Prioritizing Emotional Climate Factors in Families with Adolescent Anxiety
Keywords:
Family emotional climate, adolescent anxiety, empathy, family cohesion, emotional validationAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to identify, categorize, and prioritize the emotional climate factors influencing families with adolescents experiencing anxiety through an integrated qualitative–quantitative approach.
Methods and Materials: A mixed-methods exploratory–quantitative design was employed in two sequential phases. In the qualitative phase, an extensive literature review was conducted until theoretical saturation, and data were analyzed using NVivo 14 through thematic coding. Seven main themes were identified, including parental emotional expression, communication patterns, parental control and autonomy, family cohesion and support, parental mental health influence, emotional validation and empathy, and family stress and conflict climate. In the quantitative phase, a structured questionnaire was developed based on the qualitative findings and administered to 220 participants from Kenya, consisting of parents and adolescents aged 13–18 years. Data were analyzed using SPSS 26, applying the Friedman ranking test to determine the relative importance of emotional climate factors.
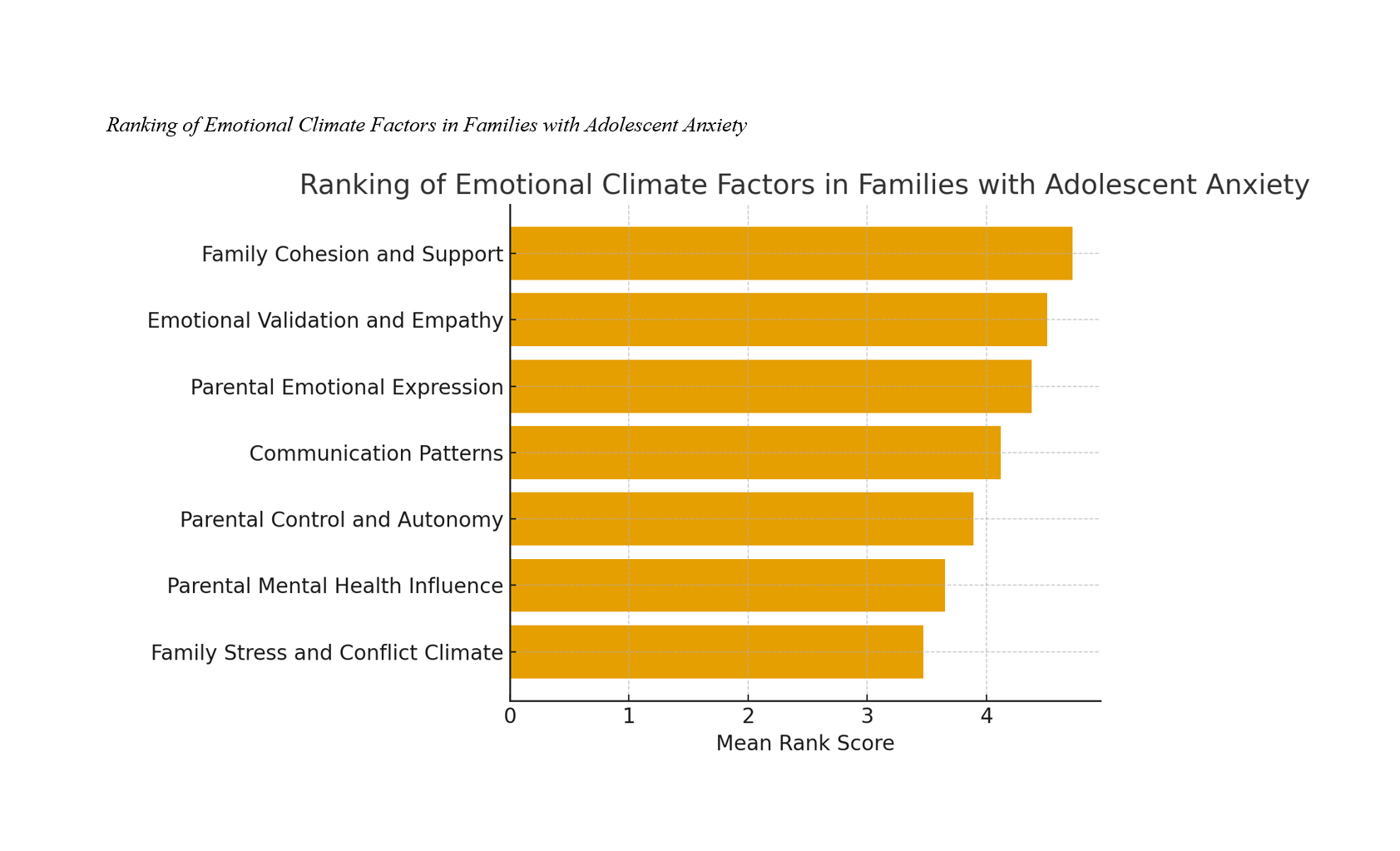
Findings: Results indicated statistically significant differences in the prioritization of emotional climate factors (p < .01). Family Cohesion and Support received the highest mean rank score (4.72), followed by Emotional Validation and Empathy (4.51), Parental Emotional Expression (4.38), and Communication Patterns (4.12). Parental Control and Autonomy (3.89), Parental Mental Health Influence (3.65), and Family Stress and Conflict Climate (3.47) ranked lower, suggesting that affective closeness and empathic validation are stronger predictors of adolescent emotional well-being than external stress factors.
Conclusion: The study highlights that family cohesion, empathy, and emotional validation are the most influential components of a healthy emotional climate in mitigating adolescent anxiety. These results emphasize the need for family-centered interventions that enhance emotional communication, promote empathy, and strengthen relational bonds as preventive and therapeutic strategies for adolescent anxiety.
Downloads
References
Akbari, A., Sharifi, H. P., Sharifi, N., & Mirhashemi, M. (2024). A Structural Model for Predicting Addiction Susceptibility in Male Adolescents Based on Family Emotional Climate With the Mediation of Resilience. Shenakht Journal of Psychology and Psychiatry, 11(03), 125-136. https://doi.org/10.32598/shenakht.11.3.125
Amanelahi, A., Andarz, R., & Abbaspour, Z. (2023). Predicting Sexual Behavior Based on Family Emotional Climate and Exposure to the Sexual Environment in Children With and Without Sexual Problems. Iranian journal of psychiatry and behavioral sciences, 17(2). https://doi.org/10.5812/ijpbs-130686
Balan, R. (2025). Negative Family Climate as a Risk Factor Among Adolescent Girls With Eating Problems. Acta Et Commentationes Științe Ale Educației, 40(2), 145-152. https://doi.org/10.36120/2587-3636.v40i2.145-152
Charmaraman, L., Cobas, S., Weed, J., Gu, Q., Kiel, E., Chin, H., Gramajo, A., & Mueller, M. K. (2022). From Regulating Emotions to Less Lonely Screen Time: Parents’ Qualitative Perspectives of the Benefits and Challenges of Adolescent Pet Companionship. Behavioral Sciences, 12(5), 143. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs12050143
Chernikova, A. A., & Oblasova, O. V. (2024). The Impact of Subjective Perception of Family on the Emotions in Adolescents. Vestnik Altaiskogo Gosudarstvennogo Pedagogiceskogo Universiteta(58), 70-76. https://doi.org/10.37386/2413-4481-2024-1-70-76
Dayasiri, K., & Anand, G. (2025). Difference in Perception and Emotional Response to Climate Change Between Male and Female Teenagers in the Colombo Education Zone, Sri Lanka. Sljo-J-BMJ, 19(1), 6-10. https://doi.org/10.4038/bmj.v19i1.64
Hadley, W., McWhirter, A. C., Franz, D., Bogner, J., Barker, D., Rizzo, C. J., & Houck, C. (2024). The Moderating Role of Poverty on Parenting, Family Climate, and Early Adolescent Emotion Regulation. The Journal of Early Adolescence, 45(3), 341-365. https://doi.org/10.1177/02724316241249486
Huang, Y. (2023). Family Factors to Predict Adolescents’ Emotional Health by Decision Tree Model: A Comparison Between Normally Developed Group and Chronic-Condition Group. Frontiers in Public Health, 11. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2023.1087547
Iacopetti, C., Londi, I., Patussi, V., & Cosci, F. (2021). Family Climate in Children Living With Parents Who Harmfully Consume Alcohol. Clinical Psychology & Psychotherapy, 28(5), 1128-1134. https://doi.org/10.1002/cpp.2562
Jiménez-Vázquez, D., Piqueras, J. A., Fernández, L. E., Canals, J., & López, L. J. G. (2025). Psychometric Properties of the Spanish Version of the Climate Anxiety Scale in Spanish-Speaking Adolescents. Frontiers in psychology, 16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2025.1631481
Kapetanovic, S., & Skoog, T. (2020). The Role of the Family’s Emotional Climate in the Links Between Parent-Adolescent Communication and Adolescent Psychosocial Functioning. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 49(2), 141-154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-020-00705-9
Khofifah, R., & Aliza, N. F. (2024). Melatih Keterampilan Regulasi Emosi Pada Remaja Di Pusat Pembelajaran Keluarga (Puspaga) Sleman. Hudan Lin Naas Jurnal Ilmu Sosial Dan Humaniora, 5(2), 217. https://doi.org/10.28944/hudanlinnaas.v5i2.1654
Kovalchuk, Z., Raіevska, Y., Beheza, L. E., Ievtushenko, I., & Odyntsova, H. (2021). Socio-Psychological Features and Legal Norms of the Life of Adolescents From Distant Families of Labor Migrants. Revista Amazonia Investiga, 10(46), 79-91. https://doi.org/10.34069/ai/2021.46.10.7
Lacomba‐Trejo, L., Casaña-Granell, S., Montoya‐Castilla, I., & Pérez‐Marín, M. (2025). Apego Y Síntomas Emocionales en Familiares De Adolescentes Con Talla Baja. Revista De Psicología De La Salud, 13(1), 77-91. https://doi.org/10.21134/pssa.v13i1.9
Lee, Y. (2024). Analysis of the Impact of Chinese Parenting Styles on Adolescent Social Competence: From a Perspective of Family Systems Theory. Journal of Education and Educational Research, 10(1), 148-156. https://doi.org/10.54097/5nb40763
Leung, J. T. Y., Shek, D. T. L., To, S. m., & Ngai, S. (2023). Maternal Distress and Adolescent Mental Health in Poor Chinese Single-Mother Families: Filial Responsibilities—Risks or Buffers? International journal of environmental research and public health, 20(7), 5363. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph20075363
Magklara, K., Kapsimalli, E., Vlassopoulos, C., Λιαράκου, Γ., & Lazaratou, E. (2025). The ClimaQ Study: Exploring Parental Accounts of Climate Crisis-Related Emotional Responses, Awareness, and Engagement in Actions Among Children in Greece. Children, 12(4), 432. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12040432
Manjarrés-Zambrano, N. V. (2025). The Role of the Family in the Development of Socio-Emotional Skills in Adolescents: A Review From the Educational Context. NSS, 2(4), 43-47. https://doi.org/10.47460/noesis.v2i4.28
Marcus, A. K. (2024). Understanding the Impact of Parent-Child Relationships on Emotion Regulation: A Comprehensive Review. Nijciam, 4(1), 25-31. https://doi.org/10.59298/nijciam/2024/4.1.253113
Maulina, Y., Fitriani, W., Yeni, P., & Maharjan, K. (2024). Analysis Dynamics of Adolescents' Lack of Openness to Parents: A Qualitative Study. Agenda Jurnal Analisis Gender Dan Agama, 6(2), 103. https://doi.org/10.31958/agenda.v6i2.12823
Munthe, L. M., Lumbantoruan, R., & Naibaho, D. (2024). Pengaruh Peran Keluarga Terhadap Kesejahteraan Emosional Remaja Di Dusun Kutambaru. Jimu, 2(02), 257-264. https://doi.org/10.70294/jimu.v2i02.360
Peláez-Fernández, M. Á., Mérida‐López, S., Yudes, C., & Extremera, N. (2024). How Can the Social Family Climate Contribute to Emotional Intelligence in Preventing Suicidal Ideation and Promoting Life Satisfaction Among Adolescents? Applied Research in Quality of Life, 19(5), 2915-2932. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11482-024-10354-5
Peng, X. (2024). The Impact of Family of Origin on Attachment Relationships and Emotional Regulation Ability. Communications in Humanities Research, 51(1), 135-140. https://doi.org/10.54254/2753-7064/51/20242515
Posokhova, S. T., & Kolpakova, A. E. (2020). The Study of the Relationship Between the Emotional Component of Family’s Informational Environment and Adolescents’ Disadaptive Behaviour. Vestnik Kostroma State University Series Pedagogy Psychology Sociokinetics, 26(3), 15-21. https://doi.org/10.34216/2073-1426-2020-26-3-15-21
Rodríguez-Rubio, P., Martín-Ávila, J., Rodríguez-Jiménez, E., Valero‐Moreno, S., Montoya‐Castilla, I., & Pérez‐Marín, M. (2025). Emotional Contagion Among Adolescents With Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus (T1DM) and Their Primary Caregivers: Benefits of Psychological Support for Family Systems in Pilot Study. Children, 12(2), 151. https://doi.org/10.3390/children12020151
Rosharudin, N. A., Hoesni, S. M., Ali, M. M., & Khairuddin, K. F. (2023). Parenting Factors and Emotion Regulation Among Asian Adolescents: A Systematic Review. International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 13(11). https://doi.org/10.6007/ijarbss/v13-i11/19492
Singh, M., Austin, A., Lindenbach, D., Steen, H. V., Habina, C., Marcoux‐Louie, G., Loeb, K. L., Engel, S. G., Grange, D. L., & Dimitropoulos, G. (2025). Ecological Momentary Assessment for Adolescents With Anorexia Nervosa and Their Parents/Caregivers In Family‐Based Treatment. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 58(3), 608-623. https://doi.org/10.1002/eat.24368
Thomson, K., Magee, C., Petteni, M. G., Oberle, E., Georgiades, K., Schonert‐Reichl, K. A., Janus, M., Guhn, M., & Gadermann, A. (2024). Changes in Peer Belonging, School Climate, and the Emotional Health of Immigrant, Refugee, and Non‐immigrant Early Adolescents. Journal of adolescence, 96(8), 1901-1916. https://doi.org/10.1002/jad.12390
Wang, Y., Zhou, K., Wang, Y., Zhang, J., Xie, Y., Wang, X., Yang, W. Y., Zhang, X., Yang, J., & Wang, F. (2024). Examining the Association of Family Environment and Children Emotional/Behavioral Difficulties in the Relationship Between Parental Anxiety and Internet Addiction in Youth. Frontiers in Psychiatry, 15. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2024.1341556
Wang, Z. (2024). Adolescent Depression: Impact of Family Relations. Tssehr, 5, 468-472. https://doi.org/10.62051/qjy8zs95
Yadav, V., & Yadav, D. (2025). Impact of Family Environment on the Academic Achievement of Secondary School Students. Nijms, 1(5), 46-56. https://doi.org/10.71126/nijms.v1i5.54
Αντωνοπούλου, Κ., Anastasopoulos, N., Alexopoulos, D. A., & Kouvava, S. (2025). Perfectionism, Family Climate and Emotion Regulation in Childhood. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202509.1370.v1