Effect of an Aerobic Exercise Program and Gymnema Supplementation on Plasma Ghrelin Levels and Sweet Taste Preference in Obese Women
Keywords:
Obesity, Ghrelin, Gymnema, Aerobic Exercise, Sweet Taste, AppetiteAbstract
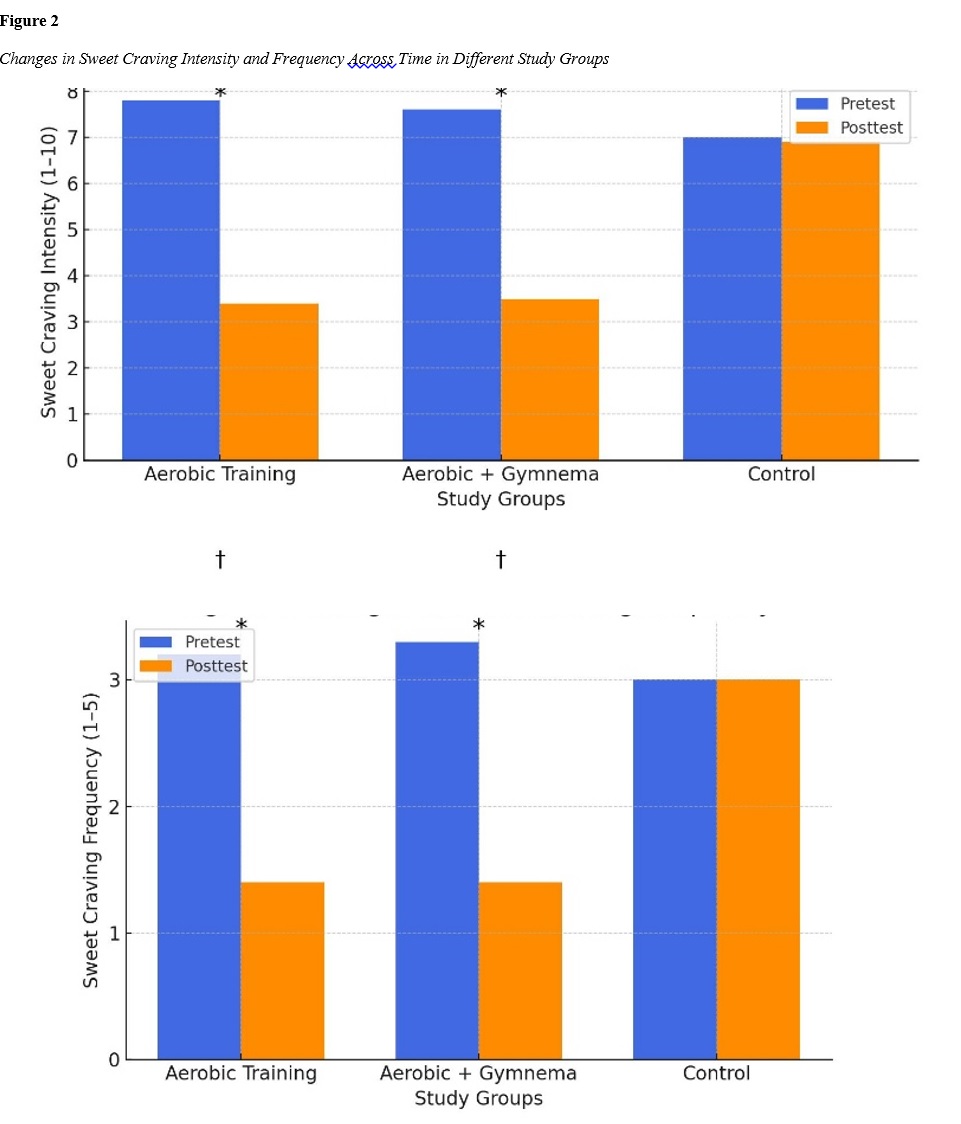
Obesity is associated with dysregulation of appetite control and a preference for sweet taste. Ghrelin is recognized as a key hormone in appetite stimulation and sweet taste preference. The aim of this study was to examine the effect of aerobic exercise and Gymnema supplementation on plasma ghrelin levels and sweet taste preference in obese women. In this quasi-experimental study, 45 obese women aged 20 to 45 were randomly assigned into three groups: aerobic training, aerobic training plus Gymnema supplementation, and a control group (15 participants per group). The intervention groups engaged in aerobic exercise for 8 weeks. The second group additionally received 400 mg of Gymnema supplement daily. Plasma ghrelin levels were measured using the ELISA method, and sweet taste preference was assessed via a questionnaire. Post-intervention, plasma ghrelin levels significantly increased in both the aerobic and combined intervention groups (P < 0.001), while no change was observed in the control group. The intensity and frequency of sweet cravings significantly decreased in both intervention groups (P < 0.001), although no significant difference was found between the two. Furthermore, anthropometric indices including weight, waist-to-hip ratio (WHR), and body mass index (BMI) were significantly reduced in the intervention groups. Aerobic exercise, whether alone or combined with Gymnema supplementation, can contribute to modulating ghrelin levels, reducing sweet cravings, and improving body composition in obese women. Gymnema supplementation may be considered a complementary strategy for managing unhealthy eating behaviors.
Downloads
References
1. Kokkorakis M, Chakhtoura M, Rhayem C, Al Rifai J, Ghezzawi M, Valenzuela-Vallejo L, et al. Emerging pharmacotherapies for obesity: A systematic review. Pharmacological Reviews. 2024:100002.[PMID: 39952695] [DOI]
2. Safaei M, Sundararajan EA, Driss M, Boulila W, Shapi'i A. A systematic literature review on obesity: Understanding the causes & consequences of obesity and reviewing various machine learning approaches used to predict obesity. Computers in Biology and Medicine. 2021;136:104754.[PMID: 34426171] [DOI]
3. Şeref B, Yıldıran H. A new perspective on obesity: Perception of fat taste and its relationship with obesity. Nutrition Reviews. 2024.[PMID: 38497969] [DOI]
4. Huang J, Wang C, Zhang HB, Zheng H, Huang T, Di JZ. Neuroimaging and neuroendocrine insights into food cravings and appetite interventions in obesity. Psychoradiology. 2023;3.[PMID: 38666104] [PMCID: PMC10917384] [DOI]
5. Jiao ZT, Luo Q. Molecular mechanisms and health benefits of ghrelin: A narrative review. Nutrients. 2022;14IS - 19:4191.[PMID: 36235843] [PMCID: PMC9572668] [DOI]
6. van Loenen MR, Geenen B, Arnoldussen IA, Kiliaan AJ. Ghrelin as a prominent endocrine factor in stress-induced obesity. Nutritional Neuroscience. 2022;25(7):1413-24.[PMID: 33373270] [DOI]
7. Sitar-Tǎut AV, Cozma A, Fodor A, Coste SC, Orasan OH, Negrean V. New insights on the relationship between leptin, ghrelin, and leptin/ghrelin ratio enforced by body mass index in obesity and diabetes. Biomedicines. 2021;9(11):1657.[PMID: 34829886] [PMCID: PMC8615809] [DOI]
8. Bellicha A, van Baak MA, Battista F, Beaulieu K, Blundell JE, Busetto L. Effect of exercise training on weight loss, body composition changes, and weight maintenance in adults with overweight or obesity: An overview of 12 systematic reviews and 149 studies. Obesity Reviews. 2021;22:e13256.[PMID: 33955140] [PMCID: PMC8365736] [DOI]
9. Johnson NA, Sachinwalla T, Walton DW, Smith K, Armstrong A, Thompson MW, et al. Aerobic exercise training reduces hepatic and visceral lipids in obese individuals without weight loss. Hepatology. 2009;50(4):1105-12.[PMID: 19637289] [DOI]
10. Stensel D. Exercise, appetite and appetite-regulating hormones: Implications for food intake and weight control. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism. 2011;57(Suppl. 2):36-42.[PMID: 21346335] [DOI]
11. Najafi R, Heidarianpour A, Shokri E, Shokri B. Ameliorative effects of aerobic training in girls with precocious puberty: Role of leptin and ghrelin. Scientific Reports. 2023;13(1):15732.[PMID: 37735188] [PMCID: PMC10575917] [DOI]
12. King JA, Wasse LK, Stensel DJ, Nimmo MA. Exercise and ghrelin: A narrative overview of research. Appetite. 2013;68:83-91.[PMID: 23624293] [DOI]
13. Sun NN, Wu TY, Chau CF. Natural dietary and herbal products in anti-obesity treatment. Molecules. 2016;21(10):1351.[PMID: 27727194] [PMCID: PMC6273667] [DOI]
14. Devangan S, Varghese B, Johny E, Gurram S, Adela R. The effect of Gymnema sylvestre supplementation on glycemic control in type 2 diabetes patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Phytotherapy Research. 2021;35(12):6802-12.[PMID: 34467577] [DOI]
15. Devi K, Jain N. Clinical evaluation of the anti-sweet effects of Gymnema sylvestre extract developed into a dispersable oral tablet. Journal of Herbal Medicine. 2015;5(4):184-9[DOI]
16. Turner SAUDC, Kruger R, Wong M, Wood W, Rutherfurd-Markwick K, Ali A. Consuming Gymnema sylvestre reduces the desire for high-sugar sweet foods. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1046.[PMID: 32290122] [PMCID: PMC7230589] [DOI]
17. Zuniga LY, Gonzalez-Ortiz M, Martinez-Abundis E. Effect of Gymnema sylvestre administration on metabolic syndrome, insulin sensitivity, and insulin secretion. Journal of Medicinal Food. 2017;20(8):750-4.[PMID: 28459647] [DOI]
18. Kashima H, Eguchi K, Miyamoto K, Fujimoto M, Endo MY, Aso-Someya N. Suppression of oral sweet taste sensation with Gymnema sylvestre affects postprandial gastrointestinal blood flow and gastric emptying in humans. Chemical Senses. 2017;42(4):295-302.[PMID: 28431091] [DOI]
19. Jacques A, Chaaya N, Beecher K, Ali SA, Belmer A, Bartlett S. The impact of sugar consumption on stress driven, emotional and addictive behaviors. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews. 2019;103:178-99.[PMID: 31125634] [DOI]
20. Kimmeswenger I, Lieder B. Novel perspective on the plasticity of taste perception: Is food-and exercise-induced inflammation associated with sweet taste sensitivity and preference? Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2024;72(27):15122-7.[PMID: 38941285] [PMCID: PMC11247480] [DOI]
21. Nishihara T, Nozaki T, Sawamoto R, Komaki G, Miyata N, Hosoi M, et al. Effects of weight loss on sweet taste preference and palatability following cognitive behavioral therapy for women with obesity. Obesity Facts. 2019;12(5):529-42.[PMID: 31494654] [PMCID: PMC6876607] [DOI]
22. Leow S, Jackson B, Alderson JA, Guelfi KJ, Dimmock JA. A role for exercise in attenuating unhealthy food consumption in response to stress. Nutrients. 2018;10(2):176.[PMID: 29415424] [PMCID: PMC5852752] [DOI]
23. Cuomo S, Mulasso A, Lupo C, Rainoldi A, Brustio PR. High-Intensity Interval Training versus Usual Care during Cancer Prehabilitation: A systematic review and meta-analysis of the impact on cardiorespiratory fitness. Sport Sciences for Health. 2024;20(Suppl.):S74-S8
24. Akalu Y, Molla MD, Dessie G, Ayelign B. Physiological effect of ghrelin on body systems. International Journal of Endocrinology. 2020;2020(1):1385138.[PMID: 32565790] [PMCID: PMC7267865] [DOI]
25. Wilk K, Korytek W, Pelczyńska MAUMM, Bogdański P. The effect of artificial sweeteners use on sweet taste perception and weight loss efficacy: A review. Nutrients. 2022;14(6):1261.[PMID: 35334918] [PMCID: PMC8954878] [DOI]
26. Alvarez-Monell A, Subias-Gusils A, Mariné-Casadó R, Boqué N, Caimari A, Solanas M, et al. Impact of Calorie-Restricted Cafeteria Diet and Treadmill Exercise on Sweet Taste in Diet-Induced Obese Female and Male Rats. Nutrients. 2022;15(1):144.[PMID: 36615803] [PMCID: PMC9823820] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
Categories
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Roya Azadi (Author); Khadijeh Irandoust (Corresponding Author); Morteza Taheri (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















