Examining the Effectiveness of a Mindfulness-Based Training Program on Achievement Motivation, Self-Confidence, and Sports Performance among Novice Football Students in Iraqi Schools
Keywords:
achievement motivation, mindfulness, self-confidence, skill, footballAbstract
Objective: The purpose of the present study was to examine the impact of a mindfulness-based training program on achievement motivation, self-confidence, and sports performance (shooting, passing, dribbling) among novice football students in Iraqi schools.
Materials and Methods: The research participants were 60 male football players, aged 14 to 16, from the city of Baghdad in 2023–2024, selected through a call for participation and randomly assigned to either a mindfulness training group or a control group. Data were collected using Hermans’s (1970) Achievement Motivation Questionnaire, the Moore-Christine tests for dribbling, passing, and shooting skills, and Willy and Knight’s (2002) Sports Self-Confidence Questionnaire. The Shapiro-Wilk test was used to check the normal distribution of the data, and Levene’s test was used to assess the homogeneity of variances. To analyze the findings, analysis of covariance (ANCOVA) was performed using SPSS statistical software, version 24.
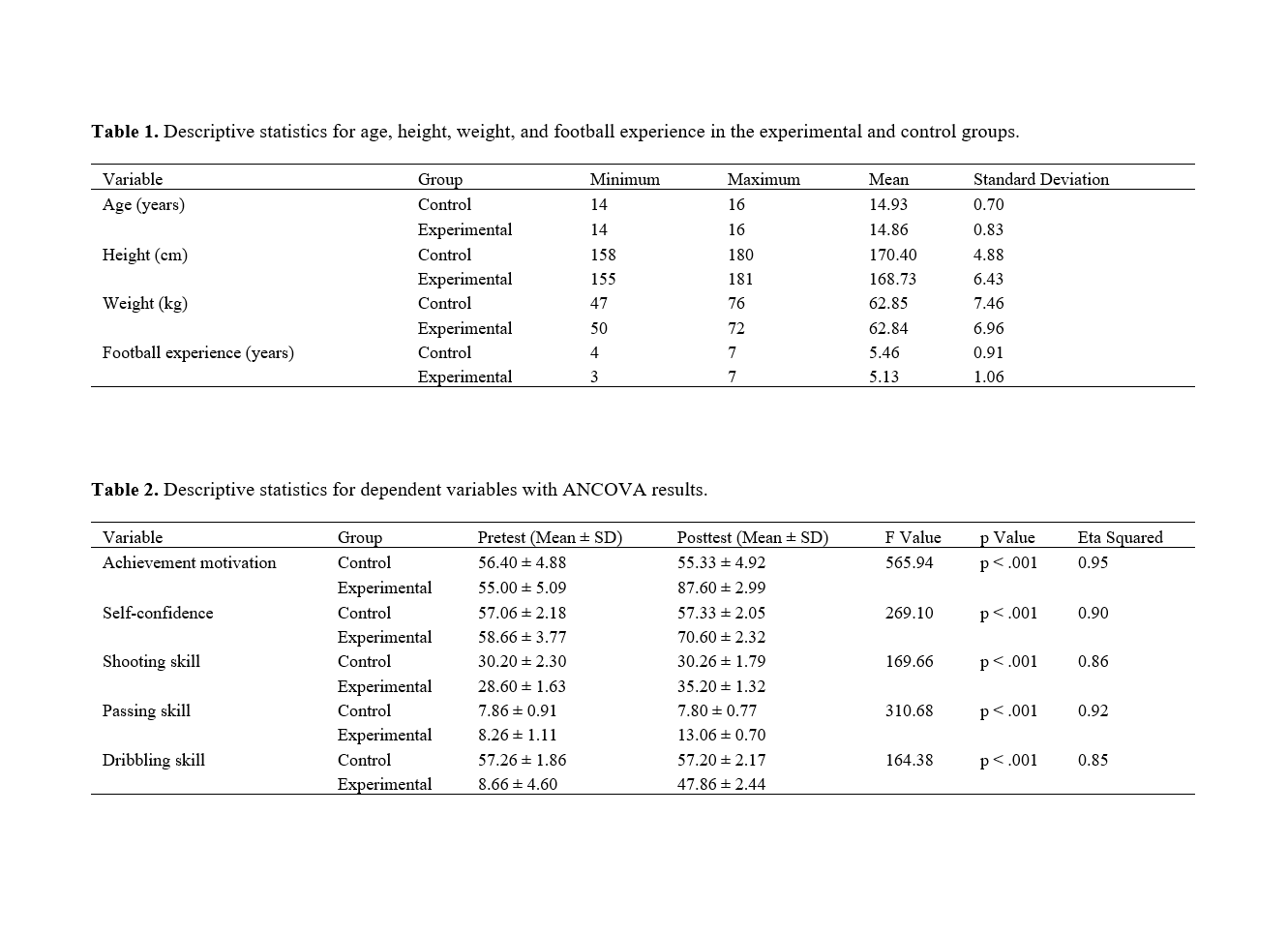
Findings: The results indicated that scores for self-confidence and the skills of shooting, passing, dribbling, as well as achievement motivation, improved in the experimental group compared to the control group. In other words, mindfulness training had a positive and significant effect on self-confidence, shooting, passing, dribbling, and achievement motivation among novice football students in Iraq.
Conclusion: Based on the findings, it can be concluded that mindfulness training plays a crucial role in enhancing skill levels, achievement motivation, and sports self-confidence in Iraqi football novices; therefore, it is recommended that coaches employ mindfulness training to improve performance and increase sports self-confidence and achievement motivation.
Downloads
References
1. Pruna R, Bahdur K. Journal of Novel Physiotherapies.
depression. 2016;21(25):29.
2. Bykova A, Coates D. Does experience matter? Salary
dispersion, coaching, and team performance. Contemporary
Economic Policy. 2020;38(1):188-205. [DOI]
3. McMorris T, Myers S, MacGillivary WW, Sexsmith JR,
Fallowfield J, Graydon J, et al. Exercise, plasma catecholamine
concentrations and decision-making performance of soccer players
on a soccer-specific test. Journal of Sports Sciences.
1999;17(8):667-76. [PMID: 10487466] [DOI]
4. Yalçın İ, Çalık F, Ramazanoğlu F, Tutar ÖF. Research
on the achievement motivation levels of the amateur football
players. SHS Web of Conferences. 2017;37:01054. [DOI]
5. Fahim Devin H, Asadollahi E. Investigating the
Mediating Role of Coaches'Sense of Humor in Causative Relation
of Transformational (Inspirational) Leadership with Sport
Achievement Motivation in Elite Athletes. Organizational
Behavior Management in Sport Studies. 2021;8(2):105-14. [DOI]
6. Yoo J, Kim B-J. Young Korean athletes' goal orientation
and sources of enjoyment. Perceptual and motor skills.
2002;94(3):1043-9. [PMID: 12081265] [DOI]
7. Moles TA, Auerbach AD, Petrie TA. Grit happens:
Moderating effects on motivational feedback and sport
performance. Journal of Applied Sport Psychology.
2017;29(4):418-33. [DOI]
8. Albert E, Petrie TA, Moore EWG. The relationship of
motivational climates, mindsets, and goal orientations to grit in
male adolescent soccer players. International Journal of Sport and
Exercise Psychology. 2021;19(2):265-78. [DOI]
9. Mohebi M, gharayagh zandi H, Khabiri M. Motivational
Profile of Succesful Taekwondo Athletes. journal of motor and
behavioral sciences. 2022;5(1):53-64. [DOI]
10. Liu F, Zhang Z, Liu S, Zhang N. Examining the effects
of brief mindfulness training on athletes’ flow: the mediating role
of resilience. Evidence‐Based Complementary and Alternative
Medicine. 2021;2021(1):6633658. [PMID: 34122602] [PMCID:
PMC8166472] [DOI]
11. Lochbaum M, Sherburn M, Sisneros C, Cooper S, Lane
AM, Terry PC. Revisiting the self-confidence and sport
performance relationship: a systematic review with meta-analysis.
International Journal of Environmental Research and Public
Health. 2022;19(11):6381. [PMID: 35681963] [PMCID:
PMC9180271] [DOI]
12. Gill D, Williams L. Psychological dynamics of sport and
exercise. 2008.
13. Zinsser N, Bunker L, Williams JM. Cognitive techniques
for building confidence and enhancing performance. Applied sport
psychology: Personal growth to peak performance. 2006;5:349-81.
14. Madsen EE, Hansen T, Rafnsson D, Krustrup P, Larsen
CH, Elbe A-M. Investigating the relationship between achievement
motive and performance in elite-level football goalkeepers.
Scandinavian Journal of Sport and Exercise Psychology.
2024;6:10-8. [DOI]
15. Noetel M, Ciarrochi J, Van Zanden B, Lonsdale C.
Mindfulness and acceptance approaches to sporting performance
enhancement: A systematic review. International Review of Sport
and Exercise Psychology. 2019;12(1):139-75. [DOI]
16. Glass CR, Spears CA, Perskaudas R, Kaufman KA.
Mindful sport performance enhancement: Randomized controlled
trial of a mental training program with collegiate athletes. Journal
of Clinical Sport Psychology. 2019;13(4):609-28. [DOI]
17. Ajilchi B, Amini HR, Ardakani ZP, Zadeh MM, Kisely
S. Applying mindfulness training to enhance the mental toughness
and emotional intelligence of amateur basketball players.
Australasian Psychiatry. 2019;27(3):291-6. [PMID: 30763131]
[DOI]
18. Samadi H, Ayatizadeh TF, Keavanloo F. Effectiveness of
Psychological Intervention Based on Mindfulness Model on
Athletes. 2022.
19. Bull SJ, Shambrook CJ, James W, Brooks JE. Towards
an understanding of mental toughness in elite English cricketers.
Journal of applied sport psychology. 2005;17(3):209-27. [DOI]
20. Costalupes B. The Effect of a Mindful Meditation
Intervention on Self Confidence and Readiness in Baseball Players:
California State University, Fresno; 2018.
21. Iranmanesh H, Saberi Kakhki A, Zarezadeh M. The
Relationship between Sport self- confidence & Motivation among
Table Tennis Athletes Based on Self-determination Theory. Sport
Psychology Studies. 2014;3(8):76-59.
22. Wang Y, Lei S-M, Fan J. Effects of mindfulness-based
interventions on promoting athletic performance and related factors
among athletes: a systematic review and meta-analysis of
randomized controlled trial. International journal of environmental
research and public health. 2023;20(3):2038. [PMID: 36767403]
[PMCID: PMC9915077] [DOI]
23. Zadkhosh SM, Gharayagh Zandi H, Hemayattalab R.
The Effects of Mindfulness on Anxiety Decrease and Athletic
Performance Enhancement of Young Football Players. Sport
Psychology Studies. 2019;8(27):41-54. [DOI]
24. Beers Dewhirst C, Goldman J. Launching motivation for
mindfulness: Introducing mindfulness to early childhood
preservice teachers. Early Child Development and Care.
2020;190(8):1299-312. [DOI]
25. Bernier M, Thienot E, Codron R, Fournier JF.
Mindfulness and acceptance approaches in sport performance.
Journal of clinical sport psychology. 2009;3(4):320-33. [DOI]
26. Hasker SM. Evaluation of the mindfulness-acceptancecommitment (MAC) approach for enhancing athletic performance:
Indiana University of Pennsylvania; 2010.
27. De Petrillo LA, Kaufman KA, Glass CR, Arnkoff DB.
Mindfulness for long-distance runners: An open trial using Mindful
Sport Performance Enhancement (MSPE). Journal of Clinical
Sport Psychology. 2009;3(4):357-76. [DOI]
28. Tang Y-Y, Hölzel BK, Posner MI. The neuroscience of
mindfulness meditation. Nature reviews neuroscience.
2015;16(4):213-25. [PMID: 25783612] [DOI]
29. Ruffault A, Bernier M, Juge N, Fournier JF. Mindfulness
may moderate the relationship between intrinsic motivation and
physical activity: A cross-sectional study. Mindfulness.
2016;7:445-52. [DOI]
30. Jackson SA, Thomas PR, Marsh HW, Smethurst CJ.
Relationships between flow, self-concept, psychological skills, and
performance. Journal of applied sport psychology. 2001;13(2):129-
53. [DOI]
31. Shonin E, Van Gordon W, Griffiths MD. Mindfulness in
psychology: a breath of fresh air? The Psychologist. 2015;28(1):28-
31.
32. Heidari F, Zandi HG, Khabiri M. Relationship of dark
triad of personality traits with sport self-confidence of elite martial
arts in iran. Journal of Psychological Science. 2020;19(91):811-9.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Husam Abbas Mashhoot, Maryam Faraeen, Akram Hoossein Algnabe , Hassan Abdi, Zohreh Meshkati (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.







