
Siokal, B., Wahyuningsih, W., Asfar, A., & Sudarman, S. (2025). The Impact of Smartphone Usage on Adolescent Social Interaction in Borongloe Village. Window of Health Jurnal Kesehatan, 73-81. https://doi.org/10.33096/woh.v8i1.1732
Son, H.-G., Cho, H. J., & Jeong, K.-H. (2021). The Effects of Korean Parents’ Smartphone Addiction on Korean Children’s Smartphone Addiction: Moderating Effects of Children’s Gender and Age. International journal of environmental research and public health, 18(13), 6685. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph18136685
Son, H., Yun, J., & Han, G. (2022). Longitudinal Analysis of Influencing Factors of Problematic Smartphone Use in Preteens. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-1356627/v1
Wang, D., Zhou, M., & Hu, Y. (2024). The Relationship Between Harsh Parenting and Smartphone Addiction Among Adolescents: Serial Mediating Role of Depression and Social Pain. Psychology research and behavior management, Volume 17, 735-752. https://doi.org/10.2147/prbm.s438014
Yun, J., Han, G., & Son, H. (2022). Protective and Risk Factors of Problematic Smartphone Use in Preteens Using Panel Study on Korean Children. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 13. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2022.981357
Yusuf, R. A., Syamsir, M. R., & Silwanah, A. S. (2023). Kecanduan Gadget Dan Aktifitas Fisik Pada Remaja: Tinjauan Literatur. Media Ilmu Kesehatan, 11(1), 85-98. https://doi.org/10.30989/mik.v11i1.651
Zhang, Q., Ran, G., & Ren, J. (2022). Parental Psychological Control and Addiction Behaviors in Smartphone and Internet: The Mediating Role of Shyness Among Adolescents. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(24), 16702. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph192416702
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















