Presenting a Model of Psychological Vulnerability Based on Alexithymia in Multiple Sclerosis Patients: The Mediating Role of Anxious Thoughts
Keywords:
Psychological Vulnerability, Alexithymia, Anxious Thoughts, Multiple SclerosisAbstract
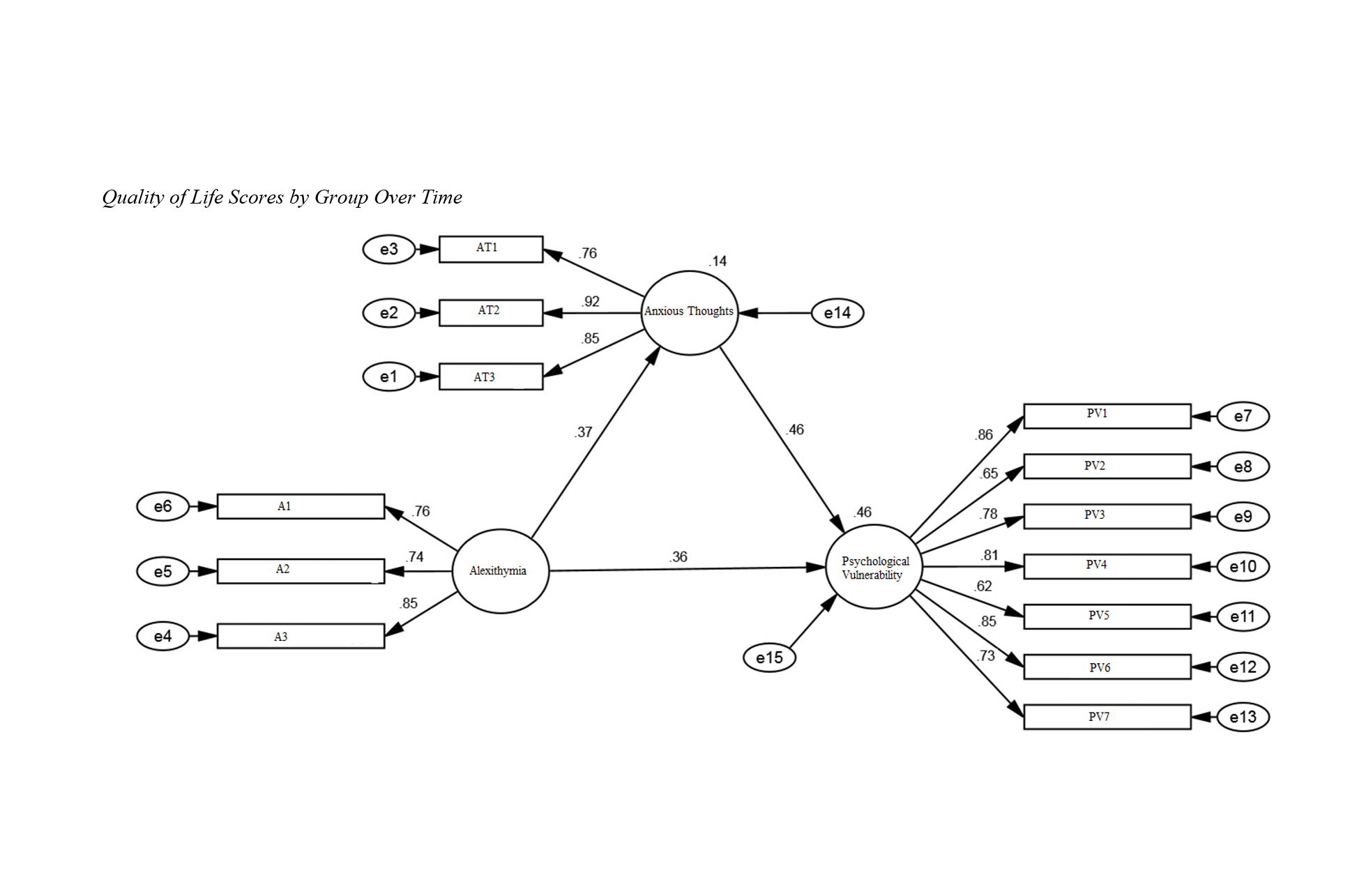
Among the stress-inducing events that impact an individual's psychological well-being, chronic illnesses such as multiple sclerosis (MS) are significant. These patients not only face physical challenges but also encounter numerous psychological issues that further exacerbate their illness and contribute to their psychological vulnerability. The current study aimed to determine the indirect effect of Alexithymia on the psychological vulnerability of MS patients, mediated by anxious thoughts. The study method was descriptive-correlational. The population consisted of members of the MS Society of Tehran in 2022. A total of 312 patients were selected using convenience sampling (n = 312). Data collection tools included the Toronto Alexithymia Scale (Bagby, Parker, & Taylor, 1994), the 25-Item Symptoms Checklist by Nejarian and Davoudi (2001), and the Wells Anxious Thoughts Questionnaire (1994). Data analysis using structural equation modeling indicated that the model of psychological vulnerability based on Alexithymia with the mediating role of anxious thoughts fits well. Also, the effect of Alexithymia on psychological vulnerability (β = 0.371; p < 0.001), the effect of anxious thoughts on psychological vulnerability (β = 0.463; p < 0.001), and the effect of Alexithymia on anxious thoughts (β = 0.367; p < 0.001) were positive and significant. The findings of this study could guide the development of comprehensive therapeutic models for patients with MS and their emotional issues.
Downloads
References
1. Oraki M, Sami, Puran. The Effect of Mindfulness Integrated Behavior- Cognitive Therapy on psychological well-being and quality of life among multiple sclerosis patients. Health Psychology. 2017;5(20):34-47.
2. Stein DJ, Phillips, K. A, Bolton, D, Fulford, K. W. M, Sadler, J. Z, Kendler, K. S. What is a mental/psychiatric disorder? From DSM-IV to DSM-V. Psychological Medicine. 2010;40(11):1759-65. [PMID: 20624327] [PMCID: PMC10949750] [DOI]
3. Alnajashi H, Jabbad, Razan. Behavioral practices of patients with multiple sclerosis during Covid-19 pandemic. PLOS ONE. 2020;15(10):e0241103. [PMID: 33091088] [PMCID: PMC7580932] [DOI]
4. Wilski M, Brola, Waldemar, Tomczak, Maciej. Health locus of control and mental health in patients with multiple sclerosis: Mediating effect of coping strategies. Research in Nursing & Health. 2019;42(4):296-305. [PMID: 31173383] [DOI]
5. Minden SL, Ding L, Cleary PD, Frankel D, Glanz BI, Healy BC, Rintell DJ. Improving the quality of mental health care in Multiple Sclerosis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2013;335(1):42-7. [PMID: 24183855] [DOI]
6. Boeschoten RE, Braamse, Annemarie M. J, Beekman, Aartjan T. F, Cuijpers, Pim, Van Oppen, Patricia, Dekker, Joost, Uitdehaag, Bernard M. J. Prevalence of depression and anxiety in Multiple Sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2017;372(no):331-41. [PMID: 28017241] [DOI]
7. Wood B, van der Mei, IAF, Ponsonby, A-L, Pittas, F, Quinn, S, Dwyer, T, Lucas, RM, Taylor, BV. Prevalence and concurrence of anxiety, depression and fatigue over time in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis Journal. 2013;19(2):217-24. [PMID: 22729988] [DOI]
8. Hanna M, Strober, Lauren Beth. Anxiety and depression in Multiple Sclerosis (MS): Antecedents, consequences, and differential impact on well-being and quality of life. Multiple Sclerosis and Related Disorders. 2020;44(no):102261. [PMID: 32585615] [PMCID: PMC7719086] [DOI]
9. Pratik Pimple BBL, Muhammad Hammadah, Kobina Wilmot, Ronnie Ramadan, Oleksiy Levantsevych, Samaah Sullivan, Jeong Hwan Kim, Belal Kaseer, Amit J. Shah, Laura Ward, Paolo Raggi, J. Douglas Bremner, John Hanfelt, Tene Lewis, Arshed A. Quyyumi, Viola Vaccarino. Psychological Distress and Subsequent Cardiovascular Events in Individuals With Coronary Artery Disease. Journal of the American Heart Association. 2019;8(9):e011866. [PMID: 31055991] [PMCID: PMC6512132] [DOI]
10. Myles LAM, Merlo, Emanuele Maria. Alexithymia and physical outcomes in psychosomatic subjects: a cross-sectional study. Journal of Mind and Medical Sciences. 2021;8(1):86-93. [DOI]
11. O’Malley P. Alexithymia in Children/ Adolescents and Psychosomatic Families. In: Maldonado-Duran JM, Jimenez-Gomez A, Saxena K, editors. Handbook of Mind/Body Integration in Child and Adolescent Development. Cham: Springer International Publishing; 2023. p. 157-66. [DOI]
12. Putica A, Van Dam, Nicholas T, Steward, Trevor, Agathos, James, Felmingham, Kim, O'Donnell, Meaghan. Alexithymia in post-traumatic stress disorder is not just emotion numbing: Systematic review of neural evidence and clinical implications. Journal of Affective Disorders. 2021;278(no):519-27. [PMID: 33017680] [DOI]
13. Oussi A, Hamid, Karim, Bouvet, Cyrille. Managing emotions in panic disorder: A systematic review of studies related to emotional intelligence, alexithymia, emotion regulation, and coping. Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry. 2023;79:101835. [PMID: 36680910] [DOI]
14. Hemming L, Haddock, Gillian, Shaw, Jennifer, Pratt, Daniel. Alexithymia and Its Associations With Depression, Suicidality, and Aggression: An Overview of the Literature. Frontiers in Psychiatry. 2019;10(no). [PMID: 31031655] [PMCID: PMC6470633] [DOI]
15. Besharat MA, Rostami, Reza, Pourhossein, R, Mirzamani, Mahmoud. Assessing reliability and validity of Farsi version of the Toronto Alexithymia Scale-20 in a sample of opioid substance use disordered patients. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology. 2006;1(no):133-9.
16. Besharat MA. Reliability and Factorial Validity of a Farsi Version of the 20-Item Toronto Alexithymia Scale with a Sample of Iranian Students. Psychological Reports. 2007;101(1):209-20. [PMID: 17958129] [DOI]
17. Barghi Irani Z, Bakhti, Mojtaba, Baghyan, Mohamad Javad, Karami, Sojae. The Relationship between the Five Factors of Personality and Alexithymia with Mental Health in MS Patients. Health Psychology. 2014;3(10):64-79.
18. Aaron RV, Fisher, Emma A, De La Vega, Rocio, Lumley, Mark A, Palermo, Tonya M. Alexithymia in individuals with chronic pain and its relation to pain intensity, physical interference, depression, and anxiety: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain. 2019;160(5):994-1006. [PMID: 31009416] [PMCID: PMC6688175] [DOI]
19. Wells A. A multi-dimensional measure of worry: Development and preliminary validation of the anxious thoughts inventory. Anxiety, Stress, & Coping. 1994;6(4):289-99. [DOI]
20. Wells A. Metacognitive Theory and Therapy for Worry and Generalized Anxiety Disorder: Review and Status. Journal of Experimental Psychopathology. 2010;1(1):jep.007910. [DOI]
21. Wells A, Fisher, Peter, Myers, Samuel, Wheatley, Jon, Patel, Trishna, Brewin, Chris R. Metacognitive therapy in treatment-resistant depression: A platform trial. Behaviour Research and Therapy. 2012;50(6):367-73. [PMID: 22498310] [DOI]
22. Patel VP, Walker, Lisa AS, Feinstein, Anthony. Revisiting cognitive reserve and cognition in multiple sclerosis: A closer look at depression. Multiple Sclerosis Journal. 2018;24(2):186-95. [PMID: 28273771] [DOI]
23. Balazadeh L, Mirzaian, Bahram, Hasanzadeh, Ramazan. Relationships of Brain Behavioral System and Anxiety Sensitivity with Psychological Vulnerability in People with Asthma under Intensive Care. Critical Care Nursing. 2020;13(4):34-43.
24. Ranjbari T, Karimi, Javad, Mohammadi, Abolfazl, Norouzi, Mohammad Reza. An evaluation of the contributions of the triple vulnerability model to the prediction of emotional disorders. Iranian Journal of Psychiatry and Clinical Psychology. 2018;23(4):408-23. [DOI]
25. Abbasi Kamal R, Sobhe, Afsane. Comparison of Automatic Thoughts and Alexithymia with Anxiety in People with Hypertension and People without Hypertension in Zanjan. Journal of Health Promotion Management. 2022;11(1):61-7.
26. Afshari A, Afshar, Hamid, Shafiee, Katayoon, Adibi, Neda. Dimentions of Alexithymia, and their relationships to Anxiety and Depression in Psychodermatologic patients. Internal Medicine Today. 2014;19(5):33-9.
27. Giordano A, Granella, Franco, Lugaresi, Alessandra, Martinelli, Vittorio, Trojano, Maria, Confalonieri, Paolo, Radice, Davide, Solari, Alessandra. Anxiety and depression in multiple sclerosis patients around diagnosis. Journal of the Neurological Sciences. 2011;307(1):86-91. [PMID: 21621796] [DOI]
28. Bagby RM, Parker, James D. A, Taylor, Graeme J. The twenty-item Toronto Alexithymia scale—I. Item selection and cross-validation of the factor structure. Journal of Psychosomatic Research. 1994;38(1):23-32. [PMID: 8126686] [DOI]
29. Najarian B, Davoodi, I. Construction and validation of a short form of the SCL-90-r (SCL-25). Journal of Psychology 2001;5(2):136-49.
30. Kline RB. Principles and practice of structural equation modeling: Guilford publications; 2023.
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Laleh Salimi (Author); Mohammadreza Zarbakhsh Bahri (Corresponding Author); Alireza Pirkhaefi (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















