The Role of Plyometric Training in Improving Explosive Power in Sprinters: A Qualitative Analysis
Keywords:
Plyometric Training, Explosive Power, Sprinters, Athletic Performance, Muscle Strength, Speed, Agility, Psychological Benefits, Training EfficiencyAbstract
Objective: The objective of this study was to explore the role of plyometric training in enhancing explosive power among sprinters.
Methods and Materials: This qualitative research employed semi-structured interviews to gather data from 17 sprinters aged 18 to 30 years, with at least three years of competitive experience. Participants were recruited from local athletic clubs and universities. Data collection continued until theoretical saturation was achieved, ensuring a comprehensive understanding of the impact of plyometric training. Thematic analysis was used to identify and analyze patterns within the data, providing detailed insights into the participants' experiences and perceptions.
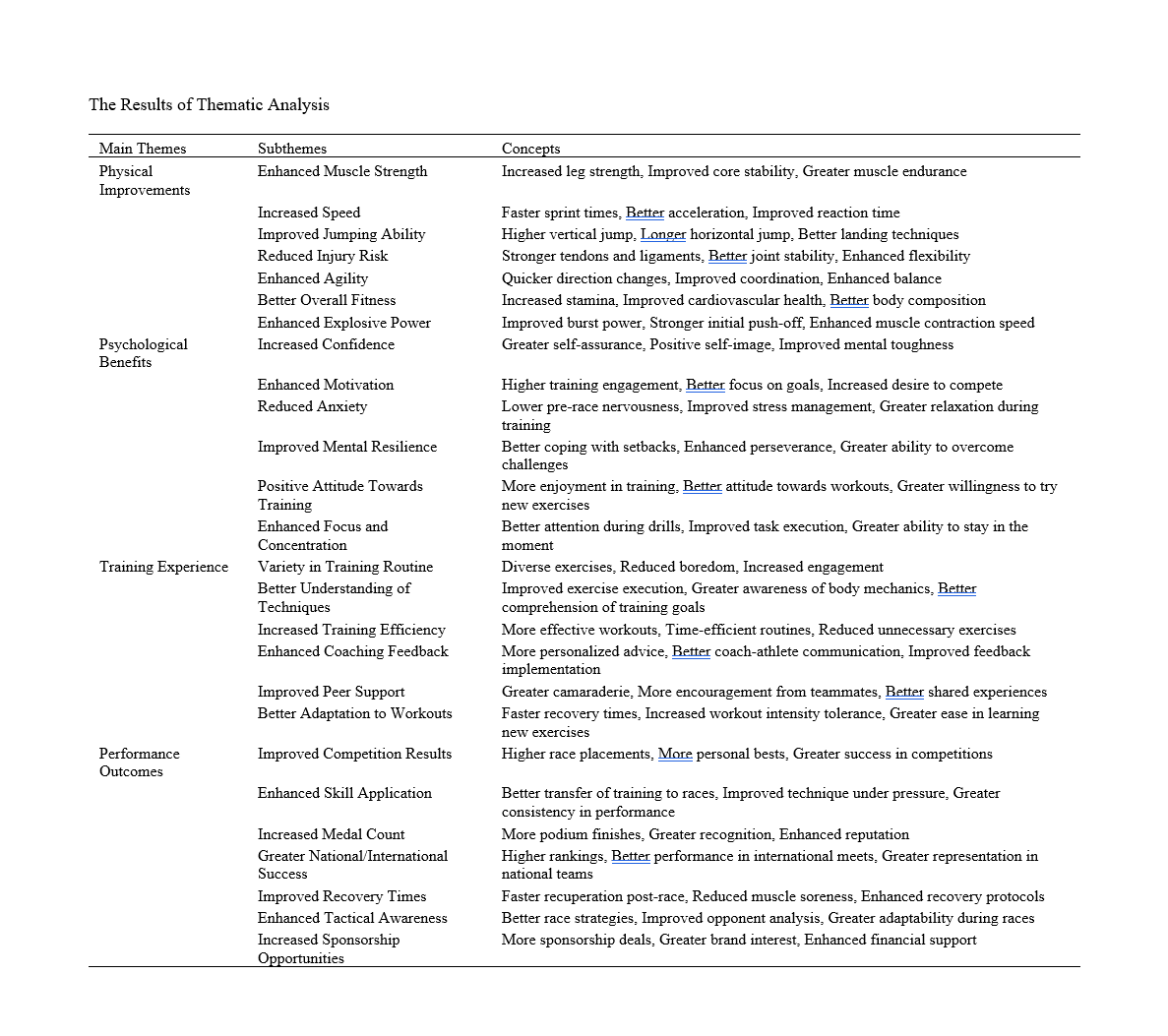
Findings: The study revealed significant physical improvements attributed to plyometric training, including enhanced muscle strength, increased speed, improved jumping ability, and reduced injury risk. Psychological benefits such as increased confidence, enhanced motivation, and improved mental resilience were also noted. Participants reported a better training experience with diverse and efficient routines, improved technique understanding, and strong peer support. Performance outcomes showed notable improvements in competition results, skill application, and recovery times. These findings align with existing literature, confirming the comprehensive benefits of plyometric training for sprinters.
Conclusion: Plyometric training significantly enhances explosive power and overall performance in sprinters. The physical, psychological, and performance-related benefits make it a crucial component of athletic training programs. Despite limitations such as the small sample size and reliance on self-reported data, the study provides valuable insights into the multifaceted advantages of plyometric exercises.
Downloads
References
1. Shedge SS. Optimizing Agility and Athletic Proficiency
in Badminton Athletes Through Plyometric Training: A Review.
Cureus. 2024. [DOI]
2. Zaman MM, Mondal P. Effect of Twelve Weeks
Plyometric Training on Leg Explosive Strength for 14 to 19 Year
Old Athletes. International Journal of Physical Education Sports
and Health. 2023;10(2):246-9. [DOI]
3. Sudirman R. Plyometric Training and Circuit Training in
Terms of Eye-Hand Coordination: How It Affects the Explosive
Power of Sickle Attacks? Retos. 2023;52:131-7. [DOI]
4. Loturco I, Pereira LA, Freitas TT, Túlio Bernardo
Macedo Alfano M, Mercer VP, Fernandes VMC, et al. Plyometric
Training Practices of Brazilian Olympic Sprint and Jump Coaches:
Toward a Deeper Understanding of Their Choices and Insights.
Journal of Human Kinetics. 2023;88:131-50. [PMID: 37559773]
[PMCID: PMC10407309] [DOI]
5. Pamuk ÖN, Hancı E, Uçar N, Hasanli N, Gundogdu A,
Özkaya YG. Resisted Plyometric Exercises Increase Muscle
Strength in Young Basketball Players. Revista Brasileira De
Medicina Do Esporte. 2022;28(4):331-6. [PMID: 36196355]
[PMCID: PMC9465740] [DOI]
6. Kosova S, Beyhan R, Kosova MK. The Effect of 8-Week
Plyometric Training on Jump Height, Agility, Speed and
Asymmetry. Pedagogy of Physical Culture and Sports.
2022;26(1):13-8. [DOI]
7. Borah P, Sajwan AS. Effect of Plyometric Training on
Repeated Countermovement Jump Performance of Collegiate
Athletes. International Journal of Physical Education Sports and
Health. 2022;9(4):168-72. [DOI]
8. Adnyana IKS, Astra IIB, Muliarta IW, Gunarto P,
Suwiwa IG. The Effect of Double Leg Bound and Incline Bound
Plyometrics Training Methods on Increasing Legs Power.
2022:133-8. [DOI]
9. Aksović N, Bjelica B, Milanović F, Jovanović N,
Zelenović M. Plyometric Training Effects on Explosive Power,
Sprint and Direction Change Speed in Basketball: A Review.
Turkish Journal of Kinesiology. 2021;7(2):73-9. [DOI]
10. Arazi H, Asadi A. The Effect of Aquatic and Land
Plyometric Training on Strength, Sprint, and Balance in Young
Basketball Players. Journal of Human Sport and Exercise.
2011;6(1):101-11. [DOI]
11. Asadi A. Muscular Performance Adaptations to ShortTerm Plyometric Training on Sand: Influence of Interday Rest.
Journal of Human Sport and Exercise. 2015;10(3). [DOI]
12. Hamzah A, Fauziah E, Wulandari TW. Plyometric
Training Combinations With Mobilization With Movement Better
Compared With Plyometric Training Combination With Strain
Counter Strains in Improving Balance in the Chronic Ankle
Instability in Barito Farma Clinic. Jurnal Kajian Ilmiah Kesehatan
Dan Teknologi. 2020;2(2):1-8. [DOI]
13. Bawiskar D, Phansopkar P. Efficacy of Agility Training
in a Police Cadet: A Case Study. Journal of Pharmaceutical
Research International. 2021:281-7. [DOI]
14. Bolger R, Lyons M, Harrison AJ, Kenny IC. Coaching
Sprinting: Expert Coaches’ Perception of Resistance-Based
Training. International Journal of Sports Science & Coaching.
2016;11(5):746-54. [DOI]
15. Ince T, Daglioglu O. The Effect of the Plyometric
Training Program on Sportive Performance Parameters in Young
Soccer Players. Turkish Journal of Sport and Exercise. 2018. [DOI]
16. Chmielewski TL, Myer GD, Kauffman DF, Tillman SM.
Plyometric Exercise in the Rehabilitation of Athletes:
Physiological Responses and Clinical Application. Journal of
Orthopaedic and Sports Physical Therapy. 2006;36(5):308-19.
[PMID: 16715831] [DOI]
17. Benito-Martínez E, Lara-Sánchez A, Berdejo-del-Fresno
D, López EJM. Effects of Combined Electrostimulation and
Plyometric Training on Vertical Jump and Speed Tests. Journal of
Human Sport and Exercise. 2011;6(4):603-15. [DOI]
18. Han G-S, Lee M, Cho B-J. Effects of Dynamic Stretch
Training on Lower Extremity Power Performance of Young
Sprinters. Journal of Physical Therapy Science. 2011;23(3):401-4.
[DOI]
19. Hentilä J, Hulmi JJ, Laakkonen EK, Ahtiainen JP,
Suominen H, Korhonen M. Sprint and Strength Training Modulates
Autophagy and Proteostasis in Aging Sprinters. Medicine &
Science in Sports & Exercise. 2020;52(9):1948-59. [PMID:
32205677] [DOI]
20. Khan W, Muhammad K, Sohail S, Khan V, Arif T,
Мухаммед К, et al. Effects of Varied Packages of Plyometric
Training on Selected Motor Ability Components Among
University Students. Physical Education of Students.
2020;24(5):278-85. [DOI]
21. Kurniawan C, Setijono H, Hidayah T, Hadi H, Sugiharto
S. The Effect Plyometric Training With Active-Passive Recovery
for 8 Weeks on Performance Physical Abilities Male Judo Athletes.
Pedagogy of Physical Culture and Sports. 2021;25(6):361-6. [DOI]
22. Lakshmikanth VP, Paul J, Ebenezer BSI, Ramanathan.
Effects of Plyometric Training and Conventional Training on
Agility Performance in Tennis Players. International Journal of
Medical and Exercise Science. 2018;04(03):492-9. [DOI]
23. Lima JB, Marin DP, Barquilha G, Silva LD, Puggina EF,
Pithon‐Curi TC, et al. Acute Effects of Drop Jump Potentiation
Protocol on Sprint and Countermovement Vertical Jump
Performance. Human Movement. 2011;12(4). [DOI]
24. Loturco I. Effects of Different Conditioning Activities on
the Sprint Performance of Elite Sprinters: A Systematic Review
With Meta-Analysis. International journal of sports physiology and
performance. 2024;19(7):712-21. [PMID: 38823792] [DOI]
25. Maciel LA, Patrício Lopes de Araújo L, Santos PA,
Barbosa LP, Gutierrez SD, Deus LA, et al. Intensity of Depression
Symptoms Is Negatively Associated With Catalase Activity in
Master Athletes. International Journal of Environmental Research
and Public Health. 2023;20(5):4397. [PMID: 36901407] [PMCID:
PMC10002178] [DOI]
26. Rimmer E, Sleivert GG. Effects of a Plyometrics
Intervention Program on Sprint Performance. The Journal of
Strength and Conditioning Research. 2000;14(3):295-301. [DOI]
27. Singh D, Singh S. Effects of Vertical and Horizontal
Plyometric Exercises on Running Speed. Human Movement.
2018;14(2):144-7. [DOI]
28. Sugisaki N, Kurokawa S. Effect of Lower-Body
Plyometric Training on Athletic Performance and Muscle–tendon
Properties. The Journal of Physical Fitness and Sports Medicine.
2014;3(2):205-9. [DOI]
29. Romadhoni WN, Irianto DP. The Effect of Plyometrics
Training and Strengths on Power Skills and Agility of Male Player
in Extracurricular Volleyball. 2018. [DOI]
30. Pereira LA, Boullosa D, Túlio Bernardo Macedo Alfano
M, Mercer VP, Fernandes V, Bishop C, et al. Post-Activation
Performance Enhancement in Sprinters: Effects of Hard Versus
Sand Surfaces. Journal of Human Kinetics. 2022;82:173-80. [DOI]
31. Villarreal ESd, Requena B, Cronin J. The Effects of
Plyometric Training on Sprint Performance: A Meta-Analysis. The
Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research. 2012;26(2):575-
84. [PMID: 22240550] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mathias Bastholm , Geoffrey Olsen (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







