Impact of Aerobic Training and Probiotic Intervention on Nrf2 and GLUT4 mRNA Levels in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Experimental Study in Male Wistar Rats
Keywords:
Aerobic Exercise, Lactobacillus Supplementation, Nrf2, GLUT4, Liver TissueAbstract
Background and Aims: Previous research has explored metabolic regulation improvements and therapeutic potential for treating fatty liver disease through various approaches. This study examines how the Impact of Aerobic Training and Probiotic Intervention on Nrf2 and GLUT4 mRNA Levels in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Experimental Study in Male Wistar Rats
Methods: We randomly assigned forty male Wistar rats (weighing 220 ± 20g) to five distinct groups: Healthy Control (HC), NAFLD Control (NC), NAFLD with Aerobic Exercise (NAE), NAFLD with Lactobacillus Supplementation (NLS), and NAFLD with combined Aerobic Exercise and Lactobacillus Supplementation (NAELS). The healthy control group maintained a standard diet, while all other groups received oral tetracycline (140 mg/kg body weight dissolved in 2 ml water) through gavage for seven days to establish NAFLD conditions. The six-week intervention protocol included treadmill running at 18 m/min for exercise groups. Probiotic intervention groups received daily L. Rhamnosus GG doses (10⁹ CFU/mL) via gavage for five weeks, administered five days per week. We conducted liver biopsies alongside these interventions and measured Nrf2 and GLUT4 expression in liver tissue using Real-Time PCR. Statistical analysis employed two-way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc tests, establishing significance at p≤0.05.
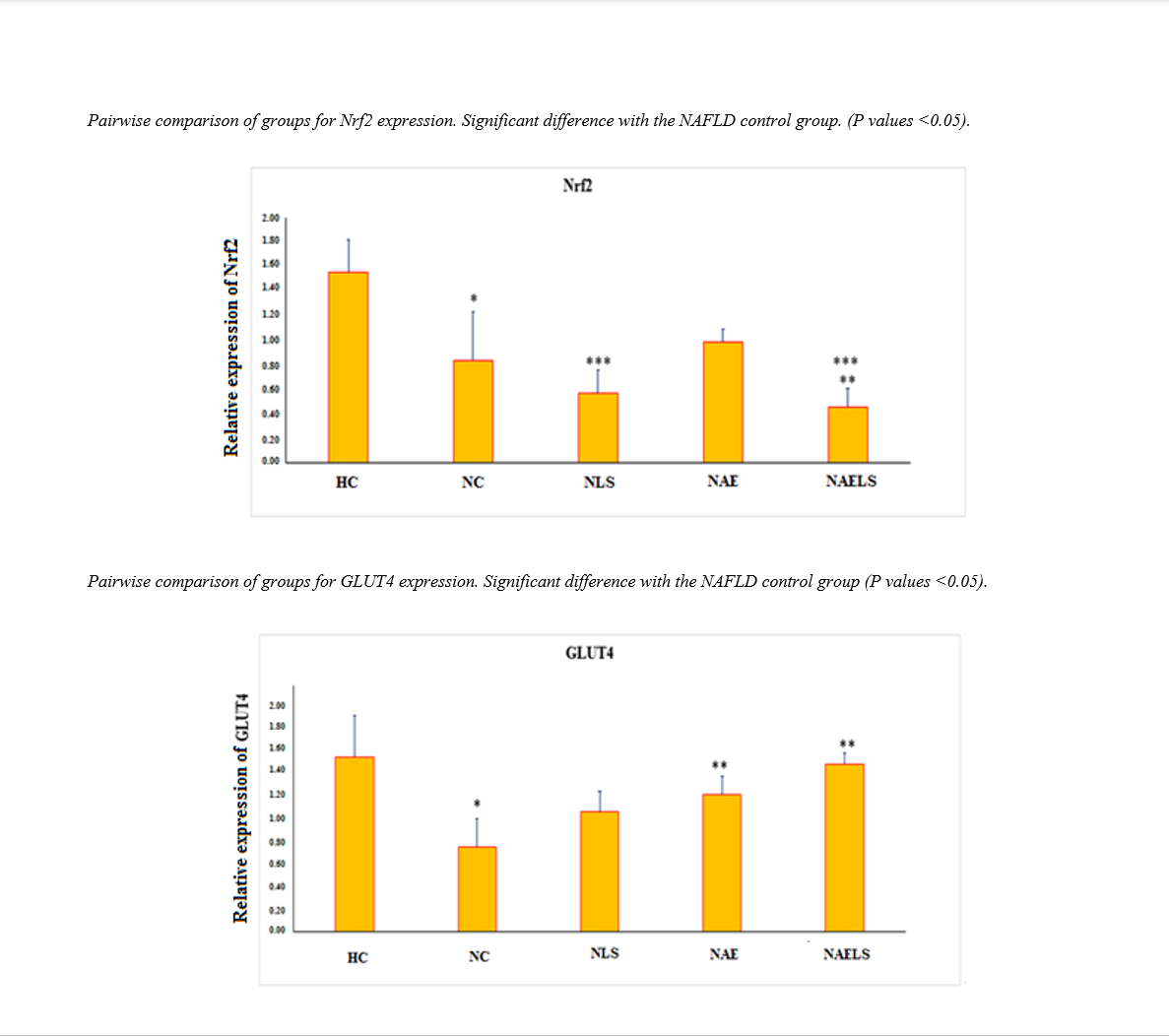
Results: We observed significant differences between the NC and HC groups (p=0.0000) as well as between NC and NAELS groups (p=0.029). The combined intervention group (NAELS) demonstrated the strongest effects on both Nrf2 (η²=0.35) and GLUT4 (η²=0.52) expression levels. These findings indicate that combining aerobic exercise with Lactobacillus supplementation substantially improves both gene expressions compared to individual interventions.
Conclusion: Our findings suggest that combining aerobic exercise with Lactobacillus supplementation enhances Nrf2 and GLUT4 expression, potentially contributing to improved metabolic health in NAFLD patients. This combined approach may offer therapeutic advantages over single interventions for managing fatty liver disease.
Downloads
References
1. Houttu V, et al. The role of the gut microbiome and exercise in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Therapeutic Advances in Gastroenterology. 2020;13:1756284820941745. [PMID: 32973925] [PMCID: PMC7495942] [DOI]
2. Sánchez Macarro M, et al. Antioxidant effect of a probiotic product on a model of oxidative stress induced by high-intensity and duration physical exercise. Antioxidants. 2021;10(2):323. [PMID: 33671691] [PMCID: PMC7926771] [DOI]
3. Bayat E, et al. Stevia rebaudiana extract attenuate metabolic disorders in diabetic rats via modulation of glucose transport and antioxidant signaling pathways and aquaporin‐2 expression in two extrahepatic tissues. Journal of Food Biochemistry. 2020;44(8):e13252. [PMID: 32515037] [DOI]
4. Bai Y, et al. Aerobic exercise and vitamin E improve high-fat diet-induced NAFLD in rats by regulating the AMPK pathway and oxidative stress. European Journal of Nutrition. 2023;62(6):2621-32. [PMID: 37219594] [DOI]
5. Vargas-Mendoza N, et al. Antioxidant and adaptative response mediated by Nrf2 during physical exercise. Antioxidants. 2019;8(6):196. [PMID: 31242588] [PMCID: PMC6617290] [DOI]
6. Park JS, Rustamov N, Roh YS. The roles of NFR2-regulated oxidative stress and mitochondrial quality control in chronic liver diseases. Antioxidants. 2023;12(11):1928. [PMID: 38001781] [PMCID: PMC10669501] [DOI]
7. Zou Y, et al. Exercise intervention mitigates pathological liver changes in NAFLD zebrafish by activating SIRT1/AMPK/NRF2 signaling. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2021;22(20):10940. [PMID: 34681600] [PMCID: PMC8536011] [DOI]
8. Zhang L, Zhang R, Li L. Effects of probiotic supplementation on exercise and the underlying mechanisms. Foods. 2023;12(9):1787. [PMID: 37174325] [PMCID: PMC10178086] [DOI]
9. Markowiak-Kopeć P, Śliżewska K. The effect of probiotics on the production of short-chain fatty acids by human intestinal microbiome. Nutrients. 2020;12(4):1107. [PMID: 32316181] [PMCID: PMC7230973] [DOI]
10. Richter EA, Hargreaves M. Exercise, GLUT4, and skeletal muscle glucose uptake. Physiological Reviews. 2013. [PMID: 23899560] [DOI]
11. Fard MK, Khajehlandi A, Mohammadi A. The effect of swimming training and cinnamon consumption on the gene expression of GLUT4 and insulin receptor in the brown adipose tissue of diabetic rats. Gene, Cell and Tissue. 2021;8(1). [DOI]
12. Santibañez-Gutierrez A, et al. Effects of probiotic supplementation on exercise with predominance of aerobic metabolism in trained population: A systematic review, meta-analysis and meta-regression. Nutrients. 2022;14(3):622. [PMID: 35276980] [PMCID: PMC8840281] [DOI]
13. Iacono A, et al. Probiotics as an emerging therapeutic strategy to treat NAFLD: focus on molecular and biochemical mechanisms. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. 2011;22(8):699-711. [PMID: 21292470] [DOI]
14. Yadegari F, Nia FR. The effect of 12 weeks of aerobic exercise and caloric restriction on Nrf2 protein expression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in rats. Journal of Shahrekord University of Medical Sciences. 2022;25(2):90-6. [DOI]
15. Fuertes-Agudo M, et al. Advances in understanding the role of NRF2 in liver pathophysiology and its relationship with hepatic-specific Cyclooxygenase-2 expression. Antioxidants. 2023;12(8):1491. [PMID: 37627486] [PMCID: PMC10451723] [DOI]
16. Choi YJ, et al. Increased hepatic fatty acid uptake and esterification contribute to tetracycline-induced steatosis in mice. Toxicological Sciences. 2015;145(2):273-82. [PMID: 25745068] [DOI]
17. Hashemi-Khah Ms, et al. An In vivo study of Lactobacillus rhamnosus (PTCC 1637) as a new therapeutic candidate in esophageal cancer. BioMed Research International. 2022;2022:7607470. [PMID: 35782061] [PMCID: PMC9249511] [DOI]
18. Qin F, et al. Maximum oxygen consumption and quantification of exercise intensity in untrained male Wistar rats. Scientific Reports. 2020;10(1):11520. [PMID: 32661254] [PMCID: PMC7359321] [DOI]
19. Boersma E, et al. Perioperative cardiovascular mortality in noncardiac surgery: validation of the Lee cardiac risk index. The American Journal of Medicine. 2005;118(10):1134-41. [PMID: 16194645] [DOI]
20. Zakaria SS, Hanafy SM. Unraveling the Beneficial Role of Resveratrol in Fructose-Induced Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis with a Focus on the AMPK/Nrf2 Signaling Axis. Medicina. 2025;61(1):139. [PMID: 39859121] [PMCID: PMC11767180] [DOI]
21. Ma Q. Role of nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annual Review of Pharmacology and Toxicology. 2013;53(1):401-26. [PMID: 23294312] [PMCID: PMC4680839] [DOI]
22. Van der Windt DJ, et al. The effects of physical exercise on fatty liver disease. Gene Expression. 2018;18(2):89. [PMID: 29212576] [PMCID: PMC5954622] [DOI]
23. Mohabbat M, Arazi H. Effect of resistance training plus enriched probiotic supplement on sestrin2, oxidative stress, and mitophagy markers in elderly male Wistar rats. Scientific Reports. 2024;14(1):7744. [PMID: 38565633] [PMCID: PMC10987664] [DOI]
24. Munteanu C, Schwartz B. The effect of bioactive aliment compounds and micronutrients on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Antioxidants. 2023;12(4):903. [PMID: 37107278] [PMCID: PMC10136128] [DOI]
25. Tang C, et al. Lactobacillus acidophilus NX2-6 improved high-fat diet-induced glucose metabolism disorder independent of promotion of insulin secretion in mice. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 2021;69(51):15598-610. [PMID: 34788040] [DOI]
26. Savini I, et al. Obesity-associated oxidative stress: strategies finalized to improve redox state. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2013;14(5):10497-538. [PMID: 23698776] [PMCID: PMC3676851] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Amin AliMohammadi (Author); Mandana Gholami (Corresponding Author); Farshad Ghazalian (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















