AI Usage in Academic Writing: Perspectives of Stakeholders
Keywords:
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Academic Writing, Generative AI, Faculty Perspectives, Student PerspectivesAbstract
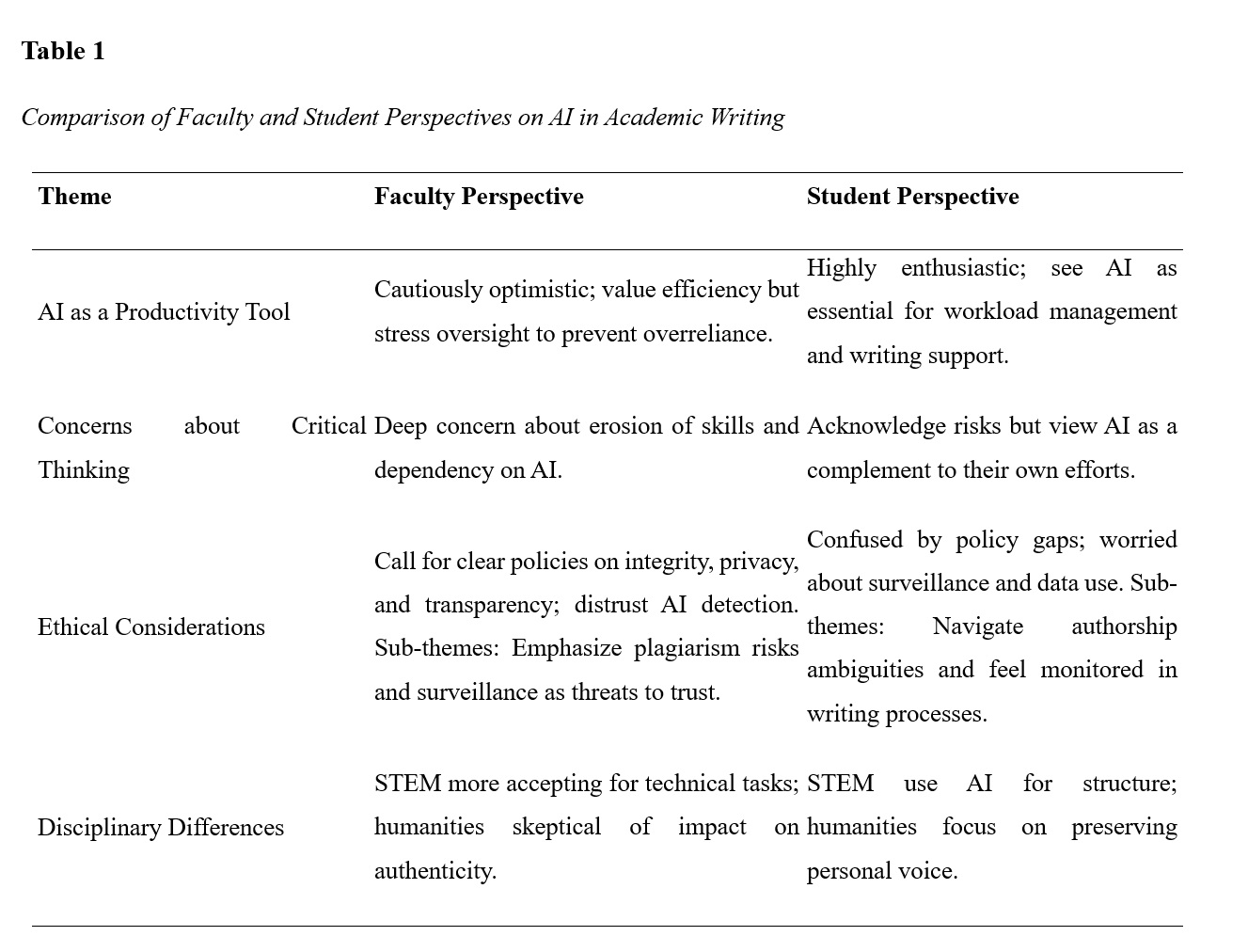
This qualitative study examines the complex attitudes, ethical considerations, and practical implications of integrating artificial intelligence (AI) in academic writing across key stakeholder groups, including university professors and students. Using semi-structured interviews with 40 participants (20 students and 20 faculty members) from diverse disciplines and institutional contexts, the research reveals divergent perspectives on AI’s role in academia. Faculty respondents expressed significant concerns about academic integrity, erosion of critical thinking, and the limitations of AI detection tools, which frequently misidentify human-written text as AI-generated. Conversely, students viewed AI as an essential productivity tool for overcoming writer’s block, refining ideas, and managing workload, though they acknowledged ethical ambiguities in its deployment. A critical tension emerged between AI’s perceived benefits—enhanced efficiency, personalized feedback, and accessibility—and its risks, including algorithmic bias, surveillance culture, and threats to student agency. Stakeholders agreed that institutional policies lag behind technological adoption, with current frameworks inadequately addressing transparency, data privacy, or equitable implementation. The study also identifies disciplinary variances: STEM educators favored AI for technical drafting, while humanities faculty emphasized its threat to authentic voice development. The findings advocate for a collaborative, multi-stakeholder approach to AI governance, emphasizing pedagogical redesign, ethical guidelines for explainable AI, and professional development to bridge digital literacy gaps. This research underscores the urgency of reimagining academic writing in the AI era, balancing innovation with the preservation of core educational values.
Downloads
References
Abduljawad, S. A. (2024). Investigating the impact of ChatGPT as an AI tool on ESL writing: Prospects and challenges in Saudi Arabian higher education. International Journal of Computer-Assisted Language Learning and Teaching, 14(1), 1-19. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJCALLT.367276
Al-Bukhrani, M., Alrefaee, Y., & Tawfik, M. (2025). Adoption of AI writing tools among academic researchers: a theory of reasoned action approach. PLoS One, 20(1), e0313837. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0313837
Alenezi, A. (2024). Obstacles to the use of AI applications in blackboard for faculty members at northern border university, Saudi Arabia. Mier Journal of Educational Studies Trends & Practices, 14(2), 248-268. https://doi.org/10.52634/mier/2024/v14/i2/2581
Alharbi, W. (2024). Mind the gap, please!: Addressing the mismatch between teacher awareness and student AI adoption in higher education. International Journal of Computer-Assisted Language Learning and Teaching, 14(1), 1-28. https://doi.org/10.4018/IJCALLT.351245
Ali, M., Suchiang, T., Saikia, T., & Gulzar, D. (2024). Perceived benefits and concerns of AI integration in higher education: insights from India. Educational Administration: Theory and Practice, 30(5), 656-668. https://doi.org/10.53555/kuey.v30i5.5122
Amirjalili, F., Neysani, M., & Nikbakht, A. (2024). Exploring the boundaries of authorship: a comparative analysis of AI-generated text and human academic writing in English literature. Frontiers in Education, 9. https://doi.org/10.3389/feduc.2024.1347421
Ardito, C. (2024). Generative ai detection in higher education assessments. New Directions for Teaching and Learning, 2025(182 Special Issue), 11-28. https://doi.org/10.1002/tl.20624
Asmara, Y., & Kastuhandani, F. (2024). Students’ lived experience in utilizing Quillbot as an online paraphrasing tool in academic writing. Globish an English-Indonesian Journal for English Education and Culture, 13(1), 56-65. https://doi.org/10.31000/globish.v13i1.10088
BaHammam, A. (2023). Balancing Innovation and Integrity: The Role of AI in Research and Scientific Writing. Nature and science of sleep, Volume 15, 1153-1156. https://doi.org/10.2147/nss.s455765
Bimpong, B., Atsise, P., & Owusu, F. (2024). Exploring the implementation of artificial intelligence (AI) writing tools in teaching and learning: faculty and students’ perspectives in higher education. East African Journal of Information Technology, 7(1), 380-393. https://doi.org/10.37284/eajit.7.1.2286
Bing, Z., & Leong, W. (2025). Ai on academic integrity and plagiarism detection. Asm Science Journal, 20(1), 1-9. https://doi.org/10.32802/asmscj.2025.1918
Bozkurt, A. (2024). GenAI et al.: cocreation, authorship, ownership, academic ethics and integrity in a time of generative AI. Open Praxis, 16(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.55982/openpraxis.16.1.654
Chanpradit, T. (2025). Generative artificial intelligence in academic writing in higher education: a systematic review. Edelweiss Applied Science and Technology, 9(4), 889-906. https://doi.org/10.55214/25768484.v9i4.6128
Conde, J., Reviriego, P., Salvachúa, J., Martínez, G., Hernández, J., & Lombardi, F. (2024). Understanding the impact of artificial intelligence in academic writing: metadata to the rescue. Computer, 57(1), 105-109. https://doi.org/10.1109/mc.2023.3327330
Creswell, J. W., & Poth, C. N. (2018). Qualitative Inquiry and Research Design: Choosing Among Five Approaches. SAGE Publications. https://uk.sagepub.com/en-gb/eur/qualitative-inquiry-and-research-design/book266033
Demirel, E. (2024). The use and perceptions towards AI tools for academic writing among university students. Innovations in Language Teaching Journal, 1(1), 1-20. https://doi.org/10.53463/innovltej.20240328
Doskaliuk, B., Zimba, O., Yessirkepov, M., Кліщ, І., & Yatsyshyn, R. (2025). Artificial intelligence in peer review: enhancing efficiency while preserving integrity. Journal of Korean medical science, 40(7). https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e92
Gao, R., Yu, D., Gao, B., Hua, H., Hui, Z., Gao, J., & Yin, C. (2025). Legal Regulation of AI-assisted Academic Writing: Challenges, Frameworks, and Pathways. Frontiers in Artificial Intelligence, 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/frai.2025.1546064
Hao, Z., Fang, F., & Peng, J. (2024). The integration of AI technology and critical thinking in English major education in China: opportunities, challenges, and future prospects. Digital Applied Linguistics, 1, 2256. https://doi.org/10.29140/dal.v1.2256
Kar, S., Bansal, T., Modi, S., & Singh, A. (2024). How sensitive are the free AI-detector tools in detecting AI-generated texts? a comparison of popular AI-detector tools. Indian Journal of Psychological Medicine, 47(3), 275-278. https://doi.org/10.1177/02537176241247934
Karadağ, N. (2023). The impact of artificial intelligence on online assessment: a preliminary review. Journal of Educational Technology and Online Learning, 6(4), 822-837. https://doi.org/10.31681/jetol.1351548
Katsamakas, E., Pavlov, O., & Saklad, R. (2024). Artificial intelligence and the transformation of higher education institutions: a systems approach. Sustainability, 16(14), 6118. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16146118
Kong, S., Lee, J., & Tsang, O. (2024). A pedagogical design for self-regulated learning in academic writing using text-based generative artificial intelligence tools: 6-p pedagogy of plan, prompt, preview, produce, peer-review, portfolio-tracking. Research and Practice in Technology Enhanced Learning, 19, 30. https://doi.org/10.58459/rptel.2024.19030
Kotsis, K. (2024). Artificial intelligence creates plagiarism or academic research? European Journal of Arts, Humanities and Social Sciences, 1(6), 169-179. https://doi.org/10.59324/ejahss.2024.1(6).18
Kouam, A. (2024). Ai in academic writing: ally or foe? International Journal of Research Publications, 148(1), 353-358. https://doi.org/10.47119/ijrp1001481520246427
Lai, Z. (2025). The impact of AI-assisted blended learning on writing efficacy and resilience. International Journal of Computer-Assisted Language Learning and Teaching, 15(1), 1-21. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijcallt.377174
Lin, M., Liu, A., Poitras, E., Chang, M., & Chang, D. (2024). An exploratory study on the efficacy and inclusivity of ai technologies in diverse learning environments. Sustainability, 16(20), 8992. https://doi.org/10.3390/su16208992
Mapletoft, N., Price, A., Smith, K., Mapletoft, O., & Elliott, M. (2024). An attempt to cheat using GPT-4: findings, discussion and recommendations for academic staff and students. Enhancing Teaching and Learning in Higher Education, 1, 52-73. https://doi.org/10.62512/etlhe.11
Miao, J., Thongprayoon, C., Suppadungsuk, S., Valencia, O., Qureshi, F., & Cheungpasitporn, W. (2023). Ethical dilemmas in using AI for academic writing and an example framework for peer review in nephrology academia: a narrative review. Clinics and Practice, 14(1), 89-105. https://doi.org/10.3390/clinpract14010008
Miller, W. (2024). Adapting to AI: reimagining the role of assessment professionals. Intersection: A Journal at the Intersection of Assessment and Learning, 5(4), 99-113. https://doi.org/10.61669/001c.121439
Moustakas, C. (1994). Phenomenological research methods. SAGE Publications.
Msambwa, M., Wen, Z., & Kangwa, D. (2025). The impact of AI on the personal and collaborative learning environments in higher education. European Journal of Education, 60(1). https://doi.org/10.1111/ejed.12909
Nadhifah, A., Syukur, H., Haryanto, M., Luthfiyyah, R., & Rozak, D. (2024). Pre-service English teacher perceptions of AI in writing skills. Journal of World Englishes and Educational Practices, 6(2), 26-32. https://doi.org/10.32996/jweep.2024.6.2.3
Namjoo, F., Liaghat, E., Shabaziasl, S., Modabernejad, Z., & Morshedi, H. (2023). Students experience on self-study through AI. AI and Tech in Behavioral and Social Sciences, 1(3), 35-42. https://doi.org/10.61838/kman.aitech.1.3.6
Nwokocha, S., Kennedy, O., Yakpir, G., Olori, E., Nchindia, C., Kachitsa, C., & Onome, O. (2025). Commentary: artificial intelligence and the future of higher education—towards inclusive, ethical, and employability-driven learning ecosystems. Critique Open Research & Review, 3(2), 18-29. https://doi.org/10.55640/corr-v03i02-04
Onal, S., Kulavuz‐Onal, D., & Childers, M. (2025). Patterns of ChatGPT usage and perceived benefits on academic performance across disciplines: insights from a survey of higher education students in the united states. Journal of Educational Technology Systems, 54(1), 34-66. https://doi.org/10.1177/00472395251341214
Pan, J. (2024). Ai-driven English language learning program and academic writing integrity in the era of intelligent interface. English Language Teaching and Linguistics Studies, 6(4), 120-135. https://doi.org/10.22158/eltls.v6n4p120
Parker, J., Richard, V., Acabá, A., Escoffier, S., Flaherty, S., Jablonka, S., & Becker, K. (2024). Negotiating meaning with machines: AI's role in doctoral writing pedagogy. International Journal of Artificial Intelligence in Education. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40593-024-00425-x
Parviz, M. (2025). Generative AI in the English composition classroom practical and adaptable strategies. International Journal of Computer-Assisted Language Learning and Teaching, 15(1), 1-5. https://doi.org/10.4018/ijcallt.371422
Perkins, M., & Roe, J. (2023). Decoding academic integrity policies: a corpus linguistics investigation of AI and other technological threats. Higher Education Policy, 37(3), 633-653. https://doi.org/10.1057/s41307-023-00323-2
Qadhi, S., Alduais, A., Chaaban, Y., & Khraisheh, M. (2024). Generative AI, research ethics, and higher education research: insights from a scientometric analysis. Information, 15(6), 325. https://doi.org/10.3390/info15060325
Rabbianty, E., Azizah, S., & Virdyna, N. (2023). Ai in academic writing: assessing current usage and future implications. Insania Jurnal Pemikiran Alternatif Kependidikan, 28(1), 14-35. https://doi.org/10.24090/insania.v28i1a.9278
Rasheed, T., Bashir, A., Hanif, S., & Gul, H. (2025). Leveraging AI to mitigate educational inequality: personalized learning resources, accessibility, and student outcomes. The Critical Review of Social Sciences Studies, 3(1), 2399-2412. https://doi.org/10.59075/j4959m50
Schneider, D., Mishra, A., Gluski, J., Shah, H., Ward, M., Brown, E., & Lo, S. (2025). Prevalence of artificial intelligence-generated text in neurosurgical publications: implications for academic integrity and ethical authorship. Cureus, 17(2), e79086. https://doi.org/10.7759/cureus.79086
Shalevska, E., & Kostadinovska-Stojchevska, B. (2024). Ethics in times of advanced AI: investigating students’ attitudes towards ChatGPT and academic integrity. Teacher(27), 72-78. https://doi.org/10.20544/teacher.27.08
Shi, J., Liu, W., & Hu, K. (2025). Exploring how AI literacy and self-regulated learning relate to student writing performance and well-being in generative AI-supported higher education. Behavioral Sciences, 15(5), 705. https://doi.org/10.3390/bs15050705
Simms, R. (2024). Work with ChatGPT, not against: 3 teaching strategies that harness the power of artificial intelligence. Nurse Educator, 49(3), 158-161. https://doi.org/10.1097/nne.0000000000001634
Subaveerapandiyan, A., Kalbande, D., & Ahmad, N. (2025). Perceptions of effectiveness and ethical use of AI tools in academic writing: a study among PhD scholars in India. Information Development, 41(3), 728-746. https://doi.org/10.1177/02666669251314840
Sudrajad, W., Fikri, M., & Putra, R. (2024). Help me ChatGPT! what ways does ChatGPT influence students' productivity and creativity in English academic writing? Educatum Scientific Journal of Education, 2(2), 48-57. https://doi.org/10.59165/educatum.v2i2.65
Sullivan, M., Kelly, A., & McLaughlan, P. (2023). ChatGPT in higher education: Considerations for academic integrity and student learning. Journal of Applied Learning & Teaching, 6(1), 1-10. https://doi.org/10.37074/jalt.2023.6.1.17
Suna, E., & Özer, M. (2025). The human complimentary usage of AI and ML for fair and unbiased educational assessments. Chinese/English Journal of Educational Measurement and Evaluation, 6(1). https://doi.org/10.59863/ypkl4338
Thong, C., Butson, R., & Lim, W. (2023). Understanding the impact of ChatGPT in education. Proceedings of ASCILITE 2023 Conference: People, Partnerships and Pedagogies, 234-243. https://doi.org/10.14742/apubs.2023.461
Trần, T. (2024). Ai tools in teaching and learning English academic writing skills. Proceedings of the 20th AsiaCALL International Conference (AsiaCALL2023), 4, 170-187. https://doi.org/10.54855/paic.23413
Wang, V. (2025). Ethics and Equity in AI-Driven Education. IGI Global Scientific Publishing. https://doi.org/10.4018/979-8-3373-0502-8.ch010
Wu, C., Zhang, H., & Carroll, J. (2024). Ai governance in higher education: case studies of guidance at big ten universities. Future Internet, 16(10), 354. https://doi.org/10.3390/fi16100354
Ya’u, M., & Mohammed, M. (2025). Ai-assisted writing and academic literacy: investigating the dual impact of language models on writing proficiency and ethical concerns in Nigerian higher education. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 13(2), 593-604. https://doi.org/10.7575/aiac.ijels.v.13n.2p.593
Yang, H. (2024). Towards responsible use: student perspectives on ChatGPT in higher education. Proceedings of the 23rd European Conference on e-Learning - ECEL 2024, 23(1), 415-422. https://doi.org/10.34190/ecel.23.1.2790
Yoo, J. (2025). Defining the boundaries of AI use in scientific writing: a comparative review of editorial policies. Journal of Korean medical science, 40(23). https://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2025.40.e187
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohammad Aliakbari (Author); Pooria Barzan (Corresponding Author); Seyyed Pedram Allahveysi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







