The Structural Relationships of Emotional Neglect with Risky Behaviors in Prisoners Considering the Mediating Role of Emotion Regulation Strategies
Keywords:
Emotional neglect, risky behaviors, cognitive emotion regulation strategies, prisonersAbstract
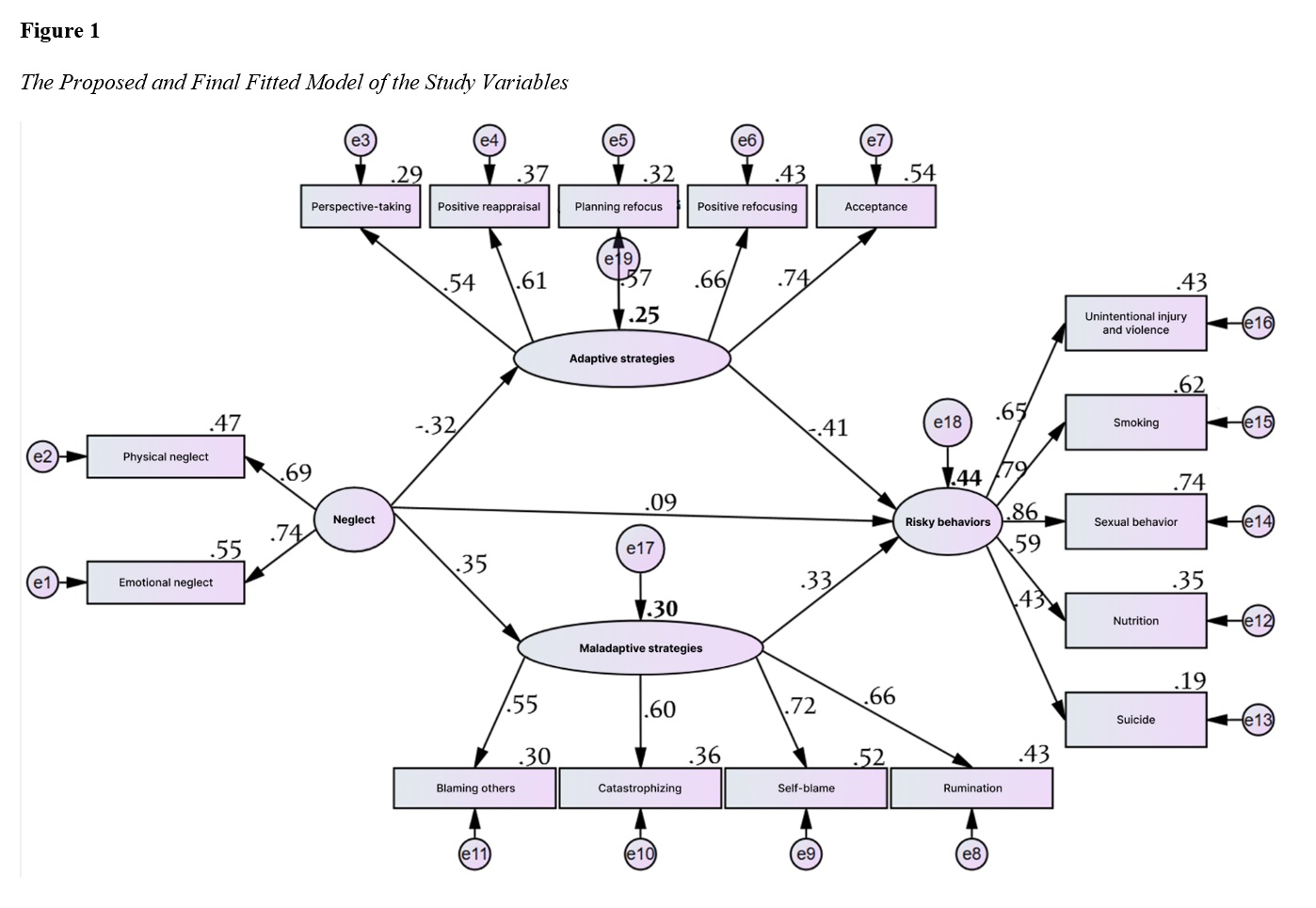
This study aimed to investigate the structural relationships of emotional neglect with risky behaviors in prisoners, considering the mediating role of emotion regulation strategies. The research method is descriptive-correlational. The statistical population consists of all prisoners in the city of Shiraz. The research sample included 409 prisoners from Shiraz, selected through purposive sampling. Data were collected using the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire (Bernstein et al., 2003), the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire (Garnefski et al., 2001), and the Youth Risk Behavior Scale (Snow et al., 2019). Structural equation modeling (SEM) was conducted using AMOS 24 and SPSS 27 to evaluate the proposed model. The correlation coefficient results indicated a negative relationship between emotional neglect and adaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies with risky behaviors (P ≤ 0.05). Additionally, there was a significant positive relationship between maladaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies and risky behaviors (P ≤ 0.05). The findings suggest an adequate fit of the proposed model with the data. The results of the structural model showed that 25% of the variance in adaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies and 30% of the variance in maladaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies were explained by emotional neglect. Furthermore, 44% of the variance in risky behaviors was explained by emotional neglect, adaptive, and maladaptive cognitive emotion regulation strategies. Based on these findings, early intervention and preventive measures are crucial in reducing the negative impact of emotional neglect. Specifically, focusing on interventions based on mentalization and emotion regulation can significantly improve emotional and relational problems arising from adverse early life experiences.
Downloads
References
1. Nishimi K, Borsari B, Marx BP, Rosen RC, Cohen BE, Woodward E, et al. Clusters of COVID-19 protective and risky behaviors and their associations with pandemic, socio-demographic, and mental health factors in the United States. Preventive Medicine Reports. 2022;25:101671. [PMID: 34926133] [PMCID: PMC8669937] [DOI]
2. Gómez-Figueroa H, Camino-Proaño A. Mental and behavioral disorders in the prison context. Revista Espanola de Sanidad Penitenciaria. 2022;24(2):66-74. [PMID: 36256558] [PMCID: PMC9578298] [DOI]
3. Yadlosky LB, Mowrey WB, Pimentel SS. Risky business: Considerations of emotion regulation and high-risk behaviors in anxious adolescents. Journal of Anxiety Disorders. 2023;99:102760. [PMID: 37672917] [DOI]
4. Tariq N, Gupta V. High Risk Behaviors. Stat Pearls: Stat Pearls Publishing; 2023
5. Choi J, Wentling R. Convict Code, Risky Lifestyles, and Violent Victimization Among Inmates in South Korea. Violence and Victims. 2021;36(2):233-50. [PMID: 33361448] [DOI]
6. Benchamas J, Senahad N, Padchasuwan NH, Laoraksawong P, Phimha S, Banchonhattakit P. Factors associated with risky sexual behaviors among undergraduate students in Thailand. BMC Public Health. 2024;24(1):2967. [PMID: 39455991] [PMCID: PMC11515101] [DOI]
7. London S, Quinn K, Scheidell JD, Frueh BC, Khan MR. Adverse Experiences in Childhood and Sexually Transmitted Infection Risk From Adolescence Into Adulthood. Sexually Transmitted Diseases. 2017;44(9):524-32. [PMID: 28809769] [PMCID: PMC5942895] [DOI]
8. Kim-Spoon J, Herd T, Brieant A, Peviani K, Deater-Deckard K, Lauharatanahirun N, et al. Maltreatment and brain development: The effects of abuse and neglect on longitudinal trajectories of neural activation during risk processing and cognitive control. Developmental Cognitive Neuroscience. 2021;48:100939. [PMID: 33706181] [PMCID: PMC7960935] [DOI]
9. Wilk K, Starowicz A, Szczecińska M, Budziszewska M. Childhood emotional neglect and its relationship with well-being: Mediation analyses. European Journal of Trauma & Dissociation. 2024;8(3):100434. [DOI]
10. Xu B, Wei S, Yin X, Jin X, Yan S, Jia L. The relationship between childhood emotional neglect experience and depressive symptoms and prefrontal resting functional connections in college students: The mediating role of reappraisal strategy. Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience. 2023;17:927389. [PMID: 36969801] [PMCID: PMC10037214] [DOI]
11. Glickman EA, Choi KW, Lussier AA, Smith BJ, Dunn EC. Childhood emotional neglect and adolescent depression: assessing the protective role of peer social support in a longitudinal birth cohort. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2021;12:681176. [PMID: 34434126] [PMCID: PMC8381469] [DOI]
12. Jin X, Xu B, Lin H, Chen J, Xu R, Jin H. The influence of childhood emotional neglect on emotional face processing in young adults. Acta Psychologica. 2023;232:103814. [PMID: 36527819] [DOI]
13. Stoltenborgh M, Bakermans‐Kranenburg MJ, Alink LR, van Ijzendoorn MH. The prevalence of child maltreatment across the globe: Review of a series of meta‐analyses. Child Abuse Review. 2015;24(1):37-50. [DOI]
14. Taillieu TL, Brownridge DA, Sareen J, Afifi TO. Childhood emotional maltreatment and mental disorders: Results from a nationally representative adult sample from the United States. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2016;59:1-12. [PMID: 27490515] [DOI]
15. Grummitt LR, Kelly EV, Barrett EL, Lawler S, Prior K, Stapinski LA, et al. Associations of childhood emotional and physical neglect with mental health and substance use in young adults. Australian & New Zealand Journal of Psychiatry. 2022;56(4):365-75. [DOI]
16. Salokangas RKR, Schultze-Lutter F, Schmidt SJ, Pesonen H, Luutonen S, Patterson P, et al. Childhood physical abuse and emotional neglect are specifically associated with adult mental disorders. Journal of Mental Health. 2020;29(4):376-84. [PMID: 30675805] [DOI]
17. Derin S, Selman SB, Alyanak B, Soylu N. The role of adverse childhood experiences and attachment styles in social anxiety disorder in adolescents. Clinical Child Psychology and Psychiatry. 2022;27(3):644-57. [PMID: 35258382] [DOI]
18. Haslam Z, Taylor EP. The relationship between child neglect and adolescent interpersonal functioning: A systematic review. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2022;125:105510. [PMID: 35078090] [DOI]
19. Müller LE, Bertsch K, Bülau K, Herpertz SC, Buchheim A. Emotional neglect in childhood shapes social dysfunctioning in adults by influencing the oxytocin and the attachment system: Results from a population-based study. International Journal of Psychophysiology. 2019;136:73-80. [PMID: 29859994] [DOI]
20. Weiss NH, Sullivan TP, Tull MT. Explicating the role of emotion dysregulation in risky behaviors: A review and synthesis of the literature with directions for future research and clinical practice. Current Opinion in Psychology. 2015;3:22-9. [PMID: 25705711] [PMCID: PMC4332392] [DOI]
21. Rothenberg WA, Di Giunta L, Lansford JE, Lunetti C, Fiasconaro I, Basili E, et al. Daily associations between emotions and aggressive and depressive symptoms in adolescence: The mediating and moderating role of emotion dysregulation. Journal of Youth and Adolescence. 2019;48:2207-21. [PMID: 31302795] [PMCID: PMC6993942] [DOI]
22. Megreya AM, Al-Emadi AA. The impact of cognitive emotion regulation strategies on math and science anxieties with or without controlling general anxiety. Scientific Reports. 2024;14(1):19726. [PMID: 39183319 ] [PMCID: PMC11345414] [DOI]
23. Kuo JR, Fitzpatrick S, Ip J, Uliaszek A. The who and what of validation: an experimental examination of validation and invalidation of specific emotions and the moderating effect of emotion dysregulation. Borderline Personality Disorder and Emotion Dysregulation. 2022;9(1):15. [PMID: 35581663] [PMCID: PMC9116024] [DOI]
24. Soper DS. A-priori Sample Size Calculator for Structural Equation Models2024.
25. Zahmatkesh Rokhi N, Ebrahimzadeh Zegami S, Jamali J, Taghipour A. Psychometric Properties of the Persian Version of the Youth Risk Behavior Survey (YRBS 2019). Isfahan Medical School Journal. 2021;39(627):390-9. [DOI]
26. Garnefski N, Kraaij V. Cognitive emotion regulation questionnaire-development of a short 18-item version (CERQ-short). Personality and Individual Differences. 2006;41(6):1045-53. [DOI]
27. Garnefski N, Kraaij V. Specificity of relations between adolescents' cognitive emotion regulation strategies and symptoms of depression and anxiety. Cognition & Emotion. 2018;32(7):1401-8. [PMID: 27648495] [DOI]
28. Garnefski N, Kraaij V, Spinhoven P. Negative life events, cognitive emotion regulation and emotional problems. Personality and Individual Differences. 2001;30(8):1311-27. [DOI]
29. Hassani J. Investigating the Reliability and Validity of the Short Form of the Cognitive Emotion Regulation Questionnaire. Behavioral Sciences Research Journal. 2011;9(4):229-40.
30. Bernstein DP, Stein JA, Newcomb MD, Walker E, Pogge D, Ahluvalia T, et al. Development and validation of a brief screening version of the Childhood Trauma Questionnaire. Child Abuse & Neglect. 2003;27(2):169-90. [PMID: 12615092] [DOI]
31. Roy A. Combination of family history of suicidal behavior and childhood trauma may represent correlate of increased suicide risk. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2011;130(1-2):205-8. [PMID: 20943272] [DOI]
32. Ebrahimi H, Dezhkam M, Saghaye-Eslami T. Childhood Trauma and Suicide Attempts in Adulthood. Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology. 2013;19(4):275-82.
33. Sánchez-López MT, Fernández-Berrocal P, Gómez-Leal R, Megías-Robles A. Evidence on the relationship between emotional intelligence and risk behavior: a systematic and meta-analytic review. Frontiers in Psychology. 2022;13:810012. [PMID: 35222197] [PMCID: PMC8863602] [DOI]
34. Bozzini AB, Bauer A, Maruyama J, Simões R, Matijasevich A. Factors associated with risk behaviors in adolescence: a systematic review. Revista Brasileira de Psiquiatria. 2021;43(2):210-21. [PMID: 32756805] [PMCID: PMC8023154] [DOI]
35. Gross JJ. Emotion regulation: Current status and future prospects. Psychological Inquiry. 2015;26(1):1-26. [DOI]
36. Bagiyan Kulehmarzi MJ, Yaztappeh JS, Khanjani S, Abasi I, Rajabi M, Mojahed AA. Study of Early Life Experiences, Temperament, Character, and Psychological Pain in Suicide Attempters and Normal Individuals. Middle East Journal of Rehabilitation and Health Studies. 2023;10(1). [DOI]
37. Hébert M, Langevin R, Oussaïd E. Cumulative childhood trauma, emotion regulation, dissociation, and behavior problems in school-aged sexual abuse victims. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2018;225:306-12. [PMID: 28843081] [PMCID: PMC5777856] [DOI]
38. Dubowitz H, Roesch S, Lewis T, Thompson R, English D, Kotch JB. Neglect in Childhood, Problem Behavior in Adulthood. Journal of Interpersonal Violence. 2022;37(23-24):NP22047-NP65. [PMID: 35156437] [PMCID: PMC9374847] [DOI]
39. Bagiyan Koulemarz MJ, Karami J, Momeni K, Elahi A. Investigating the Role of Cognitive Abilities and Emotional Regulation Difficulties in Predicting the Grouping Membership of People Attempting Suicide and Normal Individuals. Zanco Journal of Medical Sciences. 2019;19(63):42-58.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Soudabeh Ershadi Manesh (Corresponding Author); Sara Kafi Malak (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















