The Effect of Thinking Styles on Volleyball Serve Learning in Adolescent Female Students Based on Sternberg’s Model
Keywords:
thinking styles, , Strenberg, , Learning , Volleball serve, studentsAbstract
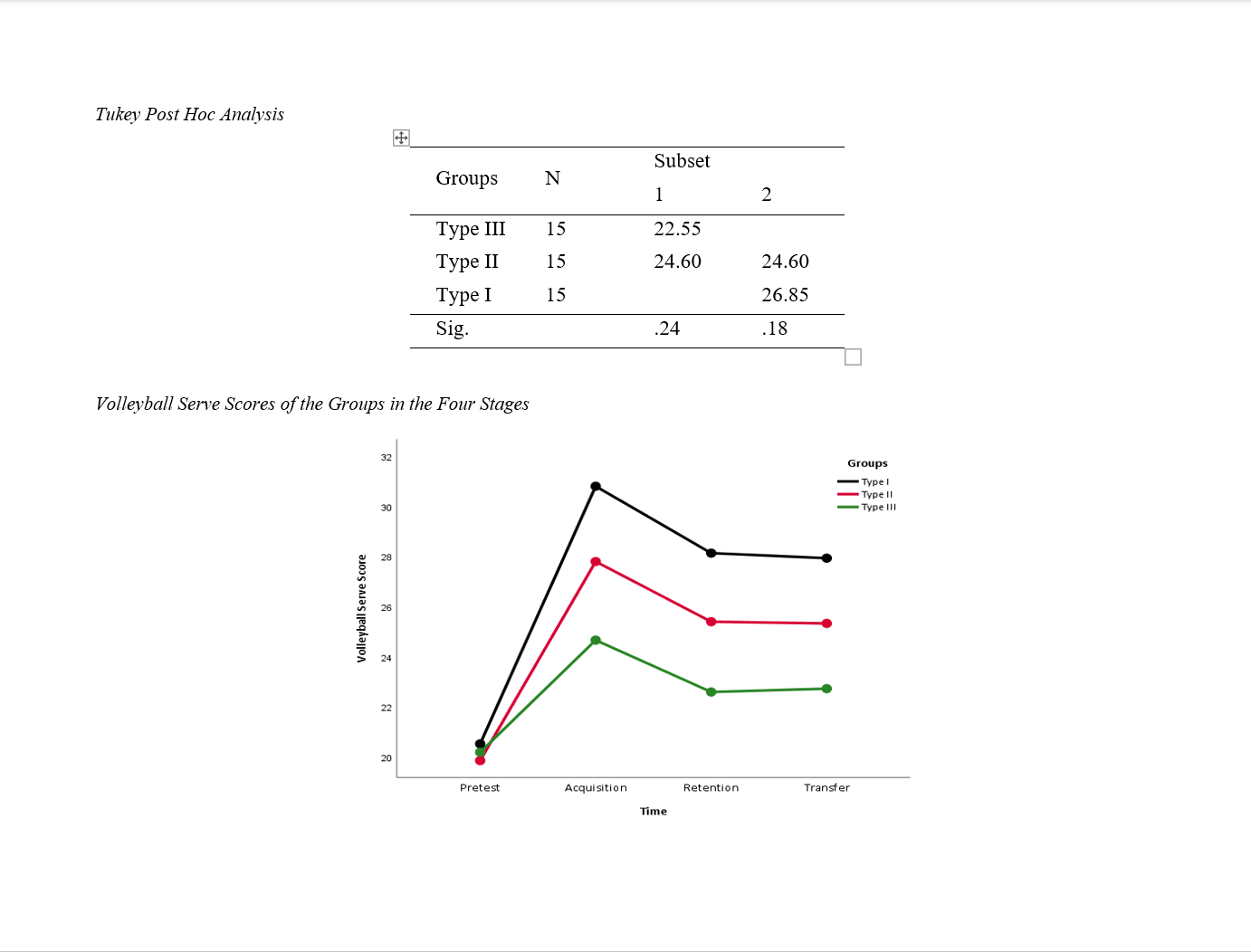
The role of thinking styles in learning psycho-motor skills, such as volleyball serve, is rarely investigated in female volleyball players. This study was an attempt to fill this gap. This quasi-experimental study with a pretest-posttest approach aimed at investigating the effect of thinking styles, based on Sternberg’s model, on volleyball serve learning in female adolescent students. To determine the sample size, G*Power v3.1 was used (α = 0.05, power = 0.95, and number of parameters = 3), and 45 female students (average age = 16.5, SD = 0.85) who met the inclusion criteria were selected through convenience sampling from one of secondary schools in Nasiriyah, Iraq. Based on the their thinking styles, after administering the Thinking Style Inventory - Short Version, they were divided into three 15-member groups, i.e., Type I, Type II, and Type III. They took AAHPERD Volleyball Skills Test as the pretest, and as the acquisition, retention and transfer tests. The training program lasted for 12 weeks, 3 sessions per week, and each session for 60 minutes in accordance with the pre-determined protocols and guidelines of AAHPERD test. The data were analyzed using a mixed ANOVA. There was a significant difference in volleyball serve learning between the groups, with Type I outperforming Type III, while no significant difference was detected between Type I and Type II, or between Type II and Type III. In teaching and evaluating psycho-motor skills, enough attention should be paid to thinking styles, as it can help teachers to employ a variety of methods in this regard. The variety and flexibility they create by taking into account the students’ thinking styles determine whether and to what extent they succeed in the teaching process.
Downloads
References
Sternberg RJ, Wagner RK (1992) Thinking styles inventory. Yale University Press, New Havan, USA.
[2] Lefrancois GR (1986) Psychologie des Lernens. Springer, Verlag.
[3] Sternberg RJ (1988) Mental self-government: A theory of intellectual styles and their development. Human Development 31: 197-224.
[4] Zhang LF, Sternberg RJ (2005) A threefold model of intellectual styles. Educational Psychology Review 17(1): 1-53.
[4] Sternberg RJ (1997) Thinking styles. New York: Cambridge University Press.
[5] Zhang LF, Sachs J (1997) Assessing thinking styles in the theory of mental self-government: A Hong Kong validity study. Psychological Reports 81: 915-928.
[6] Zhang LF (1999) Further cross-cultural validation of the theory of mental self-government. The Journal of Psychology 133: 165-181.
[7] Bernardo AB, Zhang LF, Callueng CM (2002) Thinking styles and academic achievement among Filipino students. The Journal of Genetic Psychology 163(2): 149-163.
[8] Cano-García F, Hughes EH (2000). Learning and thinking styles: An analysis of their interrelationship and influence on academic achievement. Educational Psychology 20(4): 413-430.
[9] Zhang LF, Li M, Fan W, Chang B, Postiglione GA (2022) Thinking styles and vocational identity among senior-year students in elite universities in mainland China. Thinking Skills and Creativity 45: 101-111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsc.2022.101101
[10] Hamoudi LS, Fattah MLA, Mahmoud MS, Fattah, MLA (2024) A comparative study between liberal and conservative thinking styles in fitness, mental motivation, and volleyball serving skill performance for female students. Modern Sport - Special Issue of the Second International Scientific Conference (Sports for Health and Sustainable Development): 324-339. https://doi.org/10.54702/w5n0ef18
[11] Eraslan M (2014) The analysis of the thinking styles and creativity of the sports students studying in the different fields of university. Educational Research & Reviews 9(20): 866-871. https://doi.org/10.5897/ERR2014.1783
[12] Alborzi S, Ostovar S (2007) Thinking styles of gifted and nongifted students in Iran. Psychological Reports 100(3): 1076-1082. https://doi.org/10.2466/pr0.100.4.1076-1082
[13] Sternberg RJ, Grigorenko EL (1995) Styles of thinking in the school. European Journal of High Ability 6(2): 201-219.
[14] Sternberg RJ, Grigorenko EL (1997) Are cognitive styles still in style? American Psychologist 52(7): 700-718.
[15] Zhang LF, Sternberg RJ (1998) Thinking styles, abilities, and academic achievement among Hong Kong university students. Educational Research Journal 13(1): 41-62.
[16] Albaili MA (2007) Differences in thinking styles among low-; average-; and high- achieving college students. Proceedings of the 13th International Conference on Thinking 21(1): 5-10.
[17] Zhang LF (2004) Thinking styles: University students’ preferred teaching styles and their conceptions of effective teachers. The Journal of Psychology 138(3): 233-252.
[18] Saad HM, Aljuboury DMH (2023) The effect of the active thinking model on learning the skills of serving and receiving in volleyball. Modern Sport 22(1): 86-96.
[19] Qassim S, Abdul-Ridha BK (2021) The effect of a learning strategy for mastery in learning the skills of setting volleyball for female students. Modern Sport 20(3): 89-98.
[20] Hasan DS (2022) The effect of using the mental visualization strategy in the style of cooperative groups in learning the two skills of setting from the top and receiving from the bottom in volleyball. Modern Sport 21(2): 19-24.
[21] Hussein HM, Albadry MT (2021) Self-programming of information and its relationship to some offensive skills in volleyball among female students. Modern Sport: 20(3), 55-55.
[22] Ghazi US, Abdul-Sameea H (2021) Predicting mental motivation in terms of some artistic gymnastics skills for students of the college of physical education and sports sciences. Modern Sport 20(2): 127-127.
[23] Ghazi HA, Matansh HH (2023) The effect of the constructive technique (active learning cycle) on students' development of some volleyball skills and cognitive achievement. Journal of Humanities and Social Sciences Research 2(3): 45-58.
[24] Suherman A, Budiana D, Juliantine T (2024) The influence of thinking styles and gender on students' creative thinking abilities in physical education. Edu Sportivo: Indonesian Journal of Physical Education 5(2): 198-206.
[25] Xing Z, Qi Y (2023) Development of creativity in physical education teachers using interactive technologies: Involvement and collaboration. Education and Information Technologies 28(5): 5763-5777.
[26] Ghanbari S, Papi M, Derakhshanfard S (2020) Relationship between thinking styles and the academic achievement of occupational therapy students in Iran. Journal of Education and Health Promotion 9(1): 82-101.
[27] Botagariyev T, Gabdullin A, Akhmetova A, Zhunusbekov Z, Saitbekov N (2023) The effectiveness of implementing student physical perfectness techniques for creative thinking development. IJERE 12(1): 216-224.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Mohammadtaghi Aghdasi (Corresponding Author); Sammer Razi Al Basharat Al Rakabi, Zahra Fathirezaie (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















