Explaining the Causal Relationships Between Attachment Styles and Pain in Women with Rheumatoid Arthritis: The Mediating Role of Mood Disorders
Keywords:
attachment style, pain, mood problems, rheumatoid arthritisAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to explain the causal relationships between attachment styles and pain, with the mediating role of mood disorders in women with rheumatoid arthritis.
Methods and Materials: In a cross-sectional study using structural equation modeling, 286 participants diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis were selected through purposive sampling during the period from November 2022 to June 2023. The participants were recruited from three hospitals in Tehran: Loghman, Taleghani, and Shahid Tajrish. After obtaining informed consent and confirming the eligibility criteria, the participants entered the study process. Three indices—attachment styles, pain, and mood disorders—were completed by the participants at a single time point. Data were analyzed using SPSS and AMOS version 25 software.
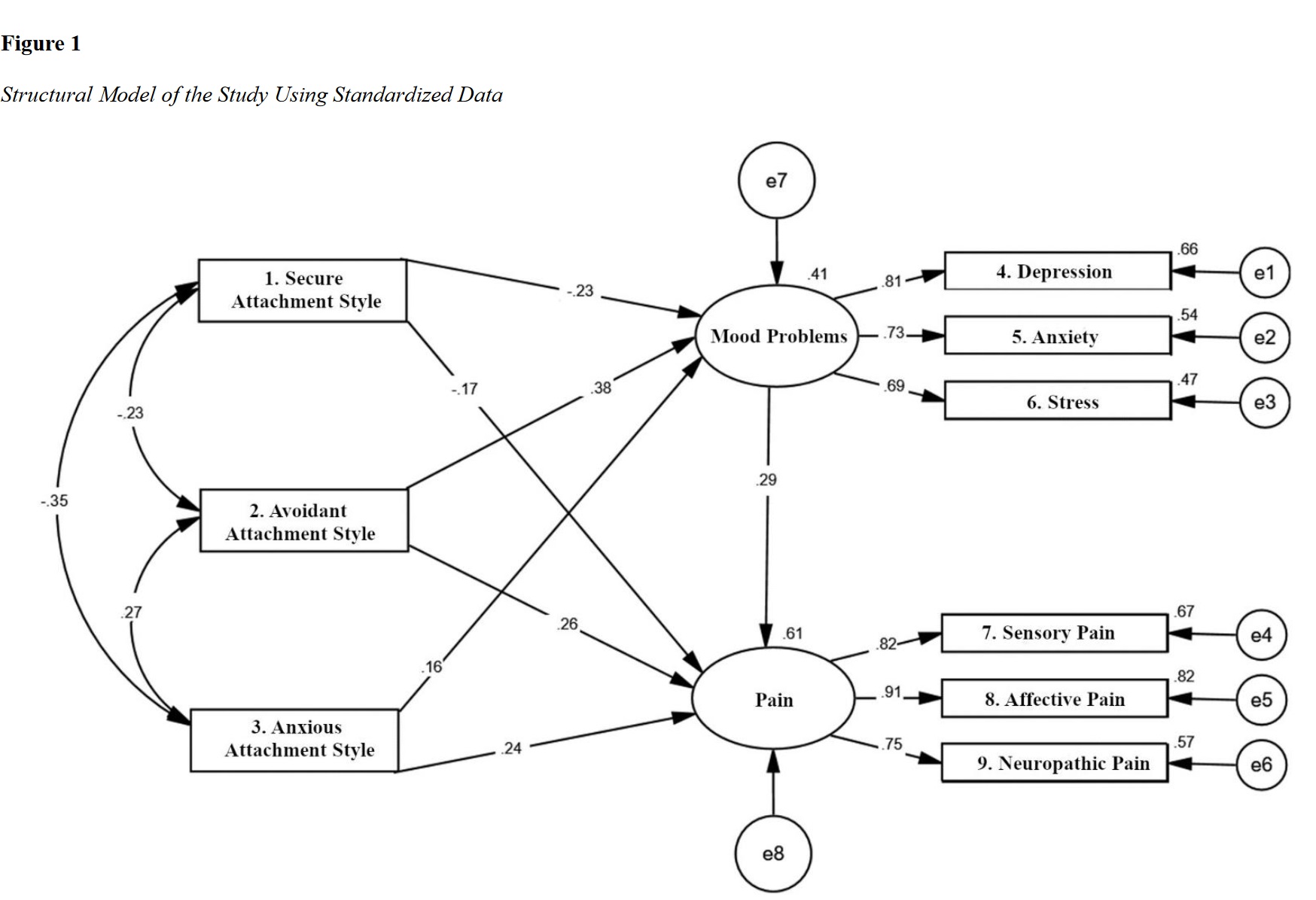
Findings: The data analysis showed that the path coefficient between mood disorders and pain was positive and significant (β = 0.291, p = 0.001). The indirect path coefficient between anxious attachment style (β = 0.045, p = 0.023) and avoidant attachment style (β = 0.111, p = 0.001) with pain was positive, while the indirect path coefficient between secure attachment style (β = -0.066, p = 0.001) and pain was negative and significant.
Conclusion: The findings of this study, consistent with prior research, indicate a relationship between attachment styles and pain, mediated by mood disorders. Overall, mood disorders and attachment styles are crucial variables in understanding the pain experience in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, and they may serve as unique therapeutic targets in the multifaceted management of such conditions.
Downloads
References
Abbasian Hadadan, M. (2024). The Effectiveness of Schema Therapy on Psychological Distress and Emotional Regulation in Individuals with Borderline Personality Disorder. Journal of Psychological Dynamics in Mood Disorders (PDMD), 3(1), 160-174. https://doi.org/10.22034/pdmd.2024.454880.1088
Abdelaziz, E. M., Alsadaan, N., Alqahtani, M., Elsharkawy, N. B., Ouda, M. M. A., Ramadan, O. M. E., Shaban, M., & Shokre, E. S. (2024). Effectiveness of Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT) on Psychological Distress among Mothers of Children with Autism Spectrum Disorder: The Role of Problem-Solving Appraisal. Behavioral Sciences, 14(1), 46. https://www.mdpi.com/2076-328X/14/1/46
Alnuaimi, A. S. M., Yousefi, Z., Aayedi, A. E. Z., & Golparvar, M. (2024). Prediction of Wisdom Based on Executive Function, Attachment Style, and Personality Traits. Journal of Adolescent and Youth Psychological Studies (JAYPS), 5(4), 1-10. https://journals.kmanpub.com/index.php/jayps/article/view/2283
Basu, N., Kaplan, C. M., Ichesco, E., Larkin, T., Harris, R. E., Murray, A., Waiter, G., & Clauw, D. J. (2018). Neurobiologic Features of Fibromyalgia Are Also Present Among Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Arthritis & Rheumatology (Hoboken, N.J.), 70(7), 1000-1007. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40451
Beurel, E., Toups, M., & Nemeroff, C. B. (2020). The Bidirectional Relationship of Depression and Inflammation: Double Trouble. Neuron, 107(2), 234-256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2020.06.002
Bowlby, J. (2008). Attachment. Basic Books. https://www.amazon.de/-/en/John-Bowlby-ebook/dp/B06XKBXDLD
Brooks, S. K., Webster, R. K., Smith, L. E., Woodland, L., Wessely, S., Greenberg, N., & Rubin, G. J. (2020). Rapid review. Lancet, 395, 912-920. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30460-8
Cohen, S., Janicki-Deverts, D., Doyle, W. J., Miller, G. E., Frank, E., Rabin, B. S., & Turner, R. B. (2012). Chronic stress, glucocorticoid receptor resistance, inflammation, and disease risk. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 109(16), 5995-5999. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1118355109
Cross, M., Smith, E., Hoy, D., Carmona, L., Wolfe, F., Vos, T., Williams, B., Gabriel, S., Lassere, M., Johns, N., Buchbinder, R., Woolf, A., & March, L. (2014). The global burden of rheumatoid arthritis: estimates from the global burden of disease 2010 study. Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases, 73(7), 1316-1322. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204627
Cush, J. J. (2021). Rheumatoid Arthritis: Early Diagnosis and Treatment. The Medical Clinics of North America, 105(2), 355-365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mcna.2020.10.006
Deini, F., & Sasani, B. (2024). Investigating the Relationship Between Perceived Parenting Styles and Attachment Styles with Internet Addiction in Middle School Girls in Tehran. 8th International Conference on Law, Psychology, Educational and Behavioral Sciences, Tehran.
Ding, Q., Hu, W., Wang, R., Yang, Q., Zhu, M., Li, M., Cai, J., Rose, P., Mao, J., & Zhu, Y. Z. (2023). Signaling pathways in rheumatoid arthritis: implications for targeted therapy. Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy, 8(1), 68. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-023-01331-9
Edwards, R. R., Cahalan, C., Mensing, G., Smith, M., & Haythornthwaite, J. A. (2011). Pain, catastrophizing, and depression in the rheumatic diseases. Nature Reviews Rheumatology, 7(4), 216-224. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2011.2
Ensandoost, T., Samari, A. A., Bayazi, M. H., & Rajaei, A. (2021). The Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment based Therapy on Pain Perception and Pain Self-Efficacy in Patients with Chronic Musculoskeletal Pain [Research]. Iranian Journal of Rehabilitation Research in Nursing, 8(1), 25-34. https://doi.org/10.22034/ijrn.8.1.25
Fazal, S. A., Khan, M., Nishi, S. E., Alam, F., Zarin, N., Bari, M. T., & Ashraf, G. M. (2018). A Clinical Update and Global Economic Burden of Rheumatoid Arthritis. Endocrine, Metabolic & Immune Disorders Drug Targets, 18(2), 98-109. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871530317666171114122417
Forsythe, L. P., Romano, J. M., Jensen, M. P., & Thorn, B. E. (2012). Attachment style is associated with perceived spouse responses and pain-related outcomes. Rehabilitative Psychology, 57, 290-300. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0030083
Hunter, J., & Maunder, R. (2015). Improving patient treatment with attachment theory: A guide for primary care practitioners and specialists. Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-23300-0
Joaquim, A. F., & Appenzeller, S. (2015). Neuropsychiatric manifestations in rheumatoid arthritis. Autoimmunity Reviews, 14(12), 1116-1122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2015.07.015
Jones Amaowei, E. E., Anwar, S., Kavanoor Sridhar, K., Shabbir, K., Mohammed, E. H., Bahar, A. R., Talpur, A. S., Bhat, S., Zafar, S., & Qadar, L. T. (2022). Correlation of Depression and Anxiety With Rheumatoid Arthritis. Cureus, 14(3), e23137. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.23137
Kowal, J., McWilliams, L. A., Péloquin, K., Wilson, K. G., Henderson, P. R., & Fergusson, D. A. (2015). Attachment insecurity predicts responses to an interdisciplinary chronic pain rehabilitation program. Journal of Behavioral Medicine, 38(3), 518-526. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10865-015-9623-8
Li, X., & Su, Y. (2020). Diagnosis and treatment of early rheumatoid arthritis. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi, 59(9), 724-727. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112138-20200703-00644
Lim, D. H. (2023). A Challenging Target: Persistent Pain During the Remission State in Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients. Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, 30(1), 1-2. https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.22.0047
Lo Cricchio, M. G., Musso, P., Lo Coco, A., Cassibba, R., & Liga, F. (2022). The Relation Between Empathy and Aggression: The Role of Attachment Style. Europe's journal of psychology, 18(3), 319-336. https://doi.org/10.5964/ejop.4509
Machin, A., Hider, S., Dale, N., & Chew-Graham, C. (2017). Improving recognition of anxiety and depression in rheumatoid arthritis: a qualitative study in a community clinic. British Journal of General Practice, 67(661), e531-e537. https://doi.org/10.3399/bjgp17X691877
Mickelson, K. D., Kessler, R. C., & Shaver, P. R. (1997). Adult attachment in a nationally representative sample. Journal of personality and social psychology, 73(5), 1092-1106. https://doi.org/10.1037//0022-3514.73.5.1092
Mikulincer, M., & Shaver, P. R. (2012). An attachment perspective on psychopathology. World Psychiatry, 11(1), 11-15. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wpsyc.2012.01.003
Minhas, D., Murphy, A., & Clauw, D. J. (2023). Fibromyalgia and centralized pain in the rheumatoid arthritis patient. Current Opinion in Rheumatology, 35(3), 170-174. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOR.0000000000000929
Pietromonaco, P. R., Uchino, B., & Dunkel Schetter, C. (2013). Close relationship processes and health: implications of attachment theory for health and disease. Health Psychology, 32, 499-513. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0029349
Porter, L. S., Keefe, F. J., Davis, D., Rumble, M., Scipio, C., & Garst, J. (2012). Attachment styles in patients with lung cancer and their spouses: associations with patient and spouse adjustment. Supportive Care in Cancer, 20, 2459-2466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00520-011-1367-6
Prabha, J., Kumar, M., Kumar, D., Chopra, S., & Bhatia, A. (2024). Nano-platform strategies of herbal components for the management of rheumatoid arthritis: a review on the battle for next-generation formulations. Current Drug Delivery. https://doi.org/10.2174/1567201821666230825102748
Romeo, A., Tesio, V., Castelnuovo, G., & Castelli, L. (2017). Attachment Style and Chronic Pain: Toward an Interpersonal Model of Pain. Frontiers in psychology, 8, 284. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00284
Roshandel, Z., Ghaffari, A., Kazemi, R., & Nadermohammadi, M. (2022). Effectiveness of Acceptance and Commitment based Therapy on Pain Severity, Fatigue, and Alexithymia in Female Patients with Rheumatic Diseases. Applied Family Therapy Journal (AFTJ), 3(5), 84-100. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.aftj.3.5.6
Sarzi-Puttini, P., Zen, M., Arru, F., Giorgi, V., & Choy, E. A. (2023). Residual pain in rheumatoid arthritis: Is it a real problem? Autoimmunity Reviews, 22(11), 103423. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2023.103423
Sirois, F. M., & Gick, M. L. (2014). An appraisal-based coping model of attachment and adjustment to arthritis. Journal of Health Psychology, 21(5), 821-831. https://doi.org/10.1177/1359105314539531
Vergne-Salle, P., Pouplin, S., Trouvin, A. P., Bera-Louville, A., Soubrier, M., Richez, C., Javier, R. M., Perrot, S., & Bertin, P. (2020). The burden of pain in rheumatoid arthritis: Impact of disease activity and psychological factors. European Journal of Pain, 24(10), 1979-1989. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejp.1651
Wilson, C. L., & Ruben, M. A. (2011). A pain in her arm: romantic attachment orientations and the tourniquet task. Personal Relationships, 18, 242-265. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1475-6811.2011.01359.x
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Fahimeh Mardan (Author); Parvaneh Ghodsi (Corresponding Author); Moloud Keykhosrovani, Naser Amini, Leida Leilabadi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.














