The Impact of a Bodyweight-Based Exercise Program (through Quadrupedal Movement Exercises) on Motor Competence and Functional Movement in Children Aged 8 to 10 Years
Keywords:
Bodyweight exercises, quadrupedal movement exercises, motor competence, functional movement, childrenAbstract
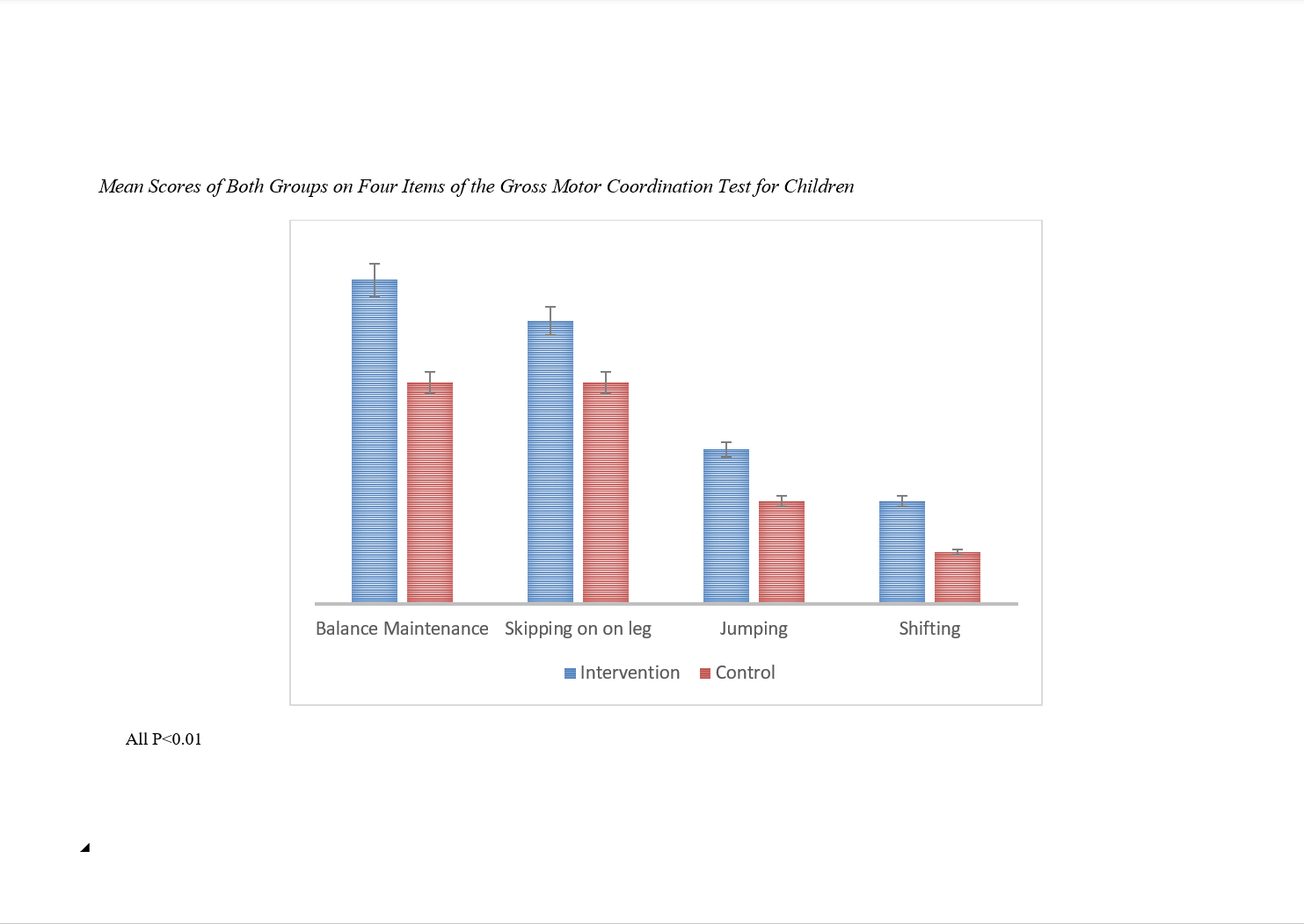
This study aimed to examine the effect of a bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movement exercises on motor competence and functional movement in children aged 8 to 10 years. In this quasi-experimental study, designed with a control group and pre-test–post-test format, 40 male participants aged 8 to 10 years from elementary schools in Bagh Malek County were selected. Participants were randomly assigned to either the intervention or control group. In the pre-test phase, functional movement and motor competence were measured using the Functional Movement Screening (FMS) test and the Pediatric Gross Motor Coordination Test, respectively. Subsequently, the intervention group participated in a bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movements for three 45-minute sessions per week over eight weeks. During this period, the control group attended only daily physical education classes. In each session, participants followed the bodyweight-based exercise protocol, which was presented through a pre-recorded video shown on a large display. All exercise sessions were conducted in groups and followed a specific system designed for these exercises, led by a certified instructor. Participants’ techniques were monitored, and adjustments were made when necessary. Finally, the dependent variables were re-measured in the post-test phase. Statistical analysis was performed using paired t-tests to compare pre- and post-test scores within each group, and independent t-tests to compare changes between the intervention and control groups. The bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movement exercises improved motor competence and functional movement in the intervention group, showing that the intervention program effectively impacted various aspects of motor competence and functional movement patterns, with all changes being significant compared to the control group (p ≤ 0.05). The bodyweight-based exercise program through quadrupedal movement exercises significantly improved motor competence and functional movement in children aged 8 to 10 years. Bodyweight-based exercises may serve as an effective intervention to enhance motor competence and functional movement in this age group.
Downloads
References
1. Haywood KM, Getchell N. Life span motor development: Human Kinetics; 2021.
2. Goodway JD, Ozmun JC, Gallahue DL. Understanding motor development: Infants, children, adolescents, adults: Jones & Bartlett Learning; 2019.
3. Logan SW, Robinson LE, Wilson AE, Lucas WA. Getting the fundamentals of movement: A meta-analysis of the effectiveness of motor skill interventions in children. Child: Care, Health and Development. 2012;38(3):305-15. [PMID: 21880055] [DOI]
4. Robinson LE, Stodden DF, Barnett LM, Lopes VP, Logan SW, Rodrigues LP, et al. Motor competence and its effect on positive developmental trajectories of health. Sports Medicine. 2015;45:1273-84. [PMID: 26201678] [DOI]
5. O'Brien W, Khodaverdi Z, Bolger L, Tarantino G, Philpott C, Neville RD. The assessment of functional movement in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Sports Medicine. 2022:1-17. [PMID: 34524655] [PMCID: PMC8761122] [DOI]
6. Cook G, Burton L, Hoogenboom B. Pre-participation screening: The use of fundamental movements as an assessment of function-part 1. North American Journal of Sports Physical Therapy: NAJSPT. 2006;1(2):62.
7. Cook G, Burton L, Hoogenboom B. Pre-participation screening: The use of fundamental movements as an assessment of function - Part 2. North American Journal of Sports Physical Therapy. 2010;5(3):132-9. [DOI]
8. Han A, Fu A, Cobley S, Sanders RH. Effectiveness of exercise intervention on improving fundamental movement skills and motor coordination in overweight/obese children and adolescents: A systematic review. Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport. 2018;21(1):89-102. [PMID: 28728887] [DOI]
9. Lubans DR, Morgan PJ, Cliff DP, Barnett LM, Okely AD. Fundamental movement skills in children and adolescents: Review of associated health benefits. Sports Medicine. 2010;40:1019-35. [PMID: 21058749] [DOI]
10. Radnor JM, Moeskops S, Morris SJ, Mathews TA, Kumar NT, Pullen BJ, et al. Developing athletic motor skill competencies in youth. Strength & Conditioning Journal. 2020;42(6):54-70. [DOI]
11. Patel K. The complete guide to bodyweight training: Bloomsbury Publishing; 2014.
12. Buxton JD, Sherman SA, Sterrett MT, Kannel KD, Blanchflower ME, Jancay KT, et al. A comparison of the energy demands of quadrupedal movement training to walking. Frontiers in Sports and Active Living. 2022;4:992687. [PMID: 36311211] [PMCID: PMC9606455] [DOI]
13. Eckart AC. Quadrupedal movement training: A brief review and practical guide. ACSM's Health & Fitness Journal. 2023;27(4):19-33. [DOI]
14. Kobesova A, Dzvonik J, Kolar P, Sardina A, Andel R. Effects of shoulder girdle dynamic stabilization exercise on hand muscle strength. Isokinetics and Exercise Science. 2015;23(1):21-32. [DOI]
15. Labaf S, Shamsoddini A, Hollisaz MT, Sobhani V, Shakibaee A. Effects of neurodevelopmental therapy on gross motor function in children with cerebral palsy. Iranian Journal of Child Neurology. 2015;9(2):36.
16. Zehr EP, Barss TS, Dragert K, Frigon A, Vasudevan EV, Haridas C, et al. Neuromechanical interactions between the limbs during human locomotion: An evolutionary perspective with translation to rehabilitation. Experimental Brain Research. 2016;234:3059-81. [PMID: 27421291] [PMCID: PMC5071371] [DOI]
17. Matthews MJ, Yusuf M, Doyle C, Thompson C. Quadrupedal movement training improves markers of cognition and subjective wellbeing in humans. Frontiers in Psychology. 2016;7:702. [PMID: 26896559] [DOI]
18. Christopher J, Bowhay S. A guide to implementing ground-based animal flow exercises with youth athletes2024.
19. Crane J, Temple V. A systematic review of dropout from organized sport among children and youth. European Physical Education Review. 2015;21(1):114-31. [DOI]
20. Dismore H, Bailey R. Fun and enjoyment in physical education: Young people's attitudes. Research Papers in Education. 2011;26(4):499-516. [DOI]
21. Hardy LL, Reinten-Reynolds T, Espinel P, Zask A, Okely AD. Prevalence and correlates of low fundamental movement skill competency in children. Pediatrics. 2012;130(2):e390-e8. [PMID: 22826575] [DOI]
22. Faigenbaum AD, Lloyd RS, MacDonald J, Myer GD. Citius, Altius, Fortius: Beneficial effects of resistance training for young athletes: narrative review. British Journal of Sports Medicine. 2016;50(1):3-7. [PMID: 26089321] [DOI]
23. Faigenbaum AD, Myer GD, Farrell A, Radler T, Fabiano M, Kang J, et al. Integrative neuromuscular training and sex-specific fitness performance in 7-year-old children: An exploratory investigation. Journal of Athletic Training. 2014;49(2):145-53. [PMID: 24490841] [PMCID: PMC3975769] [DOI]
24. Baddeley A. The episodic buffer: A new component of working memory? Trends in Cognitive Sciences. 2000;4(11):417-23. [PMID: 11058819] [DOI]
25. Koedijker JM, Poolton JM, Maxwell JP, Oudejans RR, Beek PJ, Masters RS. Attention and time constraints in perceptual-motor learning and performance: Instruction, analogy, and skill level. Consciousness and Cognition. 2011;20(2):245-56. [PMID: 20850990] [DOI]
26. Kushner AM, Kiefer AW, Lesnick S, Faigenbaum AD, Kashikar-Zuck S, Myer GD. Training the developing brain part II: Cognitive considerations for youth instruction and feedback. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 2015;14(3):235-43. [PMID: 25968858] [PMCID: PMC4435822] [DOI]
27. Myer GD, Kushner AM, Faigenbaum AD, Kiefer A, Kashikar-Zuck S, Clark JF. Training the developing brain, part I: Cognitive developmental considerations for training youth. Current Sports Medicine Reports. 2013;12(5):304-10. [PMID: 24030303] [DOI]
28. Kiphard EJ, Schilling F. Körperkoordinationstest für Kinder: Beltz Test GmbH; 2007.
29. Khazari D, Babaei L. Guidelines for conducting functional movement screening tests: Research Institute of Physical Education and Sports Sciences; 2021.
30. Vernetta-Santana M, Orbe-Moreno MD, Peláez-Barrios EM, López-Bedoya J. Movement quality evaluation through the functional movement screen in 12-and 13-year-old secondary-school adolescents. Journal of Human Sport and Exercise. 2019. [DOI]
31. Fitch M, Smith A, Evans J, Photography EB. ANIMAL FLOW® LEVEL ONE WORKSHOP STUDENT MANUAL2020.
32. Li H, Cheong JPG. Using the ADDIE model to design and develop physical education lessons incorporated with a functional training component. Frontiers in Public Health. 2023;11:1201228. [PMID: 37809003] [PMCID: PMC10001550] [DOI]
33. Li H, Cheong JPG, Hussain B. The effect of a 12-week physical functional training-based physical education intervention on students' physical fitness-A quasi-experimental study. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health. 2023;20(5):3926. [PMID: 36900937] [PMCID: PMC10001550] [DOI]
34. Zhang D, Soh KG, Chan YM, Bashir M, Xiao W. Effect of functional training on fundamental motor skills among children: A systematic review. Frontiers in Pediatrics. 2023. [DOI]
35. Fu T, Zhang D, Wang W, Geng H, Lv Y, Shen R, et al. Functional training focused on motor development enhances gross motor, physical fitness, and sensory integration in 5-6-year-old healthy Chinese children. Frontiers in Pediatrics. 2022;10:936799. [PMID: 35899135] [PMCID: PMC9309543] [DOI]
36. Khatibchi J, Meinoonjad H, Najd R, Tasoujian M. Comparison of the performance of students at different educational levels in elementary school in functional movement screening tests. Research in Sports Rehabilitation. 2022;9(18):75-84. [DOI]
37. Marcen C, Cardona-Linares AJ, Pradas F, Ortega-Zayas MÁ. Move to Flow: The benefits and barriers of a physical activity nature-based pilot programme. Sports. 2024;12. [PMID: 38535738] [PMCID: PMC10975806] [DOI]
38. Oliver JL. Strength and conditioning for young athletes: Science and application: Routledge; 2019. [DOI]
39. Wu XY, Han LH, Zhang JH, Luo S, Hu JW, Sun K. The influence of physical activity, sedentary behavior on health-related quality of life among the general population of children and adolescents: A systematic review. PLOS ONE. 2017;12(11):e0187668. [PMID: 29121640] [PMCID: PMC5679623] [DOI]
Downloads
Additional Files
Published
Submitted
Revised
Accepted
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2024 Mohamad Fatollahi (Author); Marzie Balali (Corresponding Author); Rasool Abedanzadeh , Behnam Maleki (Author)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.















