Effect of 8 weeks of Intense Intermittent Exercise with Thyme Extract on the Expression of Apoptosis Indicators Bax and p53 in Liver Tissue and Insulin Resistance in Type 2 Diabetic Rats
Keywords:
Concussion recovery, sports psychology, return to play, psychological readiness, fear of re-injury, social supportAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to investigate the effect of eight weeks of exhaustive interval training combined with thyme extract supplementation on the expression of apoptosis markers Bax and P53 in liver tissue and insulin resistance in male rats with type 2 diabetes.
Methods and Materials: The study population consisted of 36 male Wistar rats. After 20 weeks of a high-fat diet and intraperitoneal injection of 25 mg/kg STZ, the rats developed diabetes. A fasting blood glucose level between 150 to 400 mg/dL indicated type 2 diabetes. The diabetic rats were then divided into four groups: control, interval training, thyme extract, and interval training-thyme extract groups. The exercise protocol consisted of eight weeks of interval training, five sessions per week, with 2-minute high-intensity intervals (2 to 8 intervals) at 80-90% VO2max and 1-minute rest intervals at 50-56% VO2max. Thyme extract was administered at a dose of 200 mg/kg dissolved in distilled water, given orally via gavage 5 days per week before exercise.
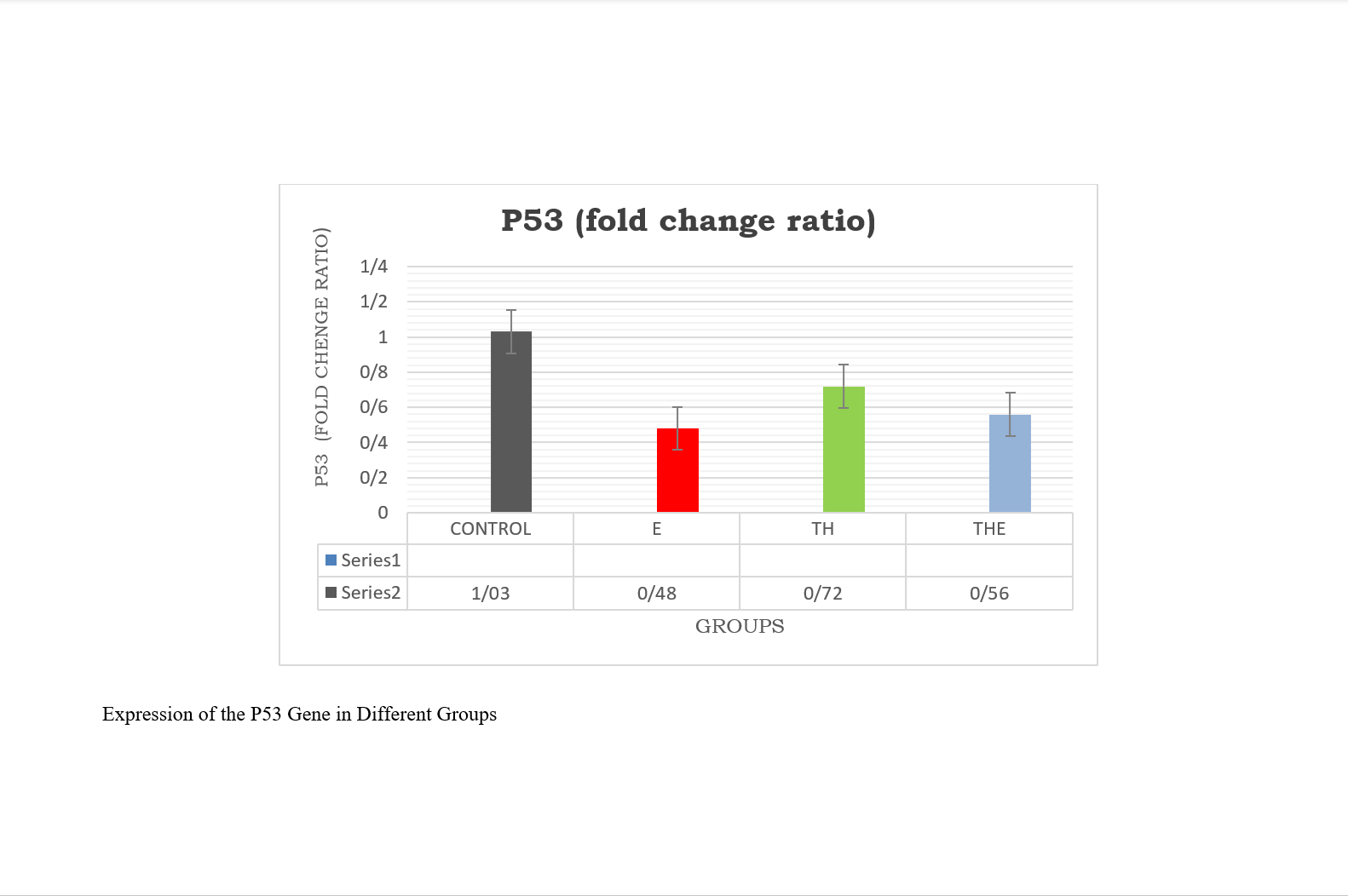
Findings: Two-way ANOVA analysis showed that the gene expression of apoptosis markers Bax and P53 in liver tissue significantly increased in the interval training and thyme extract groups compared to the diabetic control group. Moreover, the expression of these markers was significantly higher in the thyme extract group compared to the control group. However, the expression of Bax and P53 in liver tissue in the interval training and combined interval training-thyme extract groups showed a non-significant increase compared to the control group. Additionally, findings indicated an improvement in insulin resistance and glucose levels in the interval training and combined interval training-thyme extract groups, with significant results observed in the interval training group.
Conclusion: It appears that high-intensity interval training and thyme extract consumption may reduce the expression of apoptotic markers Bax and P53 in
Downloads
References
1. Davoodi M, Moosavi H, Nikbakht M. The effect of eight
weeks selected aerobic exercise on liver parenchyma and liver
enzymes (AST, ALT) of fat liver patients. Shahrekord Univ Med
Sci J. 2012;14(1):84-90.
2. Habibi P, Alihemmati A, NourAzar A, Yousefi H,
Mortazavi S, Ahmadiasl N. Expression of the Mir-133 and Bcl-2
could be affected by swimming training in the heart of
ovariectomized rats. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2016;19(4):381. [DOI]
3. Aminizadeh S, Habibi A, Marefati H, Shakerian S.
Response of estrogen-related receptor alpha (ERRα) to endurance
training and its participation in endurance training-induced
adaptations in lipid metabolism in skeletal muscle of male Wistar
rats. JSSU. 2017;25(5):414-25.
4. Shekarzadeh M, Blacksmith N, Zargari M, Gilani Z,
Shadburistan A, Omid M. Investigating the protective effect of Lcarnitine on the level of malondialdehyde in lipid peroxidation of
the cell membrane in rats exposed to diazinon toxin. J Mazandaran
Univ Med Sci. 2011;22(97):198-206.
5. Firozrai M, Mehrabi H. The activity of antioxidant
enzymes SOD and glutathione reductase of red blood cells in
patients with coronary artery occlusion. J Iran Univ Med Sci.
2002;9(28):93.
6. Ghasemi F, Yousefi Nesab A, Kargar Jahormi H. The
protective effect of vitamin E and selenium on the liver tissue of
insulin-resistant rats. Pars J Med Sci. 2014;12(2):47. [DOI]
7. Lajoie C, Calderone A, Béliveau L. Exercise training
enhanced the expression of myocardial proteins related to cell
protection in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Pflügers Arch.
2004;449(1):26-32. [PMID: 15290300] [DOI]
8. Li F, Shi W, Zhao EY, Geng X, Li X, Peng C, et al.
Enhanced apoptosis from early physical exercise rehabilitation
following ischemic stroke. J Neurosci Res. 2017;95(4):1017-24.
[PMID: 27571707] [DOI]
9. Testa R, Bonfigli AR, Genovese S, De Nigris V, Ceriello
A. The possible role of flavonoids in the prevention of diabetic
complications. Nutrients. 2016;8(5):310. [PMID: 27213445]
[PMCID: PMC4882722] [DOI]
10. Marsh SA, Laursen PB, Pat BK, Gobe GC, Coombes JS.
Bcl-2 in endothelial cells is increased by vitamin E and α-lipoic
acid supplementation but not exercise training. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
2005;38(3):445-51. [PMID: 15733904] [DOI]
11. Mirdar Harijani S, Mousavi N, Hamidian G. The effect
of endurance swimming training during pregnancy on tissue
structure and apoptotic index of rat liver. Persian Gulf Biomed Res
Inst. 2014;18(1):54-63.
12. Dostar Y, Mohajeri D, Rezaei A. Effects of grape seed
extract on cardiac cell apoptosis in streptozotocin-induced diabetic
rats. J Med Sci Islamic Azad Univ. 2011;21(3):168-74.
13. Frustaci A, Kajstura J, Chimenti C, Jakoniuk I, Leri A,
Maseri A. Myocardial cell death in human diabetes. Circ Res.
2000;87:1123-32. [PMID: 11110769] [DOI]
14. Lopes G, Bazotte RB, Curi R, Alves-Do-Prado WL. Lcarnitine induces tetanic fade in rat neuromuscular preparation.
Braz J Med Biol Res. 2003;36:1255-67. [PMID: 12937794] [DOI]
15. Ahmadi Asl N, Ghadiri Soufi F, Alipour M, Bonyadi M,
Sheikhzadeh F, Vatankhah A, et al. Effects of age increment and
36-week exercise training on antioxidant enzymes and apoptosis in
rat heart tissue. J Sports Sci Med. 2007;6:243-9.
16. Hargrius M, Esprit L. Metabolism of sports activities.
Tehran: Samt Publications; 2010.
17. Anderson EJ, Rodriguez E, Anderson CA, Thayne K,
Chitwood WR, Kypson AP. Increased propensity for cell death in
diabetic human heart is mediated by mitochondrial-dependent
pathways. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2011;300:118-24.
[PMID: 21076025] [PMCID: PMC3023249] [DOI]
18. Cai MX, Shi XC, Chen T, Tan ZN, Lin QQ, Du SJ, et al.
Exercise training activates neuregulin 1/ErbB signaling and
promotes cardiac repair in a rat myocardial infarction model. Life
Sci. 2016;149:1-9. [PMID: 26892146] [DOI]
19. Lee BJ, Lin JS, Lin YC, Lin PT. Effects of L-carnitine
supplementation on oxidative stress and antioxidant enzyme
activities in patients with coronary artery disease: a randomized,
placebo-controlled trial. Nutr J. 2014;13:79. [PMID: 25092108]
[PMCID: PMC4125592] [DOI]
20. Chen KC, Peng CC, Hsieh CL, Peng RY. Exercise
ameliorates renal cell apoptosis in chronic kidney disease by
intervening in the intrinsic and extrinsic apoptotic pathways in a rat
model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2013;2013:368450.
[PMID: 24106522] [PMCID: PMC3782870] [DOI]
21. Bagci E, Vodovotz Y, Billiar T, Ermentrout G, Bahar I.
Bistability in apoptosis: roles of bax, bcl-2, and mitochondrial
permeability transition pores. Biophys J. 2006;90:1546-59. [PMID:
16339882] [PMCID: PMC1367306] [DOI]
22. Malone JI, Malone MA, Morrison AD. Diabetic
cardiovascular risk and carnitine deficiency. J Diabetes Mellitus.
2014;4:202-8. [DOI]
23. Ansarihadipour H, Alhoseini M, Rostami S, Farahani N,
Hashemi M. Antioxidant and prooxidant effects of ascorbate during
iron-induced carbonyl formation in serum albumin. Arak Univ Med
Sci J. 2012;15(2):17-26.
24. Franziska A, Tobias M, Jennifer K, Steffi H, Anne S,
Elisabeth M, et al. Liver p53 is stabilized upon starvation and
required for amino acid catabolism and gluconeogenesis. FASEB
J. 2017;31(2):732-42. [PMID: 27811061] [PMCID: PMC5240663]
[DOI]
25. Fakhr Fatemi H, Rezaeian N, Karimi M. Effect of high
intensity interval training on adipose tissue levels of Piezo1 and
insulin resistance index in diabetic rats. J Arak Univ Med Sci.
2023;36(4):309-21. [DOI]
26. Kharghani A, Rezaeian N. Effect of aerobic training on
sirtuin 1 protein levels and insulin resistance in obese men with
type 2 diabetes. J Obes. 2023;15(30):67-76.
27. Farajtabar S, Shakeri N, Ghazalian F, Nikbakht H. Effect
of 12 weeks aerobic training on FOXO1 gene expression in
pancreatic tissue of type 2 diabetes Wistar rats. Iran J Diabetes
Obes. 2018;10(4).
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Nader Afravi , Amirali Salehi, Hassan Norinejad , Hongxiang Huang (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







