Family Economic Hardship and Adolescent Risk-Taking: The Mediating Role of Family Cohesion
Keywords:
Family economic hardship, family cohesion, adolescent risk-taking, mediation, structural equation modelingAbstract
Objective: This study aimed to examine the mediating role of family cohesion in the relationship between family economic hardship and adolescent risk-taking.
Methods and Materials: A descriptive correlational research design was employed with a sample of 520 adolescents recruited from secondary schools in India, determined through Morgan and Krejcie’s sample size table. Data were collected using standardized self-report instruments: the Adolescent Risk-Taking Questionnaire (ARQ), the Economic Hardship Questionnaire (EHQ), and the Family Adaptability and Cohesion Evaluation Scales (FACES IV). Statistical analyses were conducted using SPSS-27 and AMOS-21. Pearson correlation coefficients were calculated to determine associations among variables, and Structural Equation Modeling (SEM) was performed to test the hypothesized mediation model. Model fit was evaluated using Chi-square, χ²/df, GFI, AGFI, CFI, TLI, and RMSEA indices.
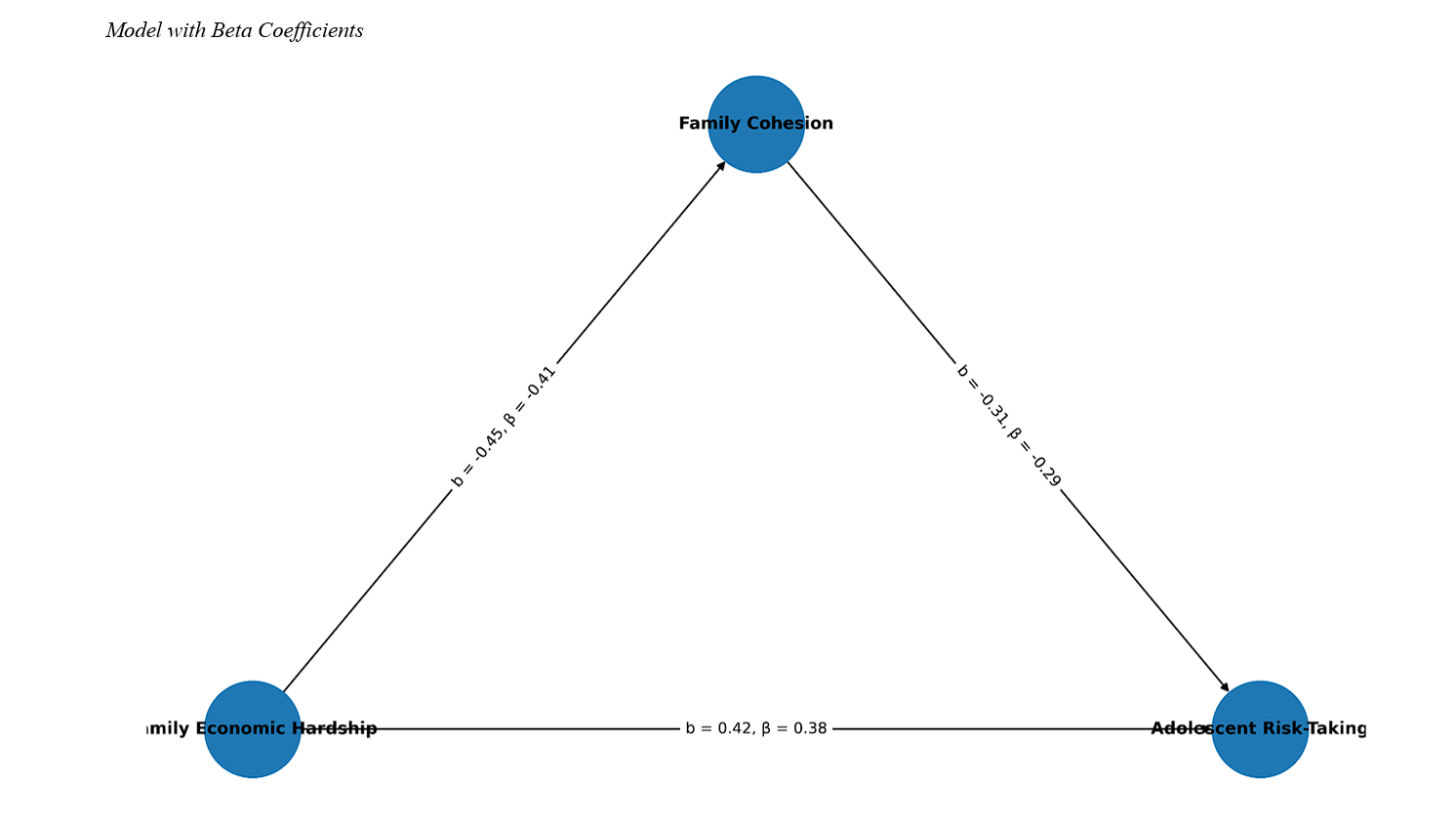
Findings: Results indicated that family economic hardship was positively correlated with adolescent risk-taking (r = .42, p = .001) and negatively correlated with family cohesion (r = −.40, p = .001). Family cohesion was inversely related to adolescent risk-taking (r = −.36, p = .002). The SEM analysis demonstrated adequate model fit (χ²/df = 2.17, GFI = .93, AGFI = .90, CFI = .95, TLI = .94, RMSEA = .048). Direct paths showed that family economic hardship significantly predicted adolescent risk-taking (β = .38, p = .001) and negatively predicted family cohesion (β = −.41, p = .001). Family cohesion negatively predicted adolescent risk-taking (β = −.29, p = .002). The indirect effect of economic hardship on risk-taking via cohesion was significant (β = .12, p = .006), supporting the mediation hypothesis.
Conclusion: Findings highlight that family cohesion partially mediates the link between economic hardship and adolescent risk-taking. Strengthening family cohesion may buffer adolescents from the adverse effects of financial strain and serve as a practical target for interventions aimed at reducing risk behaviors.
Downloads
References
Al-Matalka, F. I. M., & Hussainat, M. M. (2012). Juvenile Delinquency and Family Environment in Jordan. Journal of Sociological Research, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.5296/jsr.v3i2.2750
Bao, Z., Chen, C., Zhang, W., Zhu, J., Jiang, Y., & Xue-fen, L. (2016). Family Economic Hardship and Chinese Adolescents' Sleep Quality: A Moderated Mediation Model Involving Perceived Economic Discrimination and Coping Strategy. Journal of adolescence, 50(1), 81-90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2016.04.005
Brauer, J. R. (2016). Cultivating Conformists or Raising Rebels? Connecting Parental Control and Autonomy Support to Adolescent Delinquency. Journal of Research on Adolescence, 27(2), 452-470. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12283
Buist, K. L., Eichelsheim, V., Cook, W. L., Lier, P. A. C. v., Koot, H. M., & Meeus, W. (2020). Family Negativity and Delinquent Behavior in Adolescence: A Predictive Multivariate Latent Growth Analysis. Psychology Crime and Law, 26(9), 849-867. https://doi.org/10.1080/1068316x.2020.1742337
Chamratrithirong, A., Miller, B. A., Byrnes, H. F., Rhucharoenpornpanich, O., Cupp, P. K., Rosati, M. J., Fongkaew, W., Atwood, K. A., & Todd, M. (2012). Intergenerational Transmission of Religious Beliefs and Practices and the Reduction of Adolescent Delinquency in Urban Thailand. Journal of adolescence, 36(1), 79-89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adolescence.2012.09.011
Dargahi, S., Sharif, A. R., Sangdeh, J. K., Nazari, M. A., & Bakhtiari, Z. (2018). Comparing Parental Monitoring, Affiliation With Delinquent Peers, and High-Risk Behaviors in Single-Parent and Two-Parent Male Adolescents. Journal of Research and Health, 8(5), 411-417. https://doi.org/10.29252/jrh.8.5.411
Defoe, I. N., Dubas, J. S., & Marcel, A. G. v. A. (2018). The Relative Roles of Peer and Parent Predictors in Minor Adolescent Delinquency: Exploring Gender and Adolescent Phase Differences. Frontiers in Public Health, 6. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpubh.2018.00242
Gao, Y., Yu, Y., & Ng, T. K. (2013). A Study on the Moderating Effect of Family Functioning on the Relationship Between Deviant Peer Affiliation and Delinquency Among Chinese Adolescents. Advances in Applied Sociology, 03(03), 178-185. https://doi.org/10.4236/aasoci.2013.33024
Henneberger, A. K., Tolan, P. H., Hipwell, A. E., & Keenan, K. (2014). Delinquency in Adolescent Girls. Criminal Justice and Behavior, 41(11), 1327-1337. https://doi.org/10.1177/0093854814538624
Imran, S., Muddasir, A., & Sattar, A. (2022). Delinquent Behavior Among Adolescents: Moderating Role of Parental Involvement and Family Functioning. Aitusrj, 1(1). https://doi.org/10.63094/aitusrj.22.1.1.5
Kapetanovic, S., Boele, S., & Skoog, T. (2019). Parent-Adolescent Communication and Adolescent Delinquency: Unraveling Within-Family Processes From Between-Family Differences. Journal of youth and adolescence, 48(9), 1707-1723. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-019-01043-w
Kapetanovic, S., & Skoog, T. (2020). The Role of the Family’s Emotional Climate in the Links Between Parent-Adolescent Communication and Adolescent Psychosocial Functioning. Research on Child and Adolescent Psychopathology, 49(2), 141-154. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10802-020-00705-9
Khodabakhshi-Koolaee, A., Lor, H. S., Soleimani, A. A., & Rahmatizadeh, M. (2014). Comparison Between Family Power Structure and the Quality of Parent-Child Interaction Among the Delinquent and Non-Delinquent Adolescents. International Journal High Risk Behaviors & Addiction, 3(2). https://doi.org/10.5812/ijhrba.13188
Kroese, J., Bernasco, W., Liefbroer, A. C., & Rouwendal, J. (2024). The Anticipatory, Short-Term, and Long-Term Effects of Parental Separation and Parental Death on Adolescent Delinquency. Journal of Developmental and Life-Course Criminology, 10(2), 288-308. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40865-024-00252-7
Kwon, J. A., & Wickrama, K. A. S. (2013). Linking Family Economic Pressure and Supportive Parenting to Adolescent Health Behaviors: Two Developmental Pathways Leading to Health Promoting and Health Risk Behaviors. Journal of youth and adolescence, 43(7), 1176-1190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10964-013-0060-0
Lee, S. (2014). Structural Equation Modeling About Family Relationship, Self-Efficacy, Self-Esteem, and Delinquency of Adolescent in Single-Parent Families. The Journal of the Korea Contents Association, 14(11), 759-771. https://doi.org/10.5392/jkca.2014.14.11.759
Low, S., Sinclair, R. T., & Shortt, J. W. (2012). The Role of Economic Strain on Adolescent Delinquency: A Microsocial Process Model. Journal of Family Psychology, 26(4), 576-584. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0028785
Rina, N. (2018). Communication Pattern of Parents in Nuclear Families. https://doi.org/10.2991/icomacs-18.2018.13
Svensson, R., & Johnson, B. (2022). Does It Matter in What Family Constellations Adolescents Live? Reconsidering the Relationship Between Family Structure and Delinquent Behaviour. PLoS One, 17(4), e0265964. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0265964
Yakhnich, L., Pounko, I., & Walsh, S. D. (2019). The Hidden Matrix: Perspectives of Youth and Their Parents on Immigration and Youth Delinquent Behavior. Journal of Cross-Cultural Psychology, 50(4), 615-636. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022022119832128
Yusoff, S., Shah, K. M., Sakari, N. S. M., & Ahmad, N. S. S. (2022). The Relationship of Family Functionality and Parent Behavior on Adolescent Delinquent Behavior. International Journal of Public Health Science (Ijphs), 11(3), 1119. https://doi.org/10.11591/ijphs.v11i3.21553
Zakaria, E., Kamarudin, N. N., Mohamad, Z. S., Suzuki, M., Rathakrishnan, B., Singh, S. S. B., Rahman, Z. A., Sabramani, V., Shaari, A. H., & Kamaluddin, M. R. (2022). The Role of Family Life and the Influence of Peer Pressure on Delinquency: Qualitative Evidence From Malaysia. International journal of environmental research and public health, 19(13), 7846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph19137846
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.




















