Comparison of the Impact of Body Percussion Exercises on Executive and Balance Performance in Intellectually Disabled and Healthy Girls of Ramhormoz City
Keywords:
Balance, Executive Function, Intellectually Disabled Children, Body PercussionAbstract
Objective: The purpose of the present study was to compare the effects of body percussion exercises on the executive and balance performance of children with intellectual disabilities and their healthy counterparts.
Methods and Materials: The statistical population included healthy children and those with intellectual disabilities from Ramhormoz city, from which 20 healthy children (10 experimental, 10 control) and 20 children with intellectual disabilities (10 experimental, 10 control) aged 9 to 11 years were selected to participate in this research through pre-test and post-test evaluations using the Continuous Performance Test (sustained attention), Stroop Color and Word Test (response inhibition), Stork Stand (static balance), and Heel-Toe Walking (dynamic balance). The experimental groups (both healthy and with disabilities) received the selected body percussion intervention program in 45-minute group sessions twice a week for 8 weeks; however, the control groups (both healthy and with disabilities) engaged in usual school activities. Data analysis was performed using covariance analysis at the significance level of p ≤ 0.05.
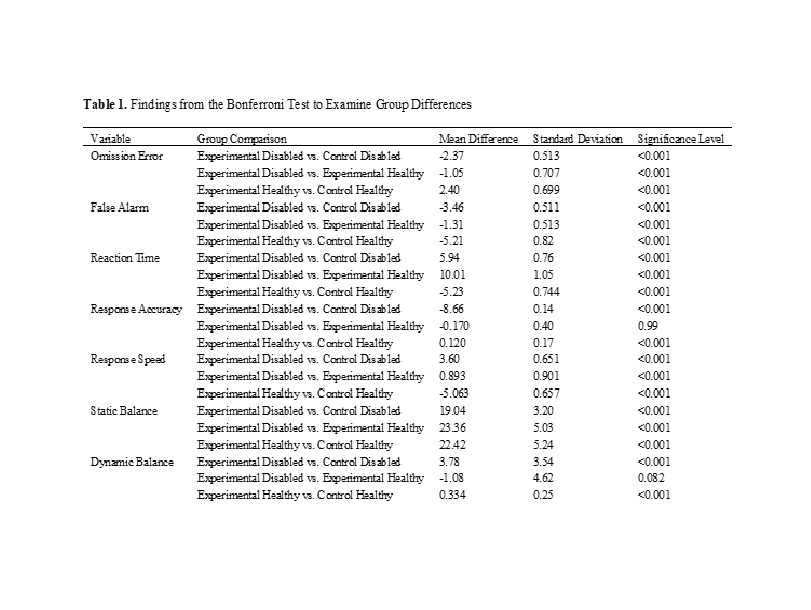
Results: The results showed that the effect of body percussion exercises on sustained attention (p = 0.001), response inhibition (p = 0.001), and static and dynamic balance (p = 0.001) was significant, and participants in the experimental groups performed better than those in the control groups (p = 0.001).
Conclusions: Based on the findings, it seems that body percussion exercises are a beneficial intervention for improving motor and cognitive skills in both healthy children and those with intellectual disabilities; therefore, it is recommended that these exercises be used in physical education programs in schools and rehabilitation centers.
Downloads
References
1. Dayan E, Casile A, Levit-Binnun N, Giese MA, Hendler
T, Flash T. Neural representations of kinematic laws of motion:
evidence for action-perception coupling. Proceedings of the
National Academy of Sciences. 2007;104(51):20582-7. [PMID:
18079289] [PMCID: PMC2154474] [DOI]
2. Bünger A, Urfer-Maurer N, Grob A. Multimethod
assessment of attention, executive functions, and motor skills in
children with and without ADHD: Children’s performance and
parents’ perceptions. Journal of attention disorders.
2021;25(4):596-606. [PMID: 30700232] [DOI]
3. Bernardi M, Leonard HC, Hill EL, Botting N, Henry LA.
Executive functions in children with developmental coordination
disorder: a 2‐year follow‐up study. Developmental Medicine &
Child Neurology. 2018;60(3):306-13. [PMID: 29238952] [DOI]
4. Amani M. Effect of strengthening executive functions on
the academic achievement in the children with nonverbal learning
disabilities. 2016.
5. Jalilvand M. Effect of Table Tennis Training Program on
Sustained Attention and Cognitive Flexibility of Children with
Developmental Coordination Disorder. The Neuroscience Journal
of Shefaye Khatam. 2020;9(1):99-109. [DOI]
6. Jalilvand M, Samadi H, Heydari Y. The Effects of
Executive Function Training Program by Physical Activity on
Response Inhibition in Children With Developmental Coordination
Disorder. Middle Eastern Journal of Disability Studies.
2021;11(0):199-.
7. Barrow WJ, Jaworski M, Accardo PJ. Persistent toe
walking in autism. Journal of Child Neurology. 2011;26(5):619-21.
[PMID: 21285033] [DOI]
8. Baccouch R, Rebai H, Sahli S. Kung-fu versus
swimming training and the effects on balance abilities in young
adolescents. Physical therapy in sport. 2015;16(4):349-54. [PMID:
26095581] [DOI]
9. Sam K-L, Smith AW, Kai LS. Visual Cognition and
Dynamic Balance in Persons with Autism Spectrum Disorder.
International Journal of Social Science and Humanity.
2017;7(5):274-7.
10. Siminghalam M, Alibakhshi H, Valikhani N, Gholami
M, Mirshoja MS. The Effects of Body Percussion Exercise on
Balance in Older Adults. Journal of Modern Rehabilitation. 2022.
[DOI]
11. Schreck KA, Mulick JA, Smith AF. Sleep problems as
possible predictors of intensified symptoms of autism. Research in
developmental disabilities. 2004;25(1):57-66. [PMID: 14733976]
[DOI]
12. Romero-Naranjo FJ. Body Percussion in the Physical
Education and Sports Sciences. An Approach to its systematization
according to the BAPNE Method. International Journal of
Innovation and Research in Educational Sciences. 2020;7(5):421-
31. [PMID: 21807670] [DOI]
13. Fong SS, Chung JW, Cheng YT, Yam TT, Chiu H-C,
Fong DY, et al. Attention during functional tasks is associated with
motor performance in children with developmental coordination
disorder: A cross-sectional study. Medicine. 2016;95(37). [PMID:
27631272] [PMCID: PMC5402615] [DOI]
14. Lotfi S, Khalafbeigi M, Matin Sadr N, Saneii SH. The
effectiveness of body percussion rhythmic exercises on motor skills
in children with mild intellectual disability between 8-12 years old.
Function and Disability Journal. 2018;1(3):40-7.
15. Bo W, Lei M, Tao S, Jie LT, Qian L, Lin FQ, Ping WX.
Effects of combined intervention of physical exercise and cognitive
training on cognitive function in stroke survivors with vascular
cognitive impairment: a randomized controlled trial. Clinical
rehabilitation. 2019;33(1):54-63. [PMID: 30064268] [DOI]
16. Sulkin I, Brodsky W, editors. The effects of handclapping songs training on temporal-motor skills among
elementary school children. Proceedings of the Summer Workshop
on Music, Language, and Movement; 2007: University of
Edinburgh Edinburgh.
17. Hadian Fard H, Najarian B, Shokrkon H, Mehrabizadeh
Honarmand M. Preparing and making the Farsi form of continuous
performance test. Psychology. 2000(16):-.
18. Jafari F, Arjmandnia AA, Rostami R. The effect of
neuropsychological rehabilitation program on working memory
and response inhibition of students with dysgraphia. Journal of
Psychological Science. 2021;20(98):233-46.
19. Amirizade F, Bagheri S, Faraji G. The effect of braille
tonic training on static, dynamic balance and psychological factors
in adult females. Journal of Psychological Science.
2019;18(83):2117-24.
20. Coetsee C, Terblanche E. The effect of three different
exercise training modalities on cognitive and physical function in a
healthy older population. European Review of Aging and Physical
Activity. 2017;14(1):13. [PMID: 28811842] [PMCID:
PMC5553712] [DOI]
21. Loprinzi PD, Kane CJ. Exercise and Cognitive Function:
A Randomized Controlled Trial Examining Acute Exercise and
Free-Living Physical Activity and Sedentary Effects. Mayo Clinic
Proceedings. 2015;90(4):450-60. [PMID: 25746399] [DOI]
22. Ziereis S, Jansen P. Effects of physical activity on
executive function and motor performance in children with ADHD.
Research in Developmental Disabilities. 2015;38:181-91. [PMID:
25561359] [DOI]
23. Ross SM, Case L, Leung W. Aligning Physical Activity
Measures With the International Classification of Functioning,
Disability and Health Framework for Childhood Disability. Quest.
2016;68(4):521-35. [DOI]
24. Peck–Murray JA. Utilizing everyday items in play to
facilitate hand therapy for pediatric patients. Journal of Hand
Therapy. 2015;28(2):228-32. [PMID: 25060856] [DOI]
25. Girgin N, Algun ZC. The effect of body percussion on
balance and coordination in elderly people. Journal of Traditional
Medical Complementary Therapies. 2021. [DOI]
26. Bugos JA. The Effects of Bimanual Coordination in
Music Interventions on Executive Functions in Aging Adults.
Frontiers in Integrative Neuroscience. 2019;13. [PMID: 31866838]
[PMCID: PMC6906951] [DOI]
27. Eskandarnejad M, Jahedi Khajeh M, Rezaee F. Impact of
Perceptual-Motor Training Basketball on Balance Function of
Children with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder. The
Scientific Journal of Rehabilitation Medicine. 2017;6(3):135-43.
28. Bressel E, Yonker JC, Kras J, Heath EM. Comparison of
static and dynamic balance in female collegiate soccer, basketball,
and gymnastics athletes. Journal of athletic training. 2007;42(1):42.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Farnaz Torabi, Sahar Abasi Hormozi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







