Parental Digital Literacy and Involvement in Blended Learning: A Mixed-Methods Psychological Analysis
Keywords:
Digital literacy, parental involvement, blended learning, mixed-methods, parental mediation, digital parentingAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine how parental digital literacy predicts and shapes parental involvement in blended learning environments using an integrated mixed-methods psychological approach.
Methods and Materials: A convergent mixed-methods design was employed with 384 parents completing validated digital literacy and parental involvement scales, while 22 parents participated in in-depth semi-structured interviews. Quantitative data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, Pearson correlations, multiple regression, and PLS-SEM to assess predictive relationships across domains of digital literacy and involvement. Qualitative data were analyzed using reflexive thematic analysis to identify psychological processes underlying digital engagement. Results from both strands were integrated through triangulation to capture convergent and complementary patterns.
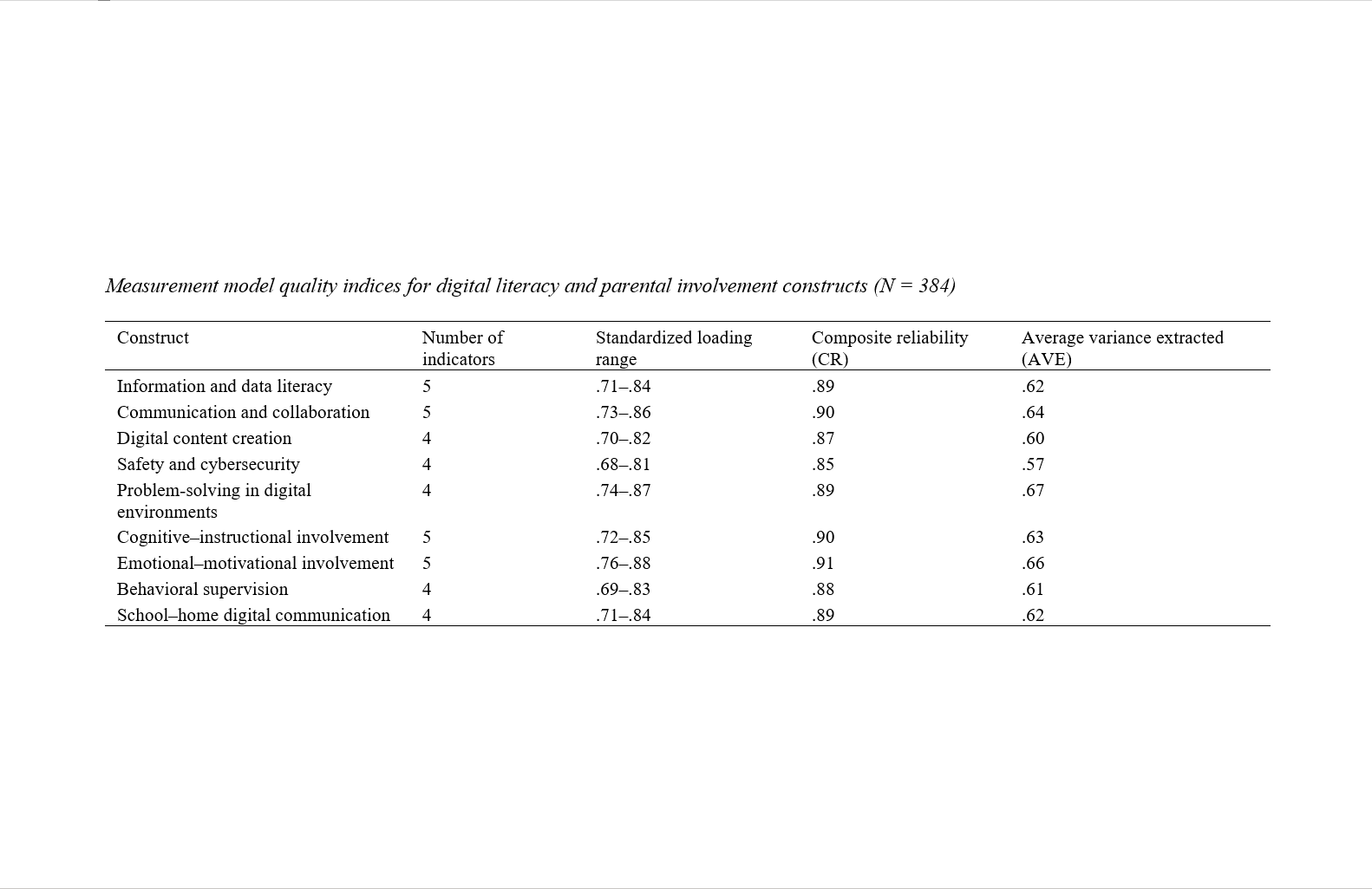
Findings: Parents demonstrated moderate digital literacy, with communication and problem-solving competencies showing the strongest associations with involvement. Correlation analyses revealed robust positive relationships between all literacy domains and involvement dimensions (r = .22 to .41, p < .01). Multiple regression showed that information literacy (β = .18, p = .003), communication literacy (β = .21, p < .001), and problem-solving skills (β = .24, p < .001) significantly predicted parental involvement, explaining 43% of its variance. PLS-SEM confirmed strong paths from problem-solving to cognitive–instructional involvement (β = .24, p < .001) and behavioral supervision (β = .21, p < .001), and from communication literacy to school–home communication (β = .27, p < .001). Digital content creation and cybersecurity skills showed weaker, nonsignificant effects. Model fit indices demonstrated strong reliability (CR = .85–.91) and convergent validity (AVE = .57–.67).
Conclusion: Parental digital literacy substantially influences the quality and depth of parental involvement in blended learning, with problem-solving, information handling, and communication competencies emerging as the most critical predictors. Strengthening parental digital literacy may therefore enhance home–school collaboration, support student engagement, and promote more equitable participation in blended learning ecosystems.
Downloads
References
Adara, R. A. (2020). Improving Early Childhood Literacy by Training Parents to Utilize Digital Storytelling. https://doi.org/10.2991/assehr.k.200808.039
Adigwe, I. (2021). Identifying the Moderating and Mediating Variables in Parental Mediation Practices in Nigerian Families in the Digital Age. Social Media + Society, 7(3). https://doi.org/10.1177/20563051211033817
Adigwe, I., Mason, J., & Gromik, N. (2024). Investigating the Relationship Between Socio-Demographic Variables of Parents, Digital Literacy and Parental Mediation Practices in the Digital Age: Nigeria in Focus. E-Learning and Digital Media, 22(3), 229-246. https://doi.org/10.1177/20427530241232495
Ashfield, S., Donelle, L., Tryphonopoulos, P., Dubé, È., & Smith, M. J. (2024). Digital Health Literacy, Vaccine Information Sources, and Vaccine Acceptance Among Parents in Ontario: Quantitative Findings From a Mixed Methods Study. Plos Global Public Health, 4(5), e0003154. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgph.0003154
Asmayawati, A. (2023). Parental Involvement in Mattering Early Childhood Digital Literacy: The Role of Balanced Screen Time and Access to Technology Evidence From Indonesia. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Research and Analysis, 06(11). https://doi.org/10.47191/ijmra/v6-i11-30
Bang, H. J., & Mackey, A. (2024). Chinese Parents’ Involvement in Their Young Children’s App-Based Language Learning. Language Teaching for Young Learners, 7(1), 106-130. https://doi.org/10.1075/ltyl.00052.ban
Choi, J. K., & Choi, J.-I. (2024). The Impact of Parents’ Digital Media Literacy and Digital Media Parenting on Young Children’s Overdependence on Smart Devices. Reg Entrep Edu Res Cent, 6(4), 135-157. https://doi.org/10.23108/decrc.2024.6.4.135
Ciboci, L., & Labaš, D. (2019). Digital Media Literacy, School and Contemporary Parenting. Medijske Studije, 10(19), 83-101. https://doi.org/10.20901/ms.10.19.5
Dianawati, D., Rohman, N., & Mujahidin, A. (2025). The Effect of Parental Involvement and Digital Financial Literacy on Student Learning Achievement of Grade Xi in the Digital Era at SMKN 1 Bojonegoro. Santhet (Jurnal Sejarah Pendidikan Dan Humaniora), 9(4), 1433-1442. https://doi.org/10.36526/santhet.v9i4.5484
Guo, D. (2025). Design of Interactive Spaces for Promoting Parental Involvement: Strategies Used by EFL Teachers. Online Learning, 29(2). https://doi.org/10.24059/olj.v29i2.4683
Karabanov, G. M., & Aram, D. (2024). ‘Let's Write a Shopping List on the Phone Together’: Parents' Digital Literacy Activities With Their Preschoolers and the Children's Early Literacy Skills. Journal of Research in Reading, 47(3), 395-411. https://doi.org/10.1111/1467-9817.12469
Kusumalestari, R. R., Oesman, M. A., Ahmadi, D., Umar, M., & Yulianita, N. (2023). Parenting Styles and Digital Literacy: Uncovering Their Correlation Among Adolescents. Jurnal Kajian Komunikasi, 11(2), 144. https://doi.org/10.24198/jkk.v11i2.46658
Liu, X.-z., Wu, J.-x., Guo, L.-j., Li, B., & Ye, B. (2023). Digital Literacy and Online Learning Satisfaction Among Junior High School Students in the Context of COVID-19: The Mediating Role of Online Learning Engagement and the Moderating Role of Parents' Educational Expectations. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3608234/v1
Maaghop, M. C., & Que, E. N. (2024). Roles of Parents and Adolescent Learners in the Use of Technology in Homeschooling. Pjes, 2(1), 54-82. https://doi.org/10.61839/29848180mc108e7
Muslih, Y. N. (2022). Layanan Konsultasi Melalui Parental Mediation Untuk Meningkatkan Literasi Digital Siswa. Islamic Counseling Jurnal Bimbingan Konseling Islam, 6(2), 169. https://doi.org/10.29240/jbk.v6i2.4689
Okela, A. H., Olatokun, W. M., Anumudu, C. E., Ziani, A., Nser, K. K., & Lagha, F. B. (2025). Parental Social Media Literacy Antecedents and Children’s Digital Media Addiction: Observations From Two African Countries. Competitiveness Review an International Business Journal Incorporating Journal of Global Competitiveness, 35(4), 685-700. https://doi.org/10.1108/cr-11-2023-0294
Robbets, C. (2023). Investigating Belgian parents' digital media literacy in childcare practices: Insights from a qualitative study. World Media Education Summit 2023,
Sarini, S. (2024). The Relationship Between Parental Mediation, Family Functioning, and Parental Digital Literacy With Children's Gadget Use. Jurnal Ilmiah Ilmu Keperawatan Indonesia, 14(02), 63-72. https://doi.org/10.33221/jiiki.v14i02.3484
Suryadi, S. (2025). Access to Digital as a Moderating Influence of Parental Role and Balanced Screen Time on Elementary School Children's Digital Literacy Educationally. Jurnal Penelitian Pendidikan Ipa, 11(7), 900-906. https://doi.org/10.29303/jppipa.v11i7.12225
Tariq, A. (2025). Impact of Digital Parenting Practices on Adolescent Mental Health and Family Well-Being: A Case Study of Urban Households. Health Education, 1-23. https://doi.org/10.1108/he-07-2025-0120
Windasari, I. W., & Dheasari, A. E. (2024). The Role of Parents and Educators in Early Childhood's Digital Literacy. Electronic Journal of Education Social Economics and Technology, 5(2), 112-117. https://doi.org/10.33122/ejeset.v5i2.331
Zhangaliyeva, R. E., & Zhukenova, G. B. (2025). Formation of Parents' Media Literacy as a Psychological and Pedagogical Condition for the Prevention of Digital Autism. pedjournal.enu, 151(2), 47-63. https://doi.org/10.32523/3080-1710-2025-151-2-47-63