Investigating the User Experience of AI Chatbots in Delivering Mental Health Support to Athletes
Keywords:
artificial intelligence, chatbots, user experience, mental health support, athletes, qualitative research, sports psychologyAbstract
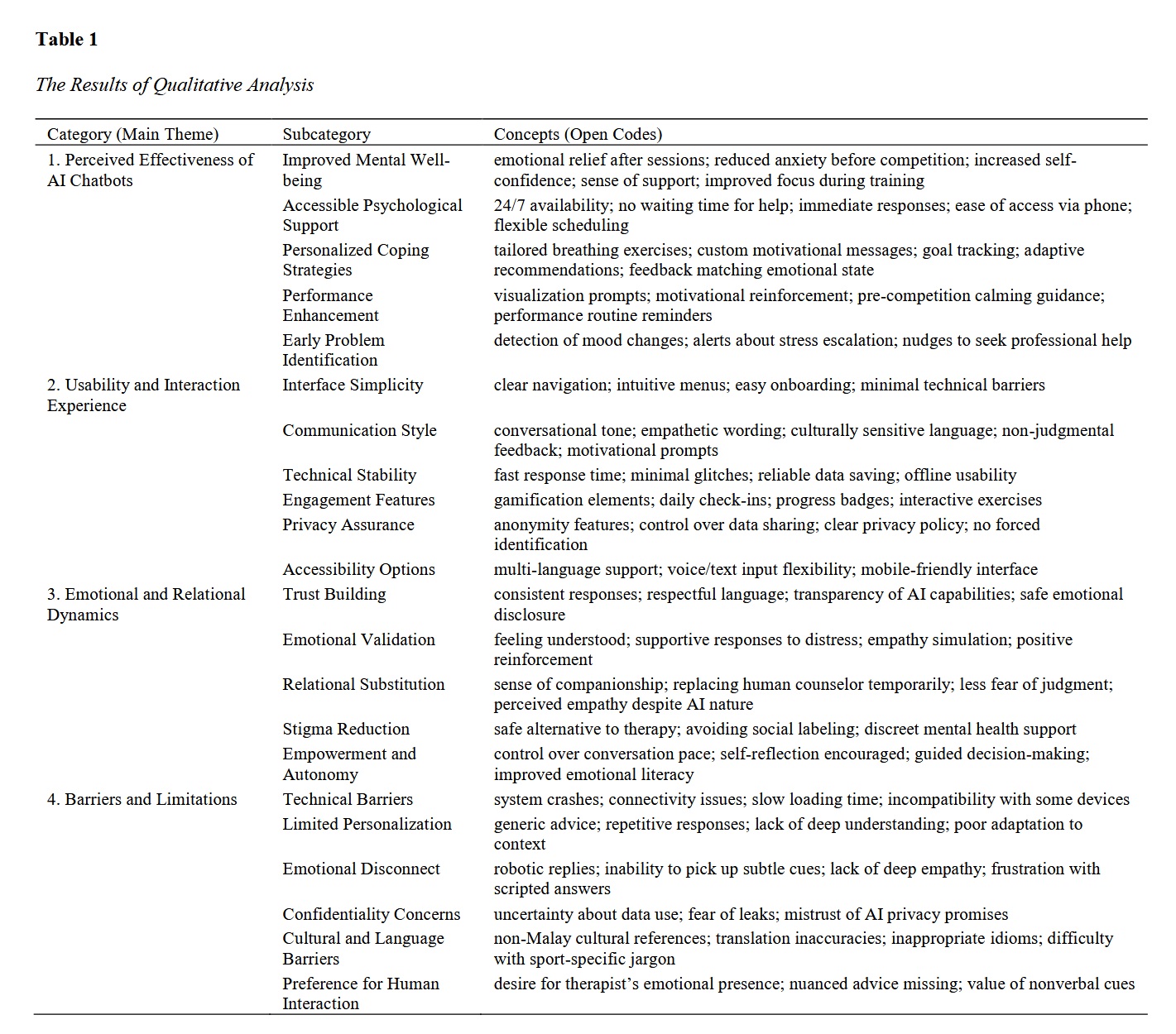
This study aimed to explore how athletes experience and perceive the use of artificial intelligence (AI) chatbots as a source of mental health support, focusing on effectiveness, usability, emotional connection, and limitations. A qualitative exploratory design was employed. Twenty-two athletes from diverse sports disciplines in Malaysia were recruited using purposive sampling. Data were collected through semi-structured, in-depth interviews conducted online to allow flexible participation and confidentiality. The sample size was guided by theoretical saturation, reached when no new themes emerged. All interviews were audio-recorded, transcribed verbatim, and analyzed using thematic analysis. NVivo 14 software supported systematic coding, with open, axial, and selective coding applied iteratively to generate categories and subthemes. Rigor and trustworthiness were ensured through member checking, peer debriefing, and an audit trail. Four main themes emerged: perceived effectiveness of AI chatbots, usability and interaction experience, emotional and relational dynamics, and barriers and limitations. Athletes reported improved mental well-being, reduced competition-related anxiety, and personalized coping strategies. They valued intuitive interfaces, empathetic conversational style, and privacy features, which encouraged engagement and disclosure. Chatbots fostered a sense of trust and emotional validation but sometimes lacked depth and produced repetitive responses. Barriers included occasional technical instability, insufficient long-term personalization, cultural mismatches, and data security concerns. Despite these limitations, participants viewed chatbots as valuable early support tools and stigma-free entry points to mental health care. AI chatbots show promise in enhancing access to psychological support for athletes, offering discreet, immediate, and personalized assistance. However, improving cultural sensitivity, personalization, technical reliability, and data transparency is crucial for sustained engagement and safety in sports mental health contexts.
Downloads
References
1. Anusha S, Hiranmayee N, Kamala PS, Sagarika N, Sushma PR, Thangavelu L, et al. AI for Mental Health Support. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Techno. 2025:1047-53. [DOI]
2. Kim M, Lee S, Kim S, Heo J-i, Lee S, Shin YB, et al. Therapeutic Potential of Social Chatbots in Alleviating Loneliness and Social Anxiety: Quasi-Experimental Mixed Methods Study. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2025;27:e65589. [PMID: 39808786] [PMCID: PMC11775481] [DOI]
3. Sowbarnika A, Patra AK, Kaur L, Suresh S, Srivastava S, Chawla D. Chatbots as Tools for Psychoeducation and Self-Help in Mental Health. 2024:55-86. [DOI]
4. Patel H, Hussain F. Do AI Chatbots Incite Harmful Behaviours in Mental Health Patients? Bjpsych Open. 2024;10(S1):S70-S1. [PMCID: PMC11738096] [DOI]
5. Yadav N. AI for Mental Health: The Use of Chatbots and NLP to Support Therapy and Early Detection. International Scientific Journal of Engineering and Management. 2025;04(05):1-7. [DOI]
6. Anamika, Rabbani MS, Perwej Y. AI-Counsellor Using Emerging Technique. International Journal of Scientific Research in Science and Technology. 2024;11(3):749-59. [DOI]
7. Patil M. “Mental Health Chatbot Using Natural Language Processing and Machine Learning Techniques”. International Scientific Journal of Engineering and Management. 2025;04(06):1-9. [DOI]
8. Singh A. Mental Health Support Chatbot. International Scientific Journal of Engineering and Management. 2025;04(06):1-7. [DOI]
9. B H, yashaswini M, Malik Y, yogashree BS, Vinay V. Mind-Balance: AI-Powered Mental Health Assistant. Computer Science & Engineering an International Journal. 2025;15(1):151-8. [DOI]
10. Nithya LM, Gupta TR, D.S S, J DC, Somasundaram S. Healthify: A Conversational AI for Mental Health Support Using Groq and LangChain Frameworks. International Journal of Innovative Science and Research Techno. 2025:2214-20. [DOI]
11. Bays DK, Verble C, Verble KMP. A Brief Review of the Efficacy in Artificial Intelligence and Chatbot-Generated Personalized Fitness Regimens. Strength and Conditioning. 2024;46(4):485-92. [DOI]
12. Moylan K, Doherty K. Expert and Interdisciplinary Analysis of AI-Driven Chatbots for Mental Health Support: Mixed Methods Study (Preprint). 2024. [PMID: 40279575] [PMCID: PMC12064976] [DOI]
13. Mughal AS. Addressing the Emotional and Ethical Risks of Using AI Chatbots in Psychotherapy. Innovapath. 2025;1(5):2. [DOI]
14. Parks AC, Travers E, Perera‐Delcourt R, Major M, Economides M, Mullan PC. Is This Chatbot Safe and Evidence-Based? A Call for the Critical Evaluation of Generative AI Mental Health Chatbots. Journal of Participatory Medicine. 2025;17:e69534-e. [PMID: 40440646] [PMCID: PMC12140500] [DOI]
15. Manole A, Cârciumaru R, Brînzaș R, Manole F. An Exploratory Investigation of Chatbot Applications in Anxiety Management: A Focus on Personalized Interventions. Information. 2024;16(1):11. [DOI]
16. Kabir JUZ, Nabil AR, Ahmed R. Developing Al-Powered Chatbots for Mental Health Support in Rural America. Journal of Computer Science and Technology Studies. 2025;7(2):23-35. [DOI]
17. Citoler AP, Lee E. End Users’ Perception on an AI Chatbot in a Snus Cessation Mobile Application. 2025. [PMCID: PMC12542903] [DOI]
18. Siddals S, Torous J, Coxon A. “It Happened to Be the Perfect Thing”: Experiences of Generative AI Chatbots for Mental Health. NPJ Mental Health Research. 2024;3(1). [PMID: 39465310] [PMCID: PMC11514308] [DOI]
19. Naomi N, Chipatso M. Mental Health Chatbot Therapist. Jaim. 2024;2(2):1. [DOI]
20. Moylan K, Doherty K. Expert and Interdisciplinary Analysis of AI-Driven Chatbots for Mental Health Support: Mixed Methods Study. Journal of Medical Internet Research. 2025;27:e67114. [DOI]
21. Khaitan A, Gupta S, Maheshwari A, Anand A, Kumar R. Generative AI and Mental Health: A New Frontier of Possibilities. International Journal of Science and Research Archive. 2025;15(2):139-45. [DOI]
22. Verma A. Social Media App With Time Capsule Messaging &Amp; Chatbot. International Scientific Journal of Engineering and Management. 2025;04(05):1-7. [DOI]
23. Lopes RM, Silva A, Rodrigues ACA, Melo V. Chatbots for Well-Being: Exploring the Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Mood Enhancement and Mental Health. European Psychiatry. 2024;67(S1):S550-S1. [PMCID: PMC11861562] [DOI]
24. Thillairam A, Prabhu S, Nithiya M, Singh D, R DP, Sathyaprakash T. Revolutionizing Mental Health Care: An AI-Driven, Multimodal, and Culturally Sensitive Approach. International Journal of Research Publication and Reviews. 2024;5(4):181-6. [DOI]
25. Sirdeshpande S. Thrive Path: Navigating Emotional Journey With AI Chatbot and Machine Learning Techniques for Mental Health. Interantional Journal of Scientific Research in Engineering and Management. 2025;09(05):1-9. [DOI]