Effectiveness of Unified Transdiagnostic Treatment on Behavioral Problems in Children with Internalizing Behavioral Problems
Keywords:
Unified transdiagnostic treatment, behavioral problems, internalizing behavioral problemsAbstract
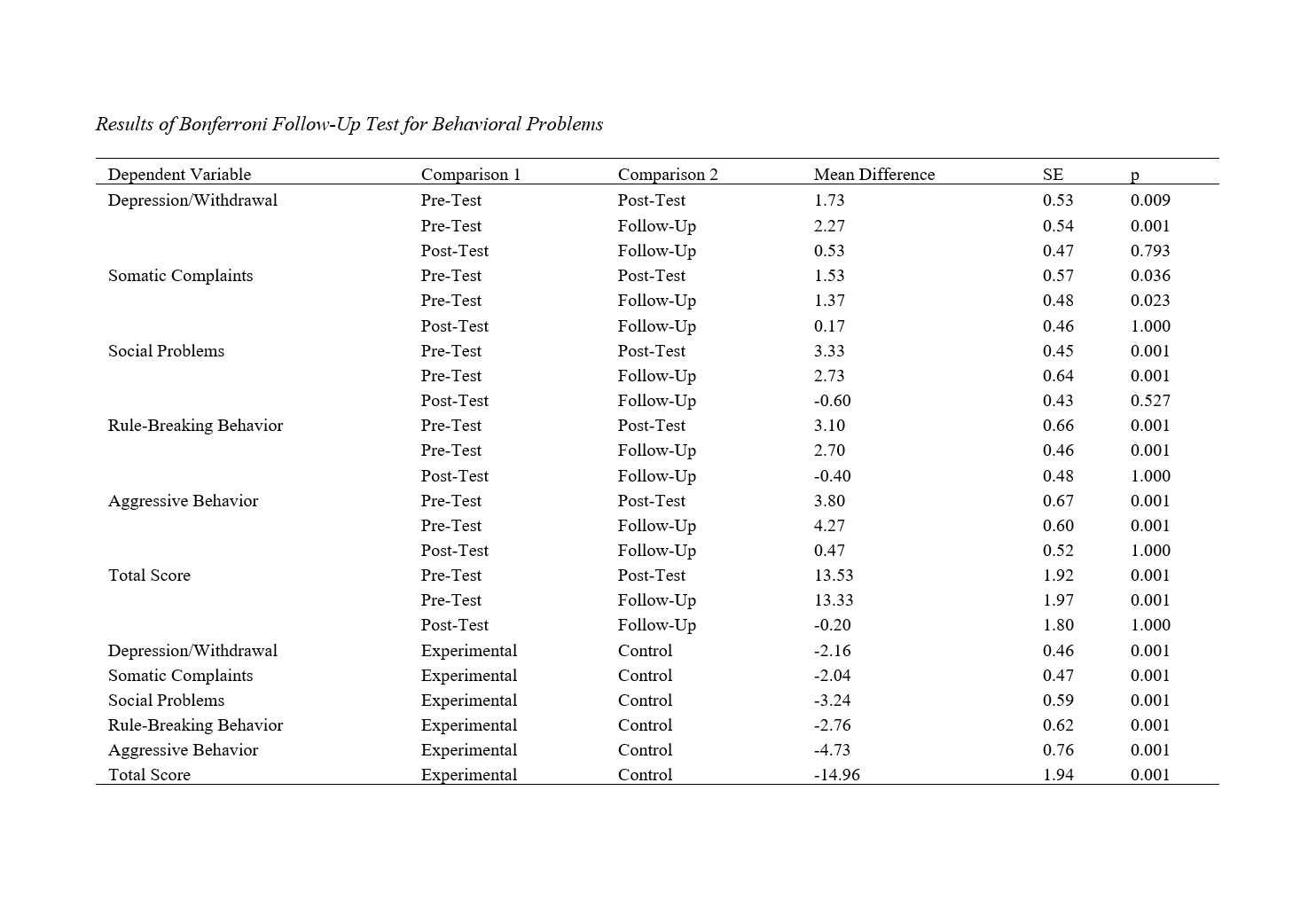
This study aimed to investigate the effectiveness of unified transdiagnostic treatment on behavioral problems in children with internalizing behavioral problems. This quasi-experimental study utilized a pre-test, post-test design with a control group and a two-month follow-up. The statistical population included 8- to 10-year-old children with internalizing behavioral problems in Najafabad during the first half of 2022. Thirty children were selected based on inclusion criteria using convenience sampling and were randomly assigned to two groups of 15 (experimental and control). The experimental group received the unified transdiagnostic treatment (child version) for 15 weekly sessions of 120 minutes each, while the control group received no intervention. The Child Behavior Checklist (Achenbach & Rescorla, 2001) was used as the research instrument. The obtained data were analyzed using repeated measures analysis of variance. The results showed that the unified transdiagnostic treatment had a significant impact on behavioral problems and their components, with the effects of the intervention being sustained over time. Based on the findings, it can be concluded that this therapeutic intervention can reduce behavioral problems in children with internalizing behavioral problems.
Downloads
References
1. Farmer RF, Gau JM, Seeley JR, Kosty DB, Sher KJ, Lewinsohn PM. Internalizing and externalizing disorders as predictors of alcohol use disorder onset during three developmental periods. Drug and Alcohol Dependence. 2016;164:38-46. [PMID: 27141839] [PMCID: PMC4893997] [DOI]
2. Basten M, Tiemeier H, Althoff RR, van de Schoot R, Jaddoe VWV, Hofman A, et al. The Stability of Problem Behavior Across the Preschool Years: An Empirical Approach in the General Population. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 2016;44(2):393-404. [PMID: 25832625] [PMCID: PMC4729812] [DOI]
3. Hinnant JB, El-Sheikh M. Codevelopment of externalizing and internalizing symptoms in middle to late childhood: Sex, baseline respiratory sinus arrhythmia, and respiratory sinus arrhythmia reactivity as predictors. Development and Psychopathology. 2013;25(2):419-36. [PMID: 23627954] [PMCID: PMC3874140] [DOI]
4. Wiggins JL, Mitchell C, Hyde LW, Monk CS. Identifying early pathways of risk and resilience: The codevelopment of internalizing and externalizing symptoms and the role of harsh parenting. Development and Psychopathology. 2015;27(4pt1):1295-312. [PMID: 26439075] [PMCID: PMC4961476] [DOI]
5. Fernández-Martínez I, Orgilés M, Morales A, Espada JP, Essau CA. One-Year follow-up effects of a cognitive behavior therapy-based transdiagnostic program for emotional problems in young children: A school-based cluster-randomized controlled trial. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2020;262:258-66. [PMID: 31733917] [DOI]
6. Takahashi F, Honda H. Prevalence of clinical-level emotional/behavioral problems in schoolchildren during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic in Japan: A prospective cohort study. JCPP Advances. 2021;1(1):e12007. [PMID: 34485986] [PMCID: PMC8206658] [DOI]
7. American Psychiatric Association A. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders: DSM-5-TR: Washington, DC: American psychiatric association; 2022.
8. Achenbach TM, Rescorla L. Child behavior checklist for ages 6-18: University of Vermont Burlington, VT; 2001.
9. Achenbach TM. International findings with the Achenbach System of Empirically Based Assessment (ASEBA): applications to clinical services, research, and training. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health. 2019;13(1):30. [PMID: 31312253] [PMCID: PMC6610912] [DOI]
10. McClintock SM. Relationship of internalizing behavior problems to intelligence and executive functioning in children 2005.
11. Oh Y, Greenberg MT, Willoughby MT, Vernon-Feagans L, Greenberg MT, Blair CB, et al. Examining Longitudinal Associations between Externalizing and Internalizing Behavior Problems at Within- and Between-Child Levels. Journal of Abnormal Child Psychology. 2020;48(4):467-80. [PMID: 31925637] [PMCID: PMC8233408] [DOI]
12. Christner N, Essler S, Hazzam A, Paulus M. Children’s psychological well-being and problem behavior during the COVID-19 pandemic: An online study during the lockdown period in Germany. PloS one. 2021;16(6):e0253473. [PMID: 34161376] [PMCID: PMC8221463] [DOI]
13. Costin J, Lichte C, Hill-Smith A, Vance A, Luk E. Parent group treatments for children with oppositional defiant disorder. Australian e-Journal for the advancement of mental health. 2004;3(1):36-43. [DOI]
14. Gallegirian S, Deireh E, Ghamarani A, Poladi Reishahri A. The Effect of Unified Trans-Diagnostic Treatment on the Experiential Avoidance and Suicidal Ideation in the Girls Victim of Domestic Violence. Psychological Methods and Models. 2022;12(46):69-84.
15. Sakiris N, Berle D. A systematic review and meta-analysis of the Unified Protocol as a transdiagnostic emotion regulation based intervention. Clinical Psychology Review. 2019;72:101751. [PMID: 31271848] [DOI]
16. Barlow DH, Farchione TJ, Bullis JR, Gallagher MW, Murray-Latin H, Sauer-Zavala S, et al. The Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders Compared With Diagnosis-Specific Protocols for Anxiety Disorders: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Psychiatry. 2017;74(9):875-84. [PMID: 28768327] [PMCID: PMC5710228] [DOI]
17. de Ornelas Maia ACC, Nardi AE, Cardoso A. The utilization of unified protocols in behavioral cognitive therapy in transdiagnostic group subjects: A clinical trial. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2015;172:179-83. [PMID: 25451415] [DOI]
18. Talkovsky AM, Green KL, Osegueda A, Norton PJ. Secondary depression in transdiagnostic group cognitive behavioral therapy among individuals diagnosed with anxiety disorders. Journal of Anxiety Disorders. 2017;46:56-64. [PMID: 27707524] [DOI]
19. Webster-Stratton C, Hammond M. Treating children with early-onset conduct problems: a comparison of child and parent training interventions. Journal of consulting and clinical psychology. 1997;65(1):93. [PMID: 9103739] [DOI]
20. Ellard KK, Fairholme CP, Boisseau CL, Farchione TJ, Barlow DH. Unified Protocol for the Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders: Protocol Development and Initial Outcome Data. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice. 2010;17(1):88-101. [PMID: 33762811] [PMCID: PMC7986982] [DOI]
21. Ehrenreich-May J, Bilek EL. The Development of a Transdiagnostic, Cognitive Behavioral Group Intervention for Childhood Anxiety Disorders and Co-Occurring Depression Symptoms. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice. 2012;19(1):41-55. [DOI]
22. Grossman RA, Ehrenreich-May J. Using the Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders With Youth Exhibiting Anger and Irritability. Cognitive and Behavioral Practice. 2020;27(2):184-201. [DOI]
23. Hawks JL, Kennedy SM, Holzman JBW, Ehrenreich–May J. Development and Application of an Innovative Transdiagnostic Treatment Approach for Pediatric Irritability. Behavior Therapy. 2020;51(2):334-49. [PMID: 32138942] [DOI]
24. Kennedy SM, Bilek EL, Ehrenreich-May J. A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial of the Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders in Children. Behavior Modification. 2018;43(3):330-60. [PMID: 29374963] [DOI]
25. Sandín B, García-Escalera J, Valiente RM, Espinosa V, Chorot P. Clinical Utility of an Internet-Delivered Version of the Unified Protocol for Transdiagnostic Treatment of Emotional Disorders in Adolescents (iUP-A): A Pilot Open Trial. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health [Internet]. 2020 PMC7697415]; 17(22).
26. Alavi Z, Ghasemzadeh S, Arjmandnia AA, Lavasani M, Vakili S. The Effectiveness of the Unified Transdiagnostic Treatment Protocol on the Social Skills of Students with Anxiety Disorders and the Self-Efficacy of their Mothers. Journal of Applied Psychological Research. 2022;13(3):225-41.
27. Loevaas MES, Lydersen S, Sund AM, Neumer SP, Martinsen KD, Holen S, et al. A 12-month follow-up of a transdiagnostic indicated prevention of internalizing symptoms in school-aged children: the results from the EMOTION study. Child and Adolescent Psychiatry and Mental Health. 2020;14(1):15. [PMID: 32336987] [PMCID: PMC7178617] [DOI]
28. Achenbach TM, Rescorla L. Multicultural understanding of child and adolescent psychopathology: Implications for mental health assessment: Guilford Press; 2007.
29. Yazdkhasti F, Oreyzi H. Standardization of child, parent and teacher’s forms of child behavior checklist in the city of Isfahan. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology. 2011;17(1):60-70.
30. Bentley KH. Applying the Unified Protocol Transdiagnostic Treatment to Nonsuicidal Self-Injury and Co-Occurring Emotional Disorders: A Case Illustration. Journal of Clinical Psychology. 2017;73(5):547-58. [PMID: 28221666] [DOI]
31. Laposa JM, Mancuso E, Abraham G, Loli-Dano L. Unified Protocol Transdiagnostic Treatment in Group Format: A Preliminary Investigation With Anxious Individuals. Behavior Modification. 2016;41(2):253-68. [PMID: 27591430] [DOI]
32. Allen LB, McHugh RK, Barlow DH. Emotional disorders: a unified protocol. 2008.
33. Joormann J, Gotlib IH. Emotion regulation in depression: Relation to cognitive inhibition. Cognition and Emotion. 2010;24(2):281-98. [PMID: 20300538] [PMCID: PMC2839199] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Maryam Sadat Hosseini Kakolaki (Author); Simindokht Rezakhani (Corresponding Author); Panteha Jahangir (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















