Changes in Oxidant–Antioxidant Status of Hippocampal Tissue Following Eight Weeks of Aerobic Exercise and Vitamin E Supplementation in Reserpine-Induced Parkinsonian Rats
Keywords:
Exercise, Vitamin E, Antioxidant, Hippocampus, Parkinson’s DiseaseAbstract
Objective: The present study aimed to investigate changes in the oxidant–antioxidant status of hippocampal tissue following eight weeks of aerobic exercise (AT) and vitamin E (VE) supplementation in reserpine-induced Parkinsonian rats.
Methods and Materials: In this experimental study, 40 male Sprague-Dawley rats (aged 14–16 months, weighing 250–270 grams) were induced with Parkinson’s disease using 2 mg/kg reserpine (Res) and were divided into the following groups: (1) PD, (2) AT, (3) VE, and (4) AT+VE. To evaluate the effects of Res on the variables, eight healthy control (HC) rats were included. Aerobic exercise was performed for eight weeks, five sessions per week, with each session lasting 15–48 minutes at a speed of 10–24 m/min. VE supplementation was administered orally at a dose of 30 mg/kg daily. Data analysis was performed using one-way ANOVA and Tukey’s post-hoc test (P ≤ 0.05).
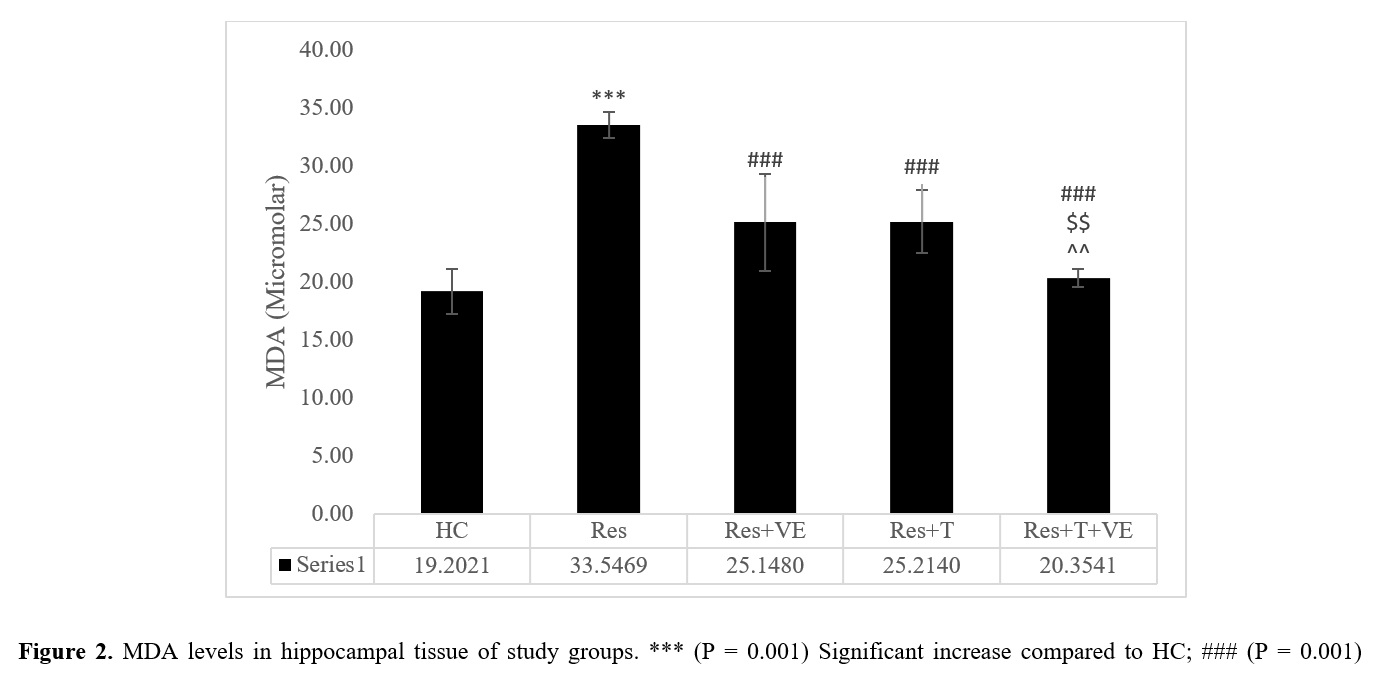
Findings: The Res+AT, Res+VE, and Res+AT+VE groups showed higher levels of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and total antioxidant capacity (TAC) and lower levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) compared to the Res group (P = 0.05). In the Res+AT+VE group, SOD levels were higher and MDA levels were lower than in the Res+AT and Res+VE groups (P = 0.001). Additionally, TAC levels in the Res+AT and Res+AT+VE groups were higher than in the Res+VE group (P = 0.001).
Conclusion: Aerobic exercise and vitamin E supplementation appear to have antioxidant effects on brain tissue, both individually and interactively. Given the more favorable effects of combining exercise with vitamin E, the simultaneous use of these two interventions is recommended in neurodegenerative diseases.
Downloads
References
1. Kang SH, Moon SJ, Kang M, Chung SJ, Cho GJ, Koh
SB. Incidence of Parkinson’s disease and modifiable risk factors in
Korean population: A longitudinal follow-up study of a nationwide
cohort. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15. [PMID: 36865411]
[PMCID: PMC9971569] [DOI]
2. Ben-Shlomo Y. The epidemiology of Parkinson’s
disease. Baillieres Clin Neurol. 1997;6(1):55-68.
3. Grotewold N, Albin RL. Update: Descriptive
epidemiology of Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord.
2024:106000. [PMID: 38879999] [DOI]
4. Houldsworth A. Role of oxidative stress in
neurodegenerative disorders: A review of reactive oxygen species
and prevention by antioxidants. Brain Commun. 2024:fcad356.
[PMID: 38214013] [PMCID: PMC10783645] [DOI]
5. Buga AM, Oancea CN. Oxidative Stress-Induced
Neurodegeneration and Antioxidative Strategies: Current Stage
and Future Perspectives. Antioxidants. 2023;12:1762. [PMID:
37760065] [PMCID: PMC10525970] [DOI]
6. Hosseini SA, Salehi OR, Farzanegi P, Farkhaie F,
Darvishpour AR, Roozegar S. Interactive Effects of Endurance
Training and Royal Jelly Consumption on Motor Balance and Pain
Threshold in Animal Model of the Alzheimer Disease. Arch
Neurosci.7(2). [DOI]
7. Sheikholeslami-Vatani D, Salehi OR, Hosseini SA.
Psycho-physiological effects of high intensity interval training and
vitamin E consumption in elderly trimethyltin-treated Alzheimer’s
rats. Metab Exerc. 2021;11(2):57-76.
8. Souza J, da Silva RA, da Luz Scheffer D, Penteado R,
Solano A, Barros L, et al. Physical-Exercise-Induced Antioxidant
Effects on the Brain and Skeletal Muscle. Antioxidants.
2022;11(5):826. [PMID: 35624690] [PMCID: PMC9138070]
[DOI]
9. Chadorneshin HT, Nayebifar S, Abtahi-Eivary SH,
Nakhaei H. Comparison of Effects of High-Intensity Interval
Training and Continuous Training on Memory and Correlation with
Antioxidant Enzyme Activity in the Rat Brain. Ann Mil Heal Sci
Res. 2021;19(2):e113888. [DOI]
10. Abbasi E, Zarin Kalam E, Ranjbar K, Mirzaei F, Komaki
A, Soleimani Asl S. Protective Effect of Exercise on Liver
Oxidative Stress, Inflammation and Histopathological Changes
after Morphine Withdrawal in Rats. J Maz Univ Med Sci.
2022;32(207):26-37.
11. Keshavarzian F, Doulah A, Rafieirad M. The Effect of
Four Weeks of Exercise and Oleurpine Supplementation on
Oxidative Stress in Brain Tissue in Experimental Model of
Parkinson’s Disease in Rat. Exp Anim Biol. 2021;10(2):67-76.
12. Al-Sowayan NS, Almarzougi RA. Vitamin E reduces
oxidative stress in brains of male albino male rats undergoing
immobilization. Saudi J Biol Sci. 2024;31(1):103900. [PMID:
38173441] [PMCID: PMC10761899] [DOI]
13. da Cunha Germano BC, de Morais LCC, Idalina Neta F,
Fernandes ACL, Pinheiro FI, do Rego ACM, et al. Vitamin E and
its molecular effects in experimental models of neurodegenerative
diseases. Int J Mol Sci. 2023;24(13):11191. [PMID: 37446369]
[PMCID: PMC10342514] [DOI]
14. Alzoubi KH, Khabour OF, Rashid BA, Damaj IM, Salah
HA. The neuroprotective effect of vitamin E on chronic sleep
deprivation-induced memory impairment: the role of oxidative
stress. Behav Brain Res. 2012;226(1):205-10. [PMID: 21944940]
[DOI]
15. Hao X, Li H, Li Q, Gao D, Wang X, Wu C, et al. Dietary
vitamin E intake and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a cross-sectional
study. Front Nutr. 2024;10:1289238. [PMID: 38249609] [PMCID:
PMC10799344] [DOI]
16. Cetin E, Top EC, Şahin G, Özkaya YG, Aydin H,
Toraman F. Effect of vitamin E supplementation with exercise on
cognitive functions and total antioxidant capacity in older people. J
Nutr Health Aging. 2010;14:763-9. [PMID: 21085907] [DOI]
17. Hajarian S, Banaeifar A, Soheili S, Arshadi S. The effect
of eight weeks aerobic training with vitamin E supplementation on
some markers of mitochondrial biogenesis in the brain tissue of rats
with Parkinson’s disease. J Appl Exerc Physiol. 2023;18(36):15-
27.
18. Dovonou A, Bolduc C, Soto Linan V, Gora C, Peralta Iii
MR, Lévesque M. Animal models of Parkinson’s disease: bridging
the gap between disease hallmarks and research questions. Transl
Neurodegener. 2023;12(1):36. [PMID: 37468944] [PMCID:
PMC10354932] [DOI]
19. Moradi S, Habibi A, Tabande MR, Shakerian S.
Comparing the effect of 6 weeks of continuous and interval aerobic
training on vascular endothelial growth factor and superoxide
dismutase enzyme in hippocampus of male rats of Parkinson’s
model. J Shahid Sadoughi Univ Med Sci. 2019. [DOI]
20. Moradi S, Moradi M, Habibi A, Shakeriyan S.
Comparison of the Effect of 6 Weeks of Continuous and Interval
Aerobic Training on Hippocampal Nerve Growth Factor and
Catalase Enzyme in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease. J Ilam
Univ Med Sci. 2019;27(4):47-57. [DOI]
21. Hamid NAA, Hasrul MA, Ruzanna RJ, Ibrahim IA,
Baruah PS, Mazlan M, et al. Effect of vitamin E (Tri E®) on
antioxidant enzymes and DNA damage in rats following eight
weeks exercise. Nutr J. 2011;10(1):1-7. [PMID: 21513540]
[PMCID: PMC3107782] [DOI]
22. Agahi MRH, Mosallanejad Z, Salehi OR. The effects of
resistance training and spirulina on the performance of the
antioxidant system with emphasis on mir125b, mir146a and
cognitive function in stanazolol-induced neurotoxicity in rats.
Chem Biol Interact. 2022:110112. [PMID: 36029803] [DOI]
23. Mirzavandi F, Sabet N, Aminzadeh A, Heidari M, Pouya
F, Moslemizadeh A, et al. Effects of varied‑intensity endurance
exercise training on oxidative and antioxidant factors in the liver of
rats with valproic acid‑induced autism. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars).
2023;83(1):25-33. [PMID: 37078811] [DOI]
24. Shirvani H, Aslani J, Fallah Mohammadi Z, Arabzadeh
E. Short-term effect of low-, moderate-, and high-intensity exercise
training on cerebral dopamine neurotrophic factor (CDNF) and
oxidative stress biomarkers in brain male Wistar rats. Comp Clin
Path. 2019;28:369-76. [DOI]
25. Usman B, Sajo MU, Adam MK, Mshelia PA, Bulama I,
Sanda KA. Effect of Vitamin E on Serum MDA and Antioxidant
Enzymes in Traumatic Brain Injury-Induced Rats. J Complement
Altern Med Res. 2023;24(1):35-42. [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Fatemeh Sadeghi , Jamshid Banai, Elham Eftekhari ghinani , Saeid Keshavarz (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







